18 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
-1.png?width=112&height=112&name=Image%20Hackathon%20%E2%80%93%20Vertical%20(54)-1.png)

BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATES
Free templates to draft effective business plans.

Updated: 07/01/24
Published: 11/08/18
Updated: July 01, 2024
Published: November 08, 2018
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
So what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing? I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Types
Business plan format, sample business plan: section by section, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ultimately, the format of your business plan will vary based on your goals for that plan. I’ve added this quick review of different business plan types that achieve differing goals.
For a more detailed exploration of business plan types, you can check out this post .
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas. If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
A strategic business plan is another business plan that's often shared internally. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
I’m going to focus on a startup business plan that needs to be detailed and research-backed as well as compelling enough to convince investors to offer funding. In my experience, the most comprehensive and convincing business plans contain the following sections.
Executive Summary
This all-important introduction to your business plan sets the tone and includes the company description as well as what you will be exchanging for money — whether that’s product lines, services, or product-service hybrids.
Market Opportunity
Information about gaps in your industry’s market and how you plan to fill them, focused on demand and potential for growth.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
An overview of your competitors that includes consideration of their strengths and how you’ll manage them, their weaknesses and how you’ll capitalize on them, and how you can differentiate your offerings in the industry.
Target Audience
Descriptions of your ideal customers, their various problems that you can solve, and your customer acquisition strategy.
Marketing Strategy
This section details how you will market your brand to achieve specific goals, the channels and tactics you’ll utilize to reach those goals, and the metrics you’ll be using to measure your progress.
Key Features and Benefits
This is where you’ll use plain language to emphasize the value of your product/service, how it solves the problems of your target audiences, and how you’ll scale up over time.
Pricing and Revenue
This section describes your pricing strategy and plans for building revenue streams that fit your audiences while achieving your business goals.
This is the final section, communicating with investors that your business idea is worth investing in via profit/loss statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets to prove viability.
Okay, so now that we have a format established, I’ll give you more specific details about each section along with examples. Truthfully, I wish I’d had this resource to help me flesh out those first business plans long ago.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan. It is essentially an overview of and introduction to your entire project.
Write this in such a way that it grabs your readers' attention and guides them through the rest of the business plan. This is important because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary: your company description and your products and services.
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front. This is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up your business goals? I’d recommend HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set meaningful goals that matter most for your business.
Products and Services
Here, you will incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive, as it is just a chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business. I recommend including snippets of information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here as well.
Keep in mind that you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. The executive summary should be clear and brief, only including the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template . What makes this executive summary good is that it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
Our Mission
Maria’s Gluten Free Bagels offers gluten-free bagels, along with various toppings, other gluten-free breakfast sandwich items, and coffee. The facility is entirely gluten free. Our team expects to catch the interest of gluten-free, celiac, or health-conscious community members who are seeking an enjoyable cafe to socialize. Due to a lack of gluten-free bagel products in the food industry currently, we expect mild competition and are confident we will be able to build a strong market position.
The Company and Management
Maria’s Gluten Free Bagels was founded in 2010 by Maria Jones, who first began selling her gluten-free bagels online from her home, using social media to spread the word. In 2012 she bought a retail location in Hamilton, MA, which now employs four full-time employees and six part-time employees. Prior to her bagel shop, Maria was a chef in New York and has extensive experience in the food industry.
Along with Maria Jones, Gluten Free Bagel Shop has a board of advisors. The advisors are:
- Jeni King, partner at Winding Communications, Ltd.
- Henry Wilson, president of Blue Robin, LLP.
Our Product
We offer gluten-free products ranging from bagels and cream cheese to blueberry muffins, coffee, and pastries. Our customers are health-conscious, community-oriented people who enjoy gluten-free products. We will create a welcoming, warm environment with opportunities for open mic nights, poetry readings, and other community functions. We will focus on creating an environment in which someone feels comfortable meeting a friend for lunch, or working remotely.
Our Competitive Advantages
While there are other coffee shops and cafes in the North Shore region, there are none that offer purely gluten-free options. This restricts those suffering from gluten-free illnesses or simply those with a gluten-free preference. This will be our primary selling point. Additionally, our market research [see Section 3] has shown a demand for a community-oriented coffee and bagel shop in the town of Hamilton, MA.
Financial Considerations
Our sales projections for the first year are $400,000. We project a 15% growth rate over the next two years. By year three, we project 61% gross margins.
We will have four full-time employees. The salary for each employee will be $50,000.
Start-up Financing Requirements
We are seeking to raise $125,000 in startup to finance year one. The owner has invested $50,000 to meet working capital requirements, and will use a loan of $100,000 to supplement the rest.
Example 2 :
Marianne and Keith Bean have been involved with the food industry for several years. They opened their first restaurant in Antlers, Oklahoma in 1981, and their second in Hugo in 1988. Although praised for the quality of many of the items on their menu, they have attained a special notoriety for their desserts. After years of requests for their flavored whipped cream toppings, they have decided to pursue marketing these products separately from the restaurants.
Marianne and Keith Bean have developed several recipes for flavored whipped cream topping. They include chocolate, raspberry, cinnamon almond, and strawberry. These flavored dessert toppings have been used in the setting of their two restaurants over the past 18 years, and have been produced in large quantities. The estimated shelf life of the product is 21 days at refrigeration temperatures and up to six months when frozen. The Beans intend to market this product in its frozen state in 8 and 12-ounce plastic tubs. They also intend to have the products available in six ounce pressurized cans. Special attention has been given to developing an attractive label that will stress the gourmet/specialty nature of the products.
Distribution of Fancy's Foods Whipped Dream product will begin in the local southeastern Oklahoma area. The Beans have an established name and reputation in this area, and product introduction should encounter little resistance.
Financial analyses show that the company will have both a positive cash flow and profit in the first year. The expected return on equity in the first year is 10.88%
Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company that showcases your mission and impact, then outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, you might emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists, whereas you might emphasize community benefits and minimal environmental impact for progressive nonprofits.
For more guidance, check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary .
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market. Ask and answer: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, SOM analysis , a SWOT analysis , and perform market research on your industry to get some insights for this section. More specifically, here’s what I’d include.
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.
Example: The market for Doggie Pause is all of the dog owners in the metropolitan area and surrounding areas of the city. We believe that this is going to be 2/3 of the population, and we have a goal of gaining a 50% market share. We have a target of a 20% yearly profit increase as the business continues.
Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape Analysis
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you‘ll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are. After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you’ll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover the following:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing.
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle.
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points.
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers.
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are. It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location. This demonstrates useful experience in the industry, helping to build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Competitive Environment
Currently, there are four primary competitors in the Greater Omaha Area: Pinot’s Palette Lakeside (franchise partner), Village Canvas and Cabernet, The Corky Canvas, and Twisted Vine Collective. The first three competitors are in Omaha and the fourth is located in Papillion.
Despite the competition, all locations have both public and private events. Each location has a few sold-out painting events each month. The Omaha locations are in new, popular retail locations, while the existing Papillion location is in a downtown business district.
There is an opportunity to take advantage of the environment and open a studio in a well-traveled or growing area. Pinot’s Palette La Vista will differentiate itself from its competitors by offering a premium experience in a high-growth, influential location.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience? I’d recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear about why you're targeting them. Here are some questions I’d ask myself:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
The Audience
Recognize that audiences are often already aware of important issues. Outreach materials should:
- Emphasize a pollution-prevention practice
- Tell audience a little about how to prevent pollution
- Tell audience where they can obtain information about prevention.
Message Content
- Focus the content for outreach materials on cost savings, such as when and where pollution prevention is as cheap as or cheaper than traditional techniques. Include facts and figures.
- Emphasize how easy it is to do the right thing and the impacts of not engaging in pollution prevention.
- Stress benefits such as efficiency or better relations with government, for businesses not primarily concerned with public image.
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you‘ll discuss how you’ll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier. I’d suggest including these details:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it.
- The goal targets you aim to achieve.
- The metrics you'll use to measure success.
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use.
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler. In my opinion, it works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
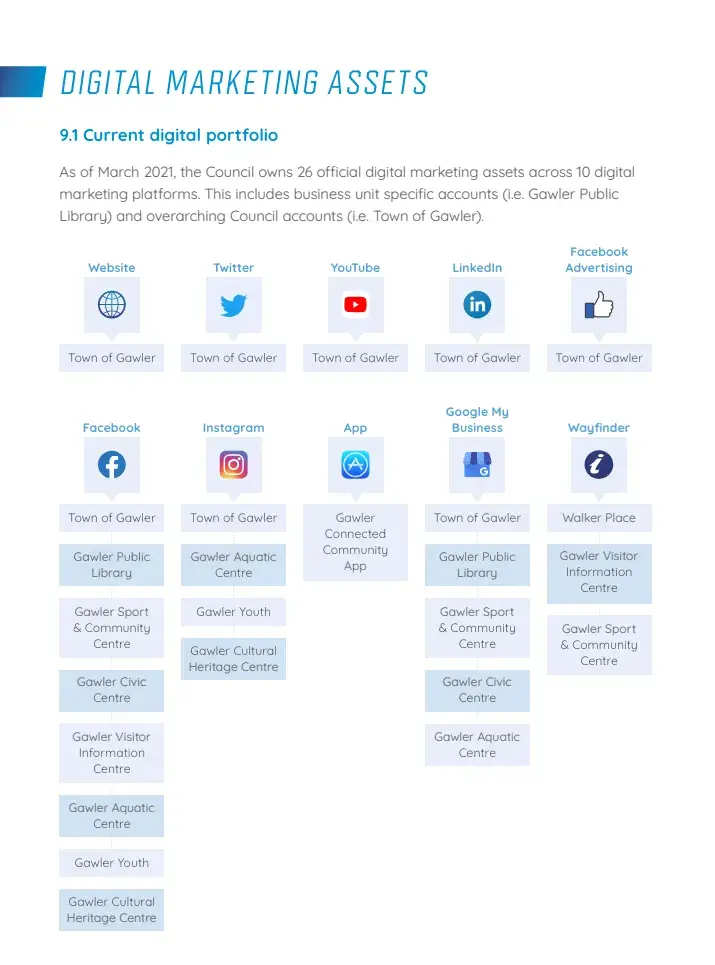
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business

What Is a Risk Assessment? My Complete Guide [+ Free Template]

The Best AI Tools for Ecommerce & How They'll Boost Your Business

23 of My Favorite Free Marketing Newsletters
![product review business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-flowchart-template-1-20240716-6679104-1.webp)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
![product review business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-1-20240625-3861486-1.webp)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![product review business plan How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
21 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
The weekly email to help take your career to the next level. No fluff, only first-hand expert advice & useful marketing trends.
Must enter a valid email
We're committed to your privacy. HubSpot uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
You've been subscribed
A Comprehensive Product Business Plan Template for Success

In today's competitive business landscape, having a well-thought-out product business plan is crucial for success. A product business plan serves as a roadmap that outlines your goals, strategies, and financial projections, ensuring that you stay focused and on track towards achieving your objectives. In this article, we will delve into the importance of a product business plan and explore the key components necessary for crafting an effective plan. We will also provide valuable tips for implementing and monitoring your plan to maximize its effectiveness.
Understanding the Importance of a Product Business Plan
Before we dive into the intricacies of crafting a product business plan, let's first understand why it is so important. A product business plan serves as a blueprint for success, providing a clear and concise overview of your business and its objectives. It acts as a guide to not only attract potential investors but also to align your team's efforts towards a common goal. Additionally, a well-defined plan helps mitigate risks and makes it easier to measure progress and make necessary adjustments along the way.
When it comes to starting a new business or launching a new product, having a solid plan in place is crucial. A product business plan serves as a roadmap, outlining the steps you need to take to achieve your goals. It helps you stay focused and organized, ensuring that you don't lose sight of your vision amidst the chaos of running a business.
Defining a Product Business Plan
So, what exactly is a product business plan? Essentially, it is a document that outlines your product, target market, business strategy, financial projections, and the steps you will take to achieve your goals. It encompasses various elements that work together to give your business direction and purpose. With a clear plan in place, you increase your chances of success by having a roadmap to follow throughout your journey.
When crafting a product business plan, it's important to consider all aspects of your product and its market. Start by defining your product and its unique selling proposition. What problem does it solve? How is it different from existing solutions? By clearly identifying what sets your product apart from the competition, you can effectively position yourself in the market and attract customers.
Another crucial component of a product business plan is conducting thorough market research and analysis. This involves understanding your target market, identifying customer needs and preferences, and evaluating the competitive landscape. By gaining insights into your target market, you can tailor your product and marketing strategies accordingly, increasing your chances of success.
Why a Product Business Plan is Crucial for Success
There are several reasons why having a product business plan is crucial for success. Firstly, it helps you define your product and its value proposition. By clearly identifying what sets your product apart from the competition, you can effectively position yourself in the market and attract customers. A well-defined value proposition helps create a strong brand identity and builds trust with your target audience.
Secondly, a product business plan provides valuable insights into your target market through extensive market analysis. This allows you to understand customer needs and preferences, enabling you to tailor your product and marketing strategies accordingly. By aligning your offerings with customer demands, you increase the likelihood of attracting and retaining customers.
Furthermore, a well-crafted product business plan outlines your operations and management plan, helping you streamline your processes and ensure efficient execution. It provides a clear overview of your organizational structure, roles and responsibilities, and key operational processes. This helps you identify areas for improvement and optimize your operations for maximum efficiency.
In addition to operations, a product business plan also includes financial projections and funding requirements. This gives investors a comprehensive understanding of your business's financial viability and growth potential. By showcasing your financial projections, you demonstrate that you have carefully considered the financial aspects of your business and have a plan in place to achieve profitability.
In conclusion, a product business plan is a crucial tool for success. It provides a roadmap for your business, helps you define your product and target market, and ensures efficient execution through streamlined operations and financial projections. By investing time and effort into crafting a well-defined plan, you increase your chances of achieving your business goals and attracting investors.
Key Components of a Product Business Plan
A successful product business plan comprises several key components that work together to form a cohesive and comprehensive document. Let's explore these components in more detail.
Product Description and Value Proposition
The first component of a product business plan is a clear and detailed description of your product or service. This includes its features, benefits, and how it solves customer pain points. Additionally, you need to define your unique value proposition - the compelling reason why customers should choose your product over competitors.
For example, if you are developing a new smartphone, your product description would include details about its design, specifications, and user interface. You would highlight how your smartphone offers innovative features, such as a longer battery life or a more intuitive user experience, that set it apart from other smartphones in the market. This value proposition would appeal to customers who are looking for a high-quality, user-friendly device that enhances their daily lives.
Market Analysis and Strategy
Next, conduct a thorough market analysis to gain a deep understanding of your target market, industry trends, and competitive landscape. This will help you identify market gaps and opportunities, allowing you to develop a winning marketing strategy. Your marketing strategy should outline how you will reach your target audience, the channels you will utilize, and the tactics you will employ to increase brand awareness and drive sales.
Continuing with the smartphone example, your market analysis would involve researching the current smartphone market, including the size of the market, key players, and consumer preferences. By analyzing this data, you can identify potential niches or untapped segments that your product can target. Your marketing strategy would then outline how you plan to position your smartphone as the go-to choice for tech-savvy individuals who value cutting-edge technology and sleek design.
Operations and Management Plan
The operations and management plan details how your business will run on a day-to-day basis. It covers areas such as production processes, supply chain management, inventory management, and quality control. Additionally, it outlines the organizational structure of your company, including key roles and responsibilities.
In the case of a smartphone business, your operations and management plan would include information on the manufacturing process, from sourcing components to assembling the final product. It would also outline your supply chain management strategy, ensuring a smooth flow of materials and timely delivery to meet customer demand. Furthermore, you would detail your quality control measures to ensure that every smartphone meets the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Financial Projections and Funding
A crucial aspect of any product business plan is the financial projections and funding requirements. This section should provide a clear overview of your expected revenue and expenses, allowing you to assess the financial feasibility of your business. Furthermore, it should outline your funding requirements, including how much money you need to start or scale your business and how you plan to secure it.
For the smartphone business, your financial projections would include estimated sales volumes, pricing, and production costs. This would give you an understanding of your potential revenue and profitability. Additionally, you would outline your funding requirements, such as the amount needed to set up manufacturing facilities and marketing campaigns. You might explore options like seeking investment from venture capitalists or securing a business loan from a financial institution.
By including these key components in your product business plan, you can create a comprehensive and compelling document that showcases the potential of your product and sets a clear roadmap for success.
Crafting an Effective Product Business Plan
Now that we understand the importance of a product business plan and its key components, let's discuss how to craft an effective plan that sets you up for success.
Setting Clear Objectives
The first step in creating an effective product business plan is setting clear and measurable objectives. Clearly define your short-term and long-term goals, ensuring they are specific, realistic, and aligned with your overall business vision.
Conducting Thorough Market Research
A comprehensive market research is vital to understand customer needs, market trends, and the competitive landscape. Gather relevant data, analyze it, and use the insights to inform your product development, marketing strategy, and pricing decisions.
Developing a Strong Marketing Strategy
Your marketing strategy should outline how you will position your product in the market, target your ideal customers, and communicate your value proposition effectively. Utilize various marketing channels such as social media, content marketing, and search engine optimization to maximize your reach and impact.
Preparing Realistic Financial Forecasts
Accurate financial forecasts play a crucial role in determining the financial viability of your business. Consider factors such as production costs, pricing, sales projections, and operating expenses to create realistic financial forecasts. Regularly review and update these forecasts to ensure they remain aligned with your actual financial performance.
Tips for Implementing Your Product Business Plan
To maximize the effectiveness of your product business plan, follow these tips for successful implementation.
Regularly Review and Update Your Plan
A product business plan is not a static document. It should evolve and adapt as your business grows and market conditions change. Regularly review and update your plan to ensure it remains relevant and aligned with your business objectives.
Communicate Your Plan to Your Team
Your entire team should be aware of the product business plan and understand their role in its execution. Regularly communicate the plan and its updates to ensure everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
Monitor Your Progress and Adjust as Necessary
Continuously monitor your progress against the objectives and milestones set in your plan. Identify areas of improvement and make necessary adjustments to keep your business on track and ensure long-term success.
By following these guidelines and creating a comprehensive product business plan, you will set yourself up for success in the competitive business landscape. Remember, a well-crafted plan acts as a roadmap, guiding your business towards its goals and helping you adapt and thrive in an ever-changing market.
Additional Resources
You might also like

The Essential Elements of a Product Strategy

Unlocking True Product Value: A Comprehensive Guide


Key Design Decisions for Product Management: A Comprehensive Guide
- Build your business
Business Tools
- Profit Margin Calculator
- Business Name Generator
- Slogan Generator
- Traffic Calculator
- Ecommerce Statistics
- Ecommerce Wiki
Free business tools
Start a business and design the life you want – all in one place.
- © 2015-2024 Oberlo

The 7 Best Business Plan Examples (2024)
As an aspiring entrepreneur gearing up to start your own business , you likely know the importance of drafting a business plan. However, you might not be entirely sure where to begin or what specific details to include. That’s where examining business plan examples can be beneficial. Sample business plans serve as real-world templates to help you craft your own plan with confidence. They also provide insight into the key sections that make up a business plan, as well as demonstrate how to structure and present your ideas effectively.
Example business plan
To understand how to write a business plan, let’s study an example structured using a seven-part template. Here’s a quick overview of those parts:
- Executive summary: A quick overview of your business and the contents of your business plan.
- Company description: More info about your company, its goals and mission, and why you started it in the first place.
- Market analysis: Research about the market and industry your business will operate in, including a competitive analysis about the companies you’ll be up against.
- Products and services: A detailed description of what you’ll be selling to your customers.
- Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market.
- Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background.
- Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even long-term) financial goals and the costs to run the business. If you’re looking for funding, this is the place to discuss your request and needs.
7 business plan examples (section by section)
In this section, you’ll find hypothetical and real-world examples of each aspect of a business plan to show you how the whole thing comes together.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary offers a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. You’ll want to include a brief description of your company, market research, competitor analysis, and financial information.
In this free business plan template, the executive summary is three paragraphs and occupies nearly half the page:
- Company description
You might go more in-depth with your company description and include the following sections:
- Nature of the business. Mention the general category of business you fall under. Are you a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer of your products?
- Background information. Talk about your past experiences and skills, and how you’ve combined them to fill in the market.
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your company —as a corporation, sole proprietorship, LLC, or other business type.
- Industry. Which business sector do you operate in? The answer might be technology, merchandising, or another industry.
- Team. Whether you’re the sole full-time employee of your business or you have contractors to support your daily workflow, this is your chance to put them under the spotlight.
You can also repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, Instagram page, or other properties that ask for a boilerplate description of your business. Hair extensions brand Luxy Hair has a blurb on it’s About page that could easily be repurposed as a company description for its business plan.
- Market analysis
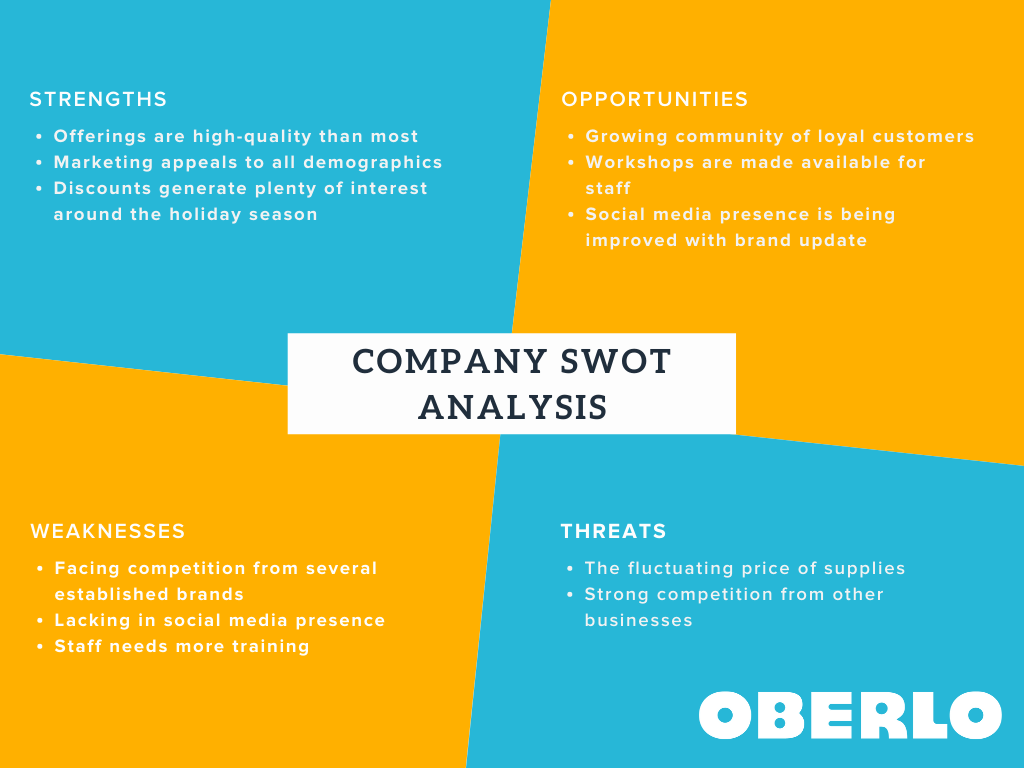
Market analysis comprises research on product supply and demand, your target market, the competitive landscape, and industry trends. You might do a SWOT analysis to learn where you stand and identify market gaps that you could exploit to establish your footing. Here’s an example of a SWOT analysis for a hypothetical ecommerce business:
You’ll also want to run a competitive analysis as part of the market analysis component of your business plan. This will show you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to gain an edge over the competition.
- Products and services
This part of your business plan describes your product or service, how it will be priced, and the ways it will compete against similar offerings in the market. Don’t go into too much detail here—a few lines are enough to introduce your item to the reader.
- Marketing plan
Potential investors will want to know how you’ll get the word out about your business. So it’s essential to build a marketing plan that highlights the promotion and customer acquisition strategies you’re planning to adopt.
Most marketing plans focus on the four Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. However, it’s easier when you break it down by the different marketing channels . Mention how you intend to promote your business using blogs, email, social media, and word-of-mouth marketing.
Here’s an example of a hypothetical marketing plan for a real estate website:

Logistics and operations
This section of your business plan provides information about your production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan (a.k.a. financial statement) offers a breakdown of your sales, revenue, expenses, profit, and other financial metrics. You’ll want to include all the numbers and concrete data to project your current and projected financial state.
In this business plan example, the financial statement for ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy includes forecasted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
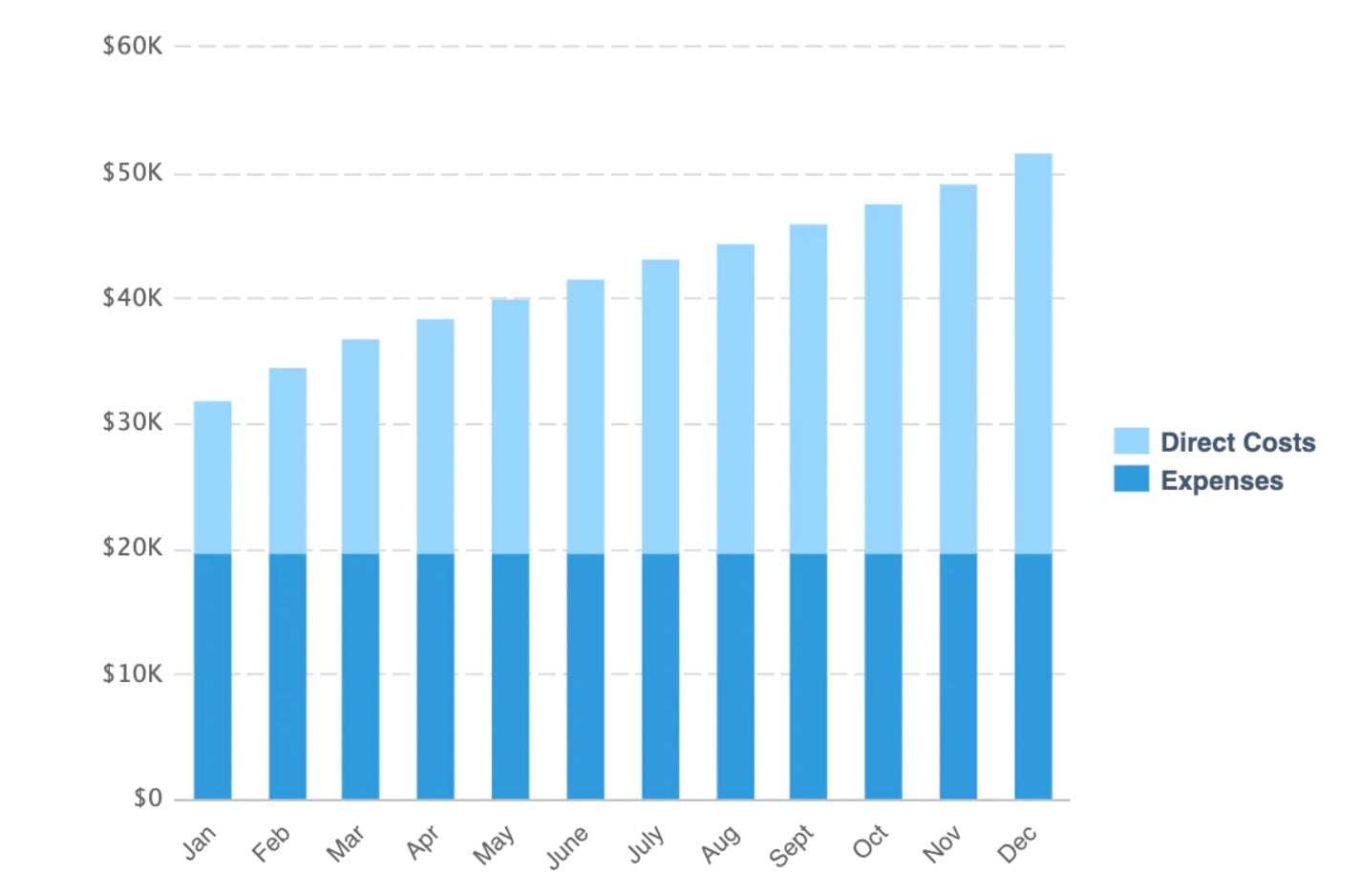
It then goes deeper into the financials, citing:
- Funding needs
- Project cash-flow statement
- Project profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
You can use Shopify’s financial plan template to create your own income statement, cash-flow statement, and balance sheet.
Types of business plans (and what to write for each)
A one-page business plan is a pared down version of a standard business plan that’s easy for potential investors and partners to understand. You’ll want to include all of these sections, but make sure they’re abbreviated and summarized:
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financials
A startup business plan is meant to secure outside funding for a new business. Typically, there’s a big focus on the financials, as well as other sections that help determine the viability of your business idea—market analysis, for example. Shopify has a great business plan template for startups that include all the below points:
- Market research: in depth
- Financials: in depth
Your internal business plan acts as the enforcer of your company’s vision. It reminds your team of the long-term objective and keeps them strategically aligned toward the same goal. Be sure to include:
- Market research
Feasibility
A feasibility business plan is essentially a feasibility study that helps you evaluate whether your product or idea is worthy of a full business plan. Include the following sections:
A strategic (or growth) business plan lays out your long-term vision and goals. This means your predictions stretch further into the future, and you aim for greater growth and revenue. While crafting this document, you use all the parts of a usual business plan but add more to each one:
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Market analysis: detailed analysis
- Marketing plan: detailed strategy
- Logistics and operations plan: detailed plan
- Financials: detailed projections
Free business plan templates
Now that you’re familiar with what’s included and how to format a business plan, let’s go over a few templates you can fill out or draw inspiration from.
Bplans’ free business plan template

Bplans’ free business plan template focuses a lot on the financial side of running a business. It has many pages just for your financial plan and statements. Once you fill it out, you’ll see exactly where your business stands financially and what you need to do to keep it on track or make it better.
PandaDoc’s free business plan template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is detailed and guides you through every section, so you don’t have to figure everything out on your own. Filling it out, you’ll grasp the ins and outs of your business and how each part fits together. It’s also handy because it connects to PandaDoc’s e-signature for easy signing, ideal for businesses with partners or a board.
Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template

Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template helps you map out the essentials of your business, like partnerships, core activities, and what makes you different. It’s a collaborative tool for you and your team to learn how everything in your business is linked.
Better business planning equals better business outcomes
Building a business plan is key to establishing a clear direction and strategy for your venture. With a solid plan in hand, you’ll know what steps to take for achieving each of your business goals. Kickstart your business planning and set yourself up for success with a defined roadmap—utilizing the sample business plans above to inform your approach.
Business plan FAQ
What are the 3 main points of a business plan.
- Concept. Explain what your business does and the main idea behind it. This is where you tell people what you plan to achieve with your business.
- Contents. Explain what you’re selling or offering. Point out who you’re selling to and who else is selling something similar. This part concerns your products or services, who will buy them, and who you’re up against.
- Cash flow. Explain how money will move in and out of your business. Discuss the money you need to start and keep the business going, the costs of running your business, and how much money you expect to make.
How do I write a simple business plan?
To create a simple business plan, start with an executive summary that details your business vision and objectives. Follow this with a concise description of your company’s structure, your market analysis, and information about your products or services. Conclude your plan with financial projections that outline your expected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
What is the best format to write a business plan?
The optimal format for a business plan arranges your plan in a clear and structured way, helping potential investors get a quick grasp of what your business is about and what you aim to achieve. Always start with a summary of your plan and finish with the financial details or any extra information at the end.
Want to learn more?
- Question: Are You a Business Owner or an Entrepreneur?
- Bootstrapping a Business: 10 Tips to Help You Succeed
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: 20 Ways to Think Like an Entrepreneur
- 101+ Best Small Business Software Programs
- Business Planning
How to Write Product and Services Section in a Business Plan

Written by Vinay Kevadiya
Published Nov. 25 2024 · 14 Min Read
People Don't Buy Your Product, They Buy Your Story - Michael Margolis . This quote perfectly encapsulates the importance of the products and services section in a business plan.
How? It provides you the opportunity to clearly and professionally present what your business offers, why it stands out, and how it benefits your target market.
Whether you're offering a physical product, a digital solution, or a service, this section is your chance to showcase the heart of your business and demonstrate its potential for success.
But how can you present your products and services in a business plan in a way that helps your stakeholders easily understand and connect with it? Worry not, you will find out in this blog.
Let's dive in.
What is the products and services section in a business plan?
The products and services section in a business plan is another section like an executive summary or marketing strategy. In a traditional business plan, this section answers critical questions such as:
- What does your business sell or offer?
- What problems do your offerings solve?
- Who benefits from your products or services?
This section helps readers understand the value your business brings to the market and why customers would choose your offerings over others.
The goal is to show potential investors, partners, or stakeholders why your business is worth their time and resources as well as demonstrate your understanding of the market needs and how your offerings effectively meet those needs.
Whether you’re creating a plan for an established business or a new business, or just wish to secure funding, the products and services section plays a vital role in ensuring your plan’s success.
What to include in the product and services section?
When it comes to what to include in your business plan's product and services section, this is your chance to shine. You want to give readers a clear picture of your offering and why it matters. Here’s what you need to include:

1) Detailed product description
Start by providing a clear and concise description of your product or service. To give your stakeholders a complete understanding, address these five key questions:
- What is it?
- Who is it for?
- Where is it available?
- When should one use it?
- How to use it?
Your detailed product description should address all five of these key questions with clear and concise answers. To help you organize your thoughts, consider using the following table to provide precise responses:
Using this table to prepare your detailed description will help you address all key questions, giving your stakeholders clear and comprehensive information about your product or service.
2) Unique features and benefits
Highlighting your product or service's unique features and benefits is essential to building trust and capturing the interest of your stakeholders.
By showcasing what sets your business apart, you demonstrate the strength of your idea and prove that it’s a worthwhile investment in your business.
To effectively showcase the uniqueness of your product or service, you can follow these steps:
Tell a story 📖💭
To create a deeper connection with your audience weave a narrative rather than just adding listening features. Unfold specific challenges you overcame or a personal story that inspired it. Try to connect your audience with your product or service emotionally.
Create a visual comparison 👀
Rather than simply comparing your product with competitors in text, create a visual chart or infographic that shows side-by-side differences. Make it easy for the reader to see what makes your offering stand out.
Show how it changes lives 🌟
Don’t just focus on what your product does—show how it transforms lives. Use before-and-after scenarios or customer journeys to show the real-world impact. People connect more with emotional stories than just facts.
Use testimonials in creative ways 🎥💬
Instead of traditional quotes, use video testimonials or customer stories. Show real customers using your product and sharing their experiences. Visual storytelling can bring more authenticity and impact to your message.
Create a “behind-the-scenes” look 🎬🔧
Give your audience an exclusive look at how your product or service is made. This could be a behind-the-scenes video, a tour of your production process, or an interview with the team. It shows transparency and authenticity.
3) Current stage of development
Including the current stage of development in your product or service section is essential because it provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of where your offering stands and what to expect moving forward.
Here’s why this is crucial and what you should cover:
By answering these questions clearly, you ensure your stakeholders are informed about the current state of your product or service and understand the roadmap ahead.
This transparency not only manages expectations but also demonstrates your strategic planning and commitment to success.
4) Pricing and delivery strategy
This is one of the most critical elements to include in your product and service section. Your stakeholders need to understand the pricing model you’ve chosen and how it aligns with your overall business strategy. It’s essential to address key questions such as:
- Why have you set this particular price?
- How does your pricing compare to competitors? If it’s higher, what justifies the premium?
- What factors influenced the pricing (e.g., cost of production, market demand)?
- What profit margins are you aiming for?
- Does the profit margin cover operational expenses and leave room for growth?
If you need additional information on pricing strategy or are confused about choosing the right pricing strategy for your product or services, then you may refer to our article on types of pricing plan strategies .
Additionally, you must clarify your delivery strategy. If your product requires delivery after production, it’s crucial to specify:
- What resources or infrastructure are in place to handle delivery?
- Will you manage delivery in-house or partner with third-party logistics providers?
- How will delivery timelines and costs affect the overall customer experience?
Addressing these points ensures stakeholders have a clear understanding of how your pricing and delivery models contribute to the sustainability and profitability of your business.
5) Intellectual property and proprietary features
This section highlights any patents, trademarks, copyrights, or proprietary technologies associated with your product or service. It demonstrates how your business is safeguarding its unique offerings and maintaining a competitive edge.
Additionally, intellectual property adds value to your business by protecting innovations and reducing the risk of imitation. This reassures stakeholders that your product or service has defensible advantages.
Here’s what you can include in your intellectual property and proprietary:
- Details about patents, trademarks, or copyrights (if applicable).
- Proprietary technologies, processes, or methodologies that differentiate your offering.
- Plans for future IP development or protection strategies.
Including this information reinforces your product’s uniqueness and assures stakeholders of your commitment to securing your market position.
6) Customer experience strategy
Highlighting your customer experience strategy shows stakeholders you’re not just selling a product but creating a lasting, value-driven relationship with your audience.
It focuses on how your product or service will deliver an exceptional customer experience, from the moment they discover your brand to post-purchase support.
Furthermore, showcasing your customer experience strategy makes your stakeholders feel confident that you understand the importance of customer satisfaction in driving business success.
Your customer experience strategy section should answer and include the following aspects:
- How you’ll ensure a seamless user journey (e.g., intuitive design, easy onboarding).
- Plans for support, feedback collection, and improvements based on insights from potential customers.
- Strategies for building long-term relationships, such as loyalty programs or personalized services.
7) Plan for growth
Your growth plan is a vital component of the product and services section especially if you’re a small business administration or new business owner. It outlines how your business will expand and evolve over time.
More importantly, demonstrating your growth plan also reassures your stakeholders that you’re thinking ahead.
Here’s what you can include in your growth plan in the product and service section:
Each element in the product and services section should work together to tell a cohesive story. Be clear, concise, and transparent—this will not only build trust with stakeholders but also showcase the thoughtfulness and strength of business plans.
Tips on writing the products and services section
Following these tips will help you enhance the quality of your business plan , making it more compelling and convincing to your stakeholders:

1) Focus on benefits, not just features
Shift the focus from simply listing the features of your product to explaining the tangible benefits it provides to the customer.
Because stakeholders want to know how your product impacts the user experience and creates value, simply stating features isn't enough—tell them how those features improve lives.
For example, instead of saying, "Our app has a calendar function," say, "Our app helps users stay organized and save time by automatically syncing appointments across all devices."
2) Make it relatable to real-world scenarios
Give your stakeholders real-world scenarios or case studies that demonstrate how your product or service is used. This shows practical application and increases its appeal.
By making your product or service tangible in everyday contexts, you can paint a clearer picture of its impact, making it easier for stakeholders to see its value.
You can take the example of Tesla , which often showcases customer stories or video testimonials to highlight how their electric cars improve daily driving experiences and contribute to a sustainable future.
3) Break your business plan into bullet points for clarity
Instead of long paragraphs, use bullet points or numbered lists to break down key aspects of your product or service. This makes the information easy to digest.
Moreover, bullet points allow for quick skimming and highlight the most critical points without overwhelming the reader with information. Notably, well-organized business plans keep your audience engaged and navigate essential aspects easily.
4) Keep the focus on the audience, not you
Shift the language from "I" or "we" to "you". Focus on how your product or service benefits the reader or customer. This builds empathy and creates a customer-centric narrative.
Stakeholders will feel that you understand their needs and that your business plan is tailored to provide solutions, not just products.
Instead of saying, "We offer a variety of services," say, "You can enjoy a wide range of services designed to meet your specific needs."
5) Keep language simple and clear
Avoid jargon or technical terms that may confuse your audience. Use clear, simple language to ensure everyone can understand your product or service regardless of expertise.
Clear communication fosters understanding and ensures your message resonates with various stakeholders.
6) Include scalability and adaptability
Describe how your product or service can scale as your business grows. Can it adapt to different markets, customer needs, or increased demand?
This gives stakeholders confidence in your ability to expand without losing quality or efficiency. Scalability is an attractive feature for investors.
Example of product and services in business plan
For a quick overview of your product or service in a business plan format, refer to the table below. It outlines what to include and how to present the key details succinctly.
Wrapping up
Remember, the products and services section is your opportunity to show stakeholders why your business deserves their attention clearly. As we've discussed throughout this blog, this section should describe your product or service in a way that's both compelling and easy to understand.
From what to include to helpful writing tips, we've covered everything you need to create a section that informs and captures interest. However, writing the product and service section can be time-consuming and complex.
If you want to make this process quicker and easier, consider using Bizplanr. It’s an AI business plan generator tool that helps you create a high-quality plan, including a thorough product and services section, all by answering a few simple business-related questions.
This tool helps save you time and effort so you can focus on what matters most—growing your business.
Get Your Business Plan Ready In Minutes
Answer a few questions, and AI will generate a detailed business plan.
Generate your Plan
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to describe products and services in a business plan?
Describing your products and services helps stakeholders understand what you offer, how it solves a problem, and why it stands out in the market. It’s crucial for building credibility and attracting investment.
How detailed should my product/service descriptions be?
Your descriptions should be clear and concise, as well as highlight key features, benefits, and your unique selling proposition. Aim for enough detail to demonstrate value without overwhelming the reader.
What if my products or services are still in development?
If your products or services are still in development, focus on outlining your development progress, expected launch timelines, and any current prototypes or beta tests. Include how you plan to bring them to market.
Should I include visuals or diagrams in this section?
Yes, including visuals, diagrams, or prototypes can help clarify your product or service and make it easier for stakeholders to understand. They add a professional touch and engage the reader.
As the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, Vinay Kevadiya has over 12 years of experience in business planning. He provides valuable insights to help entrepreneurs build and manage successful business plans.
Follow Vinay Kevadiya
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan: Step by Step Guide

Common Source of Funding for Entrepreneurs

How to Write the Operations Plan in Your Business Plan
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many, or all, of the products featured on this page are from our advertising partners who compensate us when you take certain actions on our website or click to take an action on their website. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .

What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

LLC Formation
on ZenBusiness' website
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!

550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the business plan samples in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your business plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how your business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section in our business plan examples covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section of your business plan to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this business plan section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your business plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your business plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed business plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remains stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your business plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own business plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan sample is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at business plan examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a business plan sample.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example of a business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the business plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a business plan sample that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example of a business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your business plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example of a business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your business plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their business plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your business plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily we have a round-up of real-world pitch deck examples used by successful startups that you can review and reference as you build your pitch.
For more resources, check out our full Business Pitch Guide .
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example of a business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right business plan example for your business idea.

Our biggest savings of the year
Black Friday Save 60%
for life on the #1 rated business plan software
on the #1 rated business plan software
on the #1 Business Planning Software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. ... Now that you know what's included and how to format a business plan, let's review some of my favorite templates. 1. HubSpot's One-Page Business Plan. Download a free, editable one-page business plan ...
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it's worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it's mostly centered around research. Company description; Market analysis; Products and services
A successful product business plan comprises several key components that work together to form a cohesive and comprehensive document. Let's explore these components in more detail. Product Description and Value Proposition. The first component of a product business plan is a clear and detailed description of your product or service.
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry. Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech ...
Free business plan templates. Now that you're familiar with what's included and how to format a business plan, let's go over a few templates you can fill out or draw inspiration from. Bplans' free business plan template. Bplans' free business plan template focuses a lot on the financial side of running a business.
Describe how your product or service can scale as your business grows. Can it adapt to different markets, customer needs, or increased demand? This gives stakeholders confidence in your ability to expand without losing quality or efficiency. Scalability is an attractive feature for investors. Example of product and services in business plan
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines a company's goals, strategies for achieving them, and the time frame for their achievement. It covers aspects like market analysis, financial projections, and organizational structure. Ultimately, a business plan serves as a roadmap for business growth and a tool to secure funding.
Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly. ... How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services. This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You ...
After comparing products from more than 30 business lenders, our top pick for the best startup business loan is Headway Capital. Read more Small-Business Grants: Where to Find Free Funding
It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance. It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes .