Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
How to get started, best practices, moodle how-to guides.
Workshop Links:
- Workshop Recording (Spring 2024)
- Workshop Registration
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.

Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Holistic rubrics.
A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubrics
An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubrics
A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of single point rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper.
Articulating thoughts through written communication— final paper.
- Above Average: The audience is able to easily identify the central message of the work and is engaged by the paper’s clear focus and relevant details. Information is presented logically and naturally. There are minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling.
- Sufficient : The audience is easily able to identify the focus of the student work which is supported by relevant ideas and supporting details. Information is presented in a logical manner that is easily followed. The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by errors.
- Developing : The audience can identify the central purpose of the student work without little difficulty and supporting ideas are present and clear. The information is presented in an orderly fashion that can be followed with little difficulty. Grammatical and spelling errors distract from the work.
- Needs Improvement : The audience cannot clearly or easily identify the central ideas or purpose of the student work. Information is presented in a disorganized fashion causing the audience to have difficulty following the author’s ideas. The readability of the work is seriously hampered by errors.
Single-Point Rubric
More examples:.
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Thanksgiving Worksheet Bundle for Last-Minute Activities 🦃
15 Helpful Scoring Rubric Examples for All Grades and Subjects
In the end, they actually make grading easier.

When it comes to student assessment and evaluation, there are a lot of methods to consider. In some cases, testing is the best way to assess a student’s knowledge, and the answers are either right or wrong. But often, assessing a student’s performance is much less clear-cut. In these situations, a scoring rubric is often the way to go, especially if you’re using standards-based grading . Here’s what you need to know about this useful tool, along with lots of rubric examples to get you started.
What is a scoring rubric?
In the United States, a rubric is a guide that lays out the performance expectations for an assignment. It helps students understand what’s required of them, and guides teachers through the evaluation process. (Note that in other countries, the term “rubric” may instead refer to the set of instructions at the beginning of an exam. To avoid confusion, some people use the term “scoring rubric” instead.)
A rubric generally has three parts:
- Performance criteria: These are the various aspects on which the assignment will be evaluated. They should align with the desired learning outcomes for the assignment.
- Rating scale: This could be a number system (often 1 to 4) or words like “exceeds expectations, meets expectations, below expectations,” etc.
- Indicators: These describe the qualities needed to earn a specific rating for each of the performance criteria. The level of detail may vary depending on the assignment and the purpose of the rubric itself.
Rubrics take more time to develop up front, but they help ensure more consistent assessment, especially when the skills being assessed are more subjective. A well-developed rubric can actually save teachers a lot of time when it comes to grading. What’s more, sharing your scoring rubric with students in advance often helps improve performance . This way, students have a clear picture of what’s expected of them and what they need to do to achieve a specific grade or performance rating.
Learn more about why and how to use a rubric here.
Types of Rubric
There are three basic rubric categories, each with its own purpose.
Holistic Rubric

Source: Cambrian College
This type of rubric combines all the scoring criteria in a single scale. They’re quick to create and use, but they have drawbacks. If a student’s work spans different levels, it can be difficult to decide which score to assign. They also make it harder to provide feedback on specific aspects.
Traditional letter grades are a type of holistic rubric. So are the popular “hamburger rubric” and “ cupcake rubric ” examples. Learn more about holistic rubrics here.
Analytic Rubric
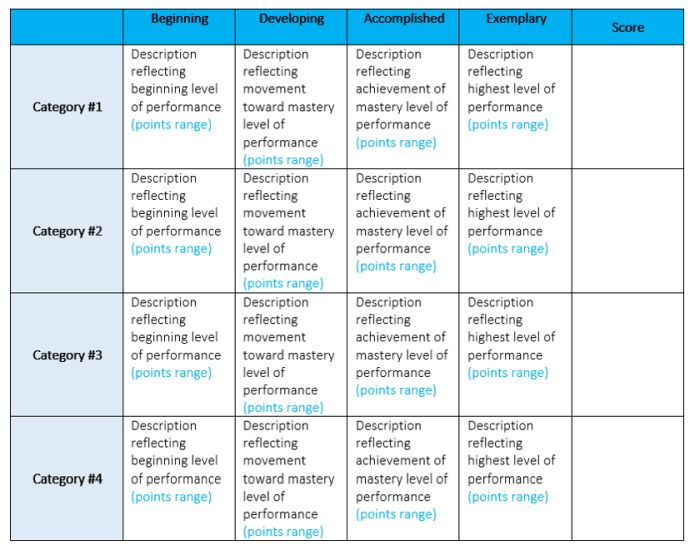
Source: University of Nebraska
Analytic rubrics are much more complex and generally take a great deal more time up front to design. They include specific details of the expected learning outcomes, and descriptions of what criteria are required to meet various performance ratings in each. Each rating is assigned a point value, and the total number of points earned determines the overall grade for the assignment.
Though they’re more time-intensive to create, analytic rubrics actually save time while grading. Teachers can simply circle or highlight any relevant phrases in each rating, and add a comment or two if needed. They also help ensure consistency in grading, and make it much easier for students to understand what’s expected of them.
Learn more about analytic rubrics here.
Developmental Rubric
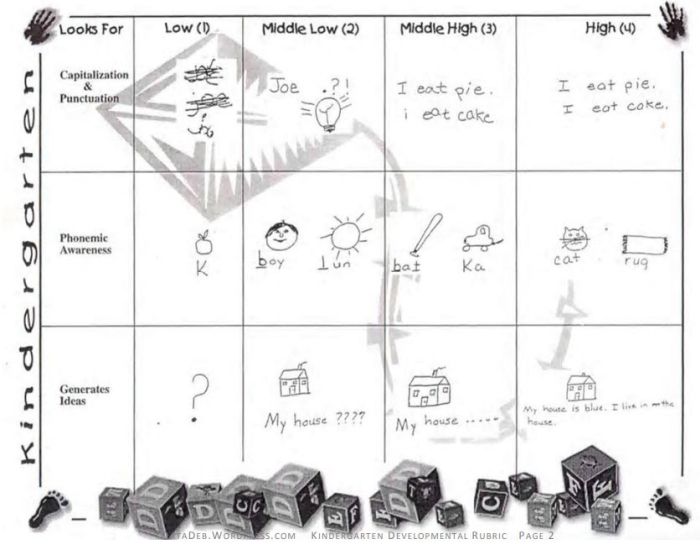
Source: Deb’s Data Digest
A developmental rubric is a type of analytic rubric, but it’s used to assess progress along the way rather than determining a final score on an assignment. The details in these rubrics help students understand their achievements, as well as highlight the specific skills they still need to improve.
Developmental rubrics are essentially a subset of analytic rubrics. They leave off the point values, though, and focus instead on giving feedback using the criteria and indicators of performance.
Learn how to use developmental rubrics here.
Ready to create your own rubrics? Find general tips on designing rubrics here. Then, check out these examples across all grades and subjects to inspire you.

Elementary School Rubric Examples
These elementary school rubric examples come from real teachers who use them with their students. Adapt them to fit your needs and grade level.
Reading Fluency Rubric
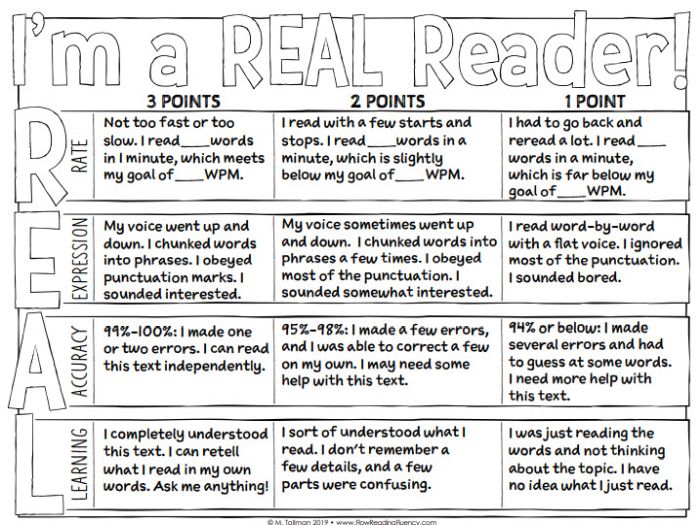
You can use this one as an analytic rubric by counting up points to earn a final score, or just to provide developmental feedback. There’s a second rubric page available specifically to assess prosody (reading with expression).
Learn more: Teacher Thrive
Reading Comprehension Rubric
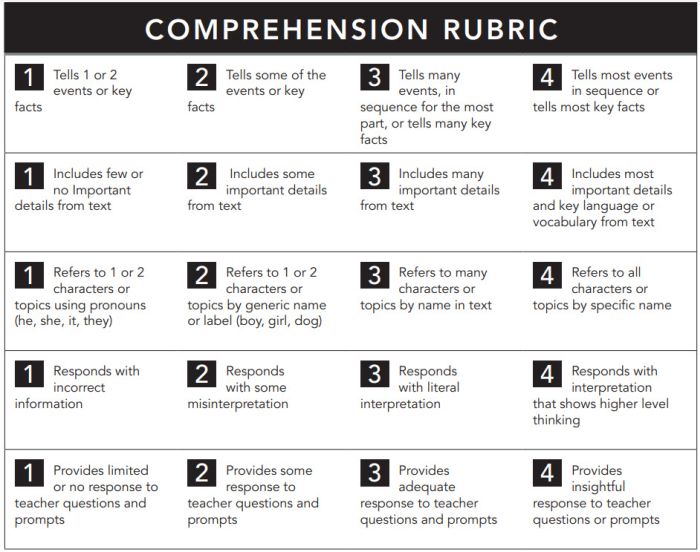
The nice thing about this rubric is that you can use it at any grade level, for any text. If you like this style, you can get a reading fluency rubric here too.
Learn more: Pawprints Resource Center
Written Response Rubric

Rubrics aren’t just for huge projects. They can also help kids work on very specific skills, like this one for improving written responses on assessments.
Learn more: Dianna Radcliffe: Teaching Upper Elementary and More
Interactive Notebook Rubric
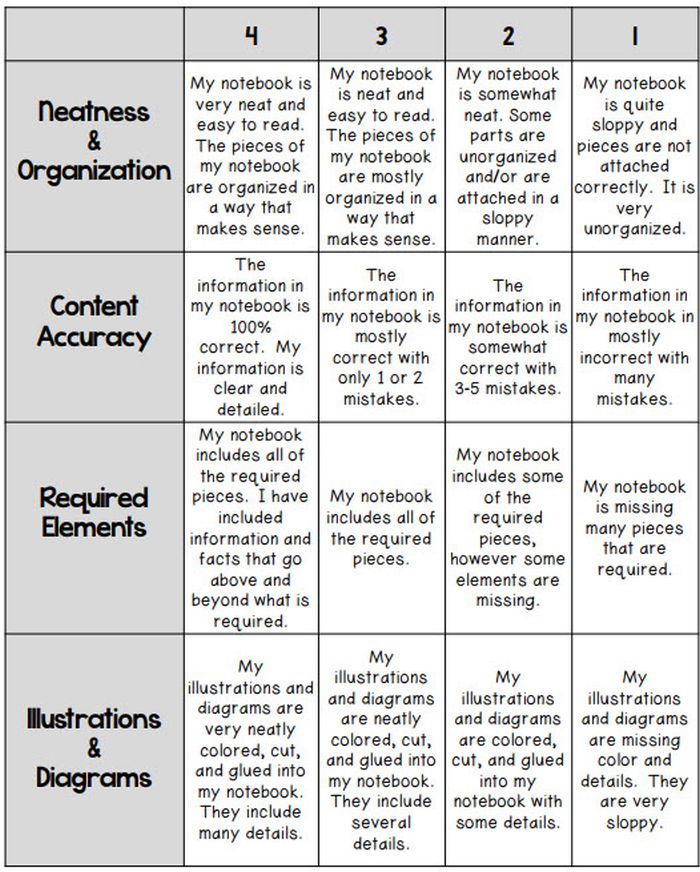
If you use interactive notebooks as a learning tool , this rubric can help kids stay on track and meet your expectations.
Learn more: Classroom Nook
Project Rubric
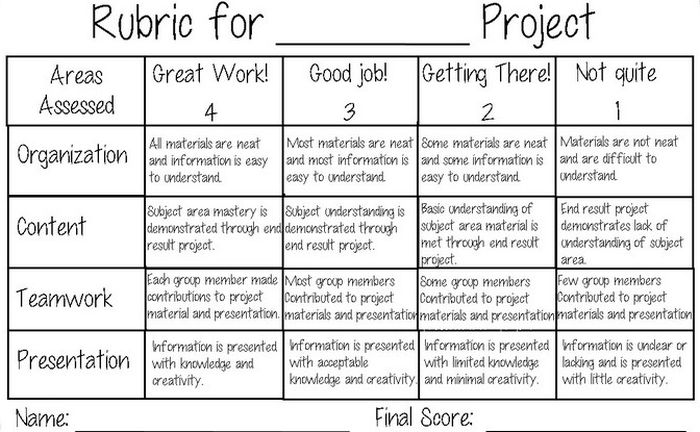
Use this simple rubric as it is, or tweak it to include more specific indicators for the project you have in mind.
Learn more: Tales of a Title One Teacher
Behavior Rubric
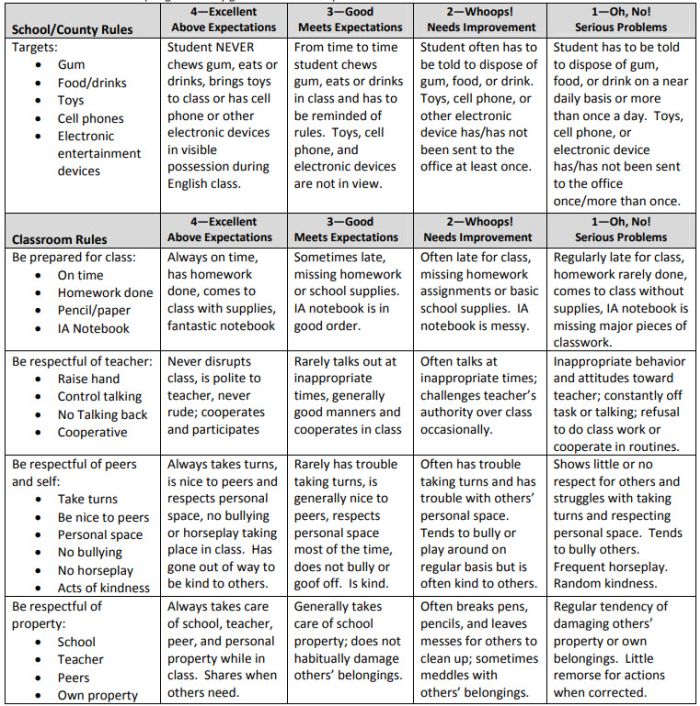
Developmental rubrics are perfect for assessing behavior and helping students identify opportunities for improvement. Send these home regularly to keep parents in the loop.
Learn more: Teachers.net Gazette
Middle School Rubric Examples
In middle school, use rubrics to offer detailed feedback on projects, presentations, and more. Be sure to share them with students in advance, and encourage them to use them as they work so they’ll know if they’re meeting expectations.
Argumentative Writing Rubric
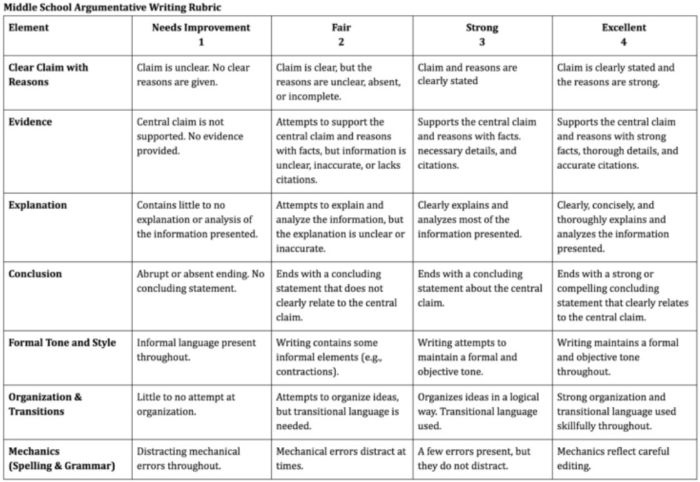
Argumentative writing is a part of language arts, social studies, science, and more. That makes this rubric especially useful.
Learn more: Dr. Caitlyn Tucker
Role-Play Rubric
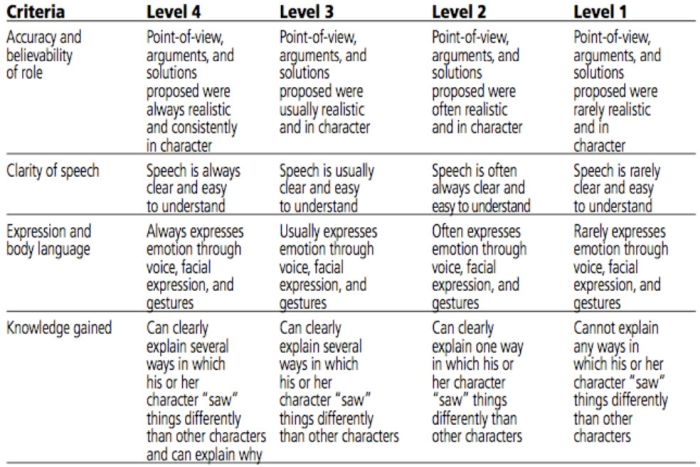
Role-plays can be really useful when teaching social and critical thinking skills, but it’s hard to assess them. Try a rubric like this one to evaluate and provide useful feedback.
Learn more: A Question of Influence
Art Project Rubric
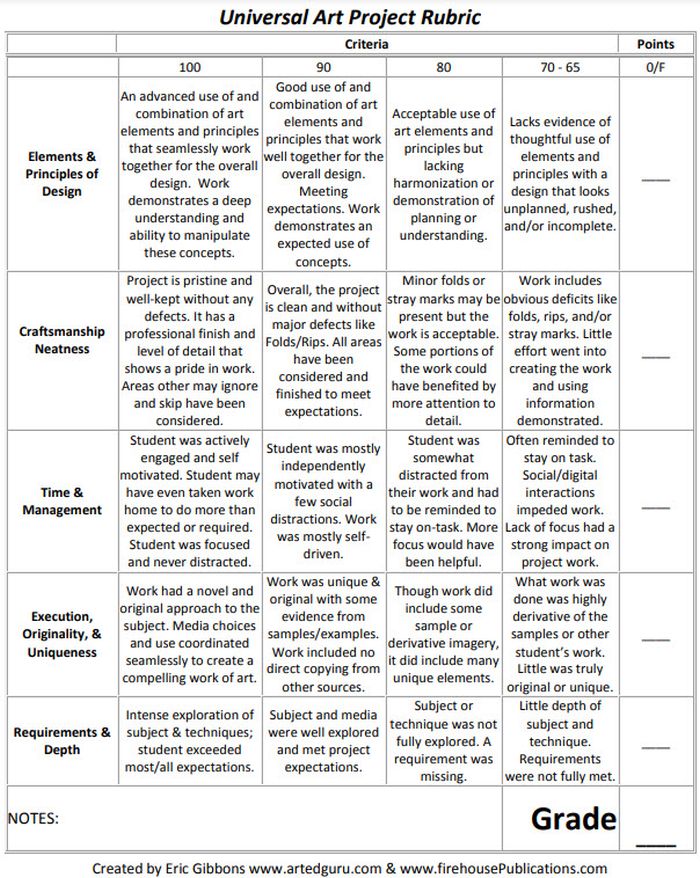
Art is one of those subjects where grading can feel very subjective. Bring some objectivity to the process with a rubric like this.
Source: Art Ed Guru
Diorama Project Rubric
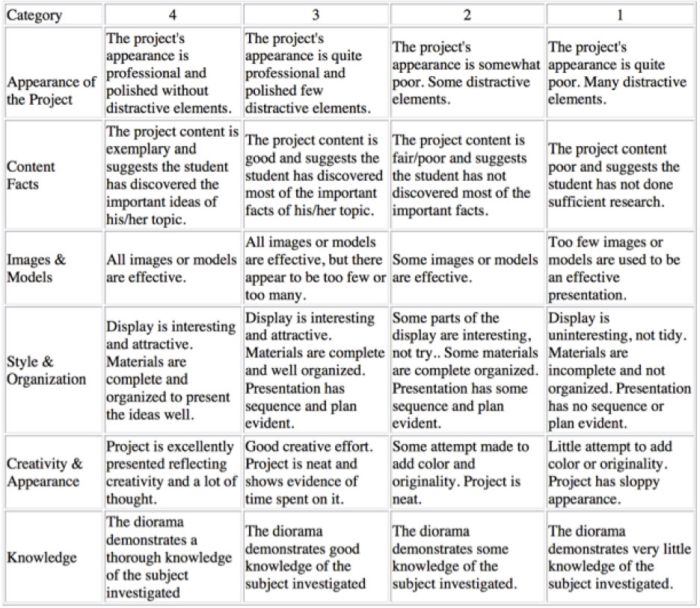
You can use diorama projects in almost any subject, and they’re a great chance to encourage creativity. Simplify the grading process and help kids know how to make their projects shine with this scoring rubric.
Learn more: Historyourstory.com
Oral Presentation Rubric
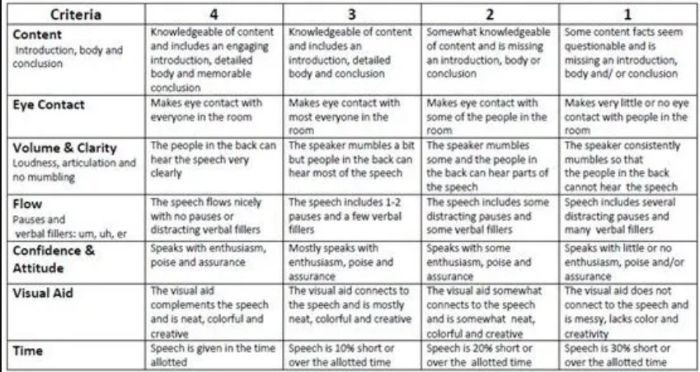
Rubrics are terrific for grading presentations, since you can include a variety of skills and other criteria. Consider letting students use a rubric like this to offer peer feedback too.
Learn more: Bright Hub Education
High School Rubric Examples
In high school, it’s important to include your grading rubrics when you give assignments like presentations, research projects, or essays. Kids who go on to college will definitely encounter rubrics, so helping them become familiar with them now will help in the future.
Presentation Rubric
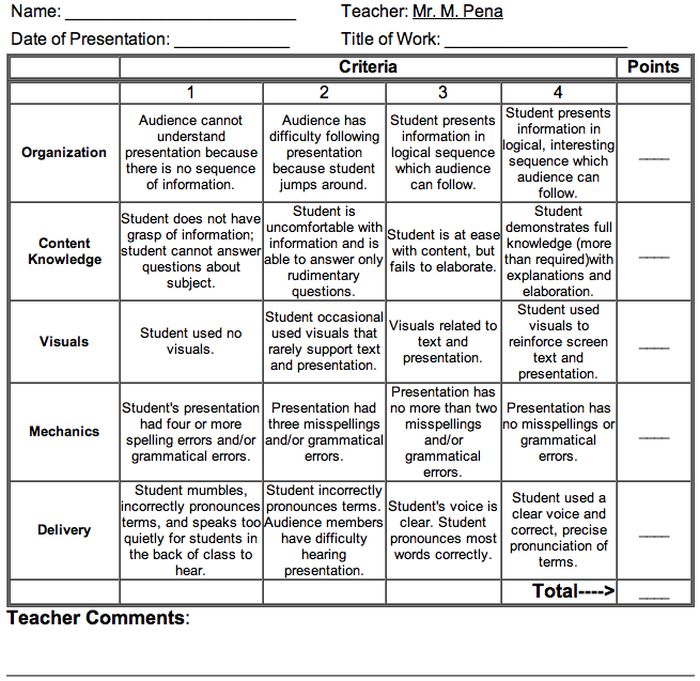
Analyze a student’s presentation both for content and communication skills with a rubric like this one. If needed, create a separate one for content knowledge with even more criteria and indicators.
Learn more: Michael A. Pena Jr.
Debate Rubric
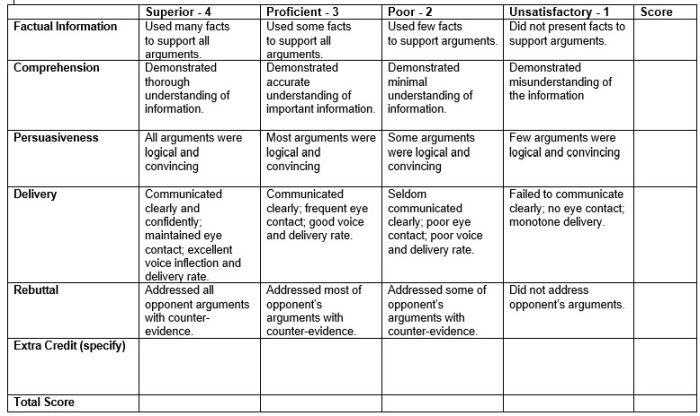
Debate is a valuable learning tool that encourages critical thinking and oral communication skills. This rubric can help you assess those skills objectively.
Learn more: Education World
Project-Based Learning Rubric
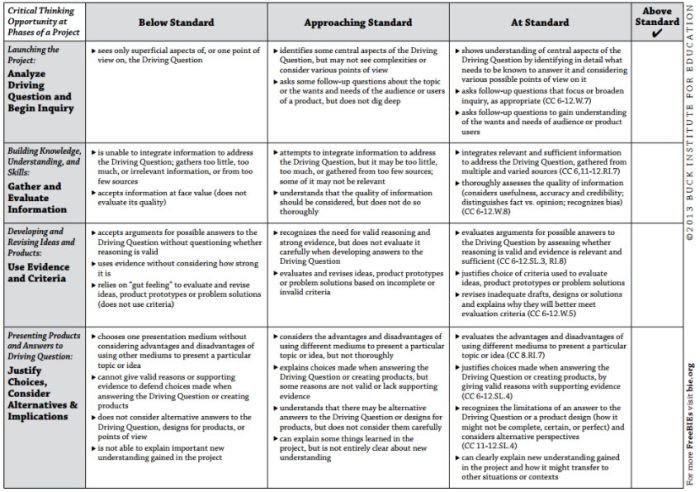
Implementing project-based learning can be time-intensive, but the payoffs are worth it. Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier.
Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers
100-Point Essay Rubric
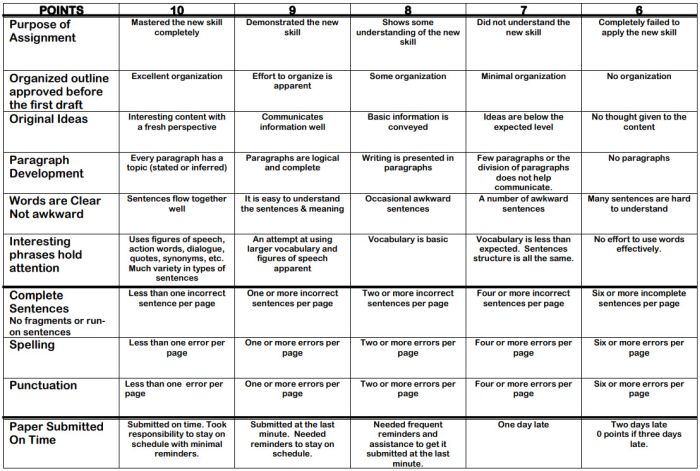
Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points.
Learn more: Learn for Your Life
Drama Performance Rubric
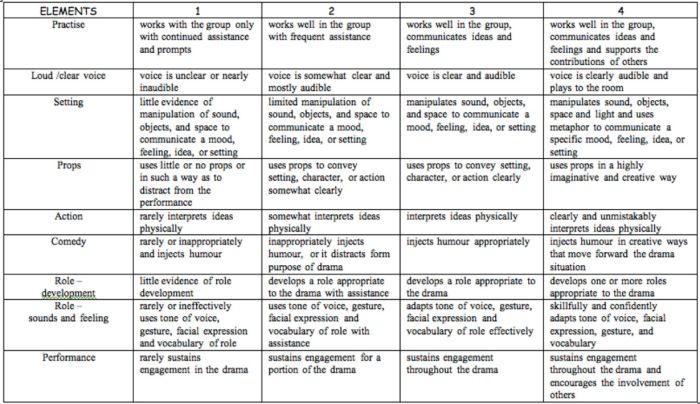
If you’re unsure how to grade a student’s participation and performance in drama class, consider this example. It offers lots of objective criteria and indicators to evaluate.
Learn more: Chase March
How do you use rubrics in your classroom? Come share your thoughts and exchange ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, 25 of the best alternative assessment ideas ..

You Might Also Like
What Is Project-Based Learning and How Can I Use It With My Students?
There's a difference between regular projects and true-project based learning. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

IMAGES
VIDEO