
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods
Published by Logan Singleton Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods"— Presentation transcript:

Chapter 22 Evaluating a Research Report Gay, Mills, and Airasian

The Robert Gordon University School of Engineering Dr. Mohamed Amish

Research Methods in Crime and Justice

Brief Overview of Qualitative & Quantitative Research.

Modes of Enquiry A Comparison of the Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches.

Methodology A preview. What is Methodology Choosing a method of data collection Structure of the research Builds on and draws from problem statement.

Observing Behavior A nonexperimental approach. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE APPROACHES Quantitative Focuses on specific behaviors that can be easily quantified.

Data Analysis, Interpretation, and Reporting

Introduction to Qualitative Research

Chapter 3 Preparing and Evaluating a Research Plan Gay and Airasian

Copyright c 2001 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.1 Chapter 4 Introduction to Qualitative Research Effective in capturing complexity of communication phenomena.

Lecture 2 Research Questions: Defining and Justifying Problems; Defining Hypotheses.

Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches

Outline: Research Methodology: Case Study - what is case study

Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches Dr. William M. Bauer

Qualitative vs. Quantitative QUANTITATIVE Hypothesis: All beans are alike. NULL: No beans are different. Method: Count the beans. QUALITATIVE Question:

QUANTITATIVE & QUALITATIVE RESEARCH IN SOCIAL SCIENCE NGUYEN THU QUYNH – I34035 Introduction to International Relations.
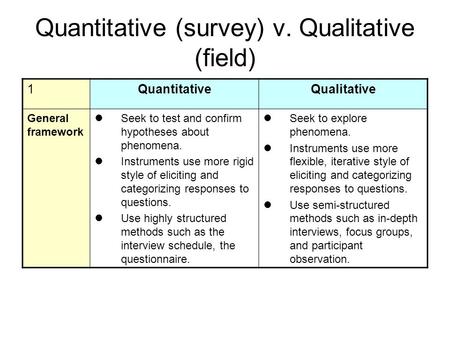
Quantitative (survey) v. Qualitative (field) 1QuantitativeQualitative General framework Seek to test and confirm hypotheses about phenomena. Instruments.

Introduction to Theory & Research Design
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Quantitative Research Methods
This document discusses quantitative and qualitative research methods. Quantitative research involves systematic procedures like questionnaires and scales to measure variables and test relationships between variables statistically. It generally requires large sample sizes to generalize findings to populations. Qualitative research explores human experiences to understand behaviors and interpret their meanings through descriptive, inductive, and interpretive approaches. Both methods are useful for designing studies, reading other research, and gathering related information. Read less

More Related Content
- 1. Quantitative methods and experimental design Research methods
- 2. Why do we need research methods?. • Research is very close to science • In other words, academician in the behavioral sciences believes in the research methods of science to collect and interpret the information.
- 3. For example? • Suppose that a psychologist wanted to see whether a children were raised from different characteristics of a mother (working mother vs full-time mother) would have grown differently, in terms of their self – efficacy, emotional control, or kid and mother attachment. The psychologist would develop an instrument and analyse the data, so the results can be reduced from the bias, instead of giving an interpretation subjectively.
- 4. Another reason why we must take research method? • Design a study • Once you have learned about research method, it’d be useful if you design your study soon. • Reading and evaluating other People’s studies • Having strong fundamental concept of research methods and the terminology as well will allow you to read and understand research articles. • Gathering and evaluating information around you that related to your study
- 5. Qualitative Research Methods Qualitative research explores the side of human experience to understand the background or reasons for the emergence of such behavior. In addition, qualitative research also wants to interpret the meaning of a behavior. The characteristics of qualitative research include: Inductive Descriptive Interpretive
- 6. Quantitative Research Methods Quantitative research involves formal or systematic procedures in gathering information to be measured. The procedure is in the form of a questionnaire, scale, and also uses statistical analysis. This approach can be used to describe a relationship between variables and test the significance of the relationship. Further, quantitative approaches are used to test causal relationships between variables.
- 7. Quantitative Research Methods • Generally quantitative research requires a relatively large number of samples (n). • It aims to generalize research findings to population groups. • As such, the findings of quantitative research must be relevant and useful in large population groups. • Quantitative research requires a description of the data using statistical analysis, whether it is only a description of the data, even to the level of decision making (inferential statistics).
- 8. Types of Quantitative Research Quantitative Non Experimental Univariate Descriptive Bivariate / Multivariate Correlation; Regression Experimental Single Design Two Designs Multiple Designs
- 9. Qualitative and Quantitative Research Paradigms

Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods
Apr 19, 2012
370 likes | 1.76k Views
Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods. Gillian Livesey LTSN-ICS University of Ulster. TEACHING RESEARCH METHODS LTSN-BEST/ICS Workshop 3 rd October 2003. Overview. Qualitative and Quantitative Research Purpose of Research Qualitative and Quantitative Methods Teaching
Share Presentation
- deep learning strategies
- william gossett
- ulster teaching research methods
- qualitative -v-
- systems planning
- encourage students

Presentation Transcript
Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods Gillian Livesey LTSN-ICS University of Ulster TEACHING RESEARCH METHODS LTSN-BEST/ICS Workshop 3rd October 2003
Overview • Qualitative and Quantitative Research • Purpose of Research • Qualitative and Quantitative Methods • Teaching • Resources • Assessment
Research Methods • Research methods are generally categorised as being either quantitative or qualitative. • What matters is that the methods used fit the intended purposes of the research!
Qualitative and Quantitative Paradigms • The qualitative paradigm concentrates on investigating subjective data, in particular, the perceptions of the people involved. The intention is to illuminate these perceptions and, thus, gain greater insight and knowledge. • The quantitative paradigm concentrates on what can be measured. It involves collecting and analysing objective (often numerical) data that can be organised into statistics.
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Research The purposes of research can be categorised as: • Description (fact finding) • Exploration (looking for patterns) • Analysis (explaining why or how) • Prediction (forecasting the likelihood of particular events) • Problem Solving (improvement of current practice)
Descriptive Research • Seeks to accurately describe current or past phenomena - to answer such questions as: • What is the absentee rate for particular lectures? • What is the pass rate for particular courses? • What is the dropout rate on particular degree programmes? • What effect does a particularly quality audit process have on teacher morale?
Analytical Research • Seeking to explain the reasons behind a particular occurrence by discovering causal relationships. Once causal relationships have been discovered, the search then shifts to factors that can be changed (variables) in order to influence the chain of causality. Typical questions are: • Why is there a preponderance of female students on 1st level teacher training programmes? • What factors might account for the high drop-our rate on a particular degree programme?
Predictive Research • Seeks to forecast the likelihood of particular phenomena occurring in given circumstances. It seeks to answer such questions as: • Will changing the start time achieve a higher attendance rate at our lectures? • Will introducing anonymous marking reduce the gender imbalance in the achievement of 1st class degrees? • Will increasing the weighting for course work encourage students to adopt deep learning strategies?
Problem Solving Research / Action Research • Action-research is a form of problem solving based on increasing knowledge through observation and reflection, then following this with a deliberate intervention intended to improve practice. • Educational action-research describes a family of activities in curriculum development, professional development, school improvement programmes, and systems planning and policy development. • Participants in the action being considered are intricately involved with all of these activities.
Typical Methods
Research Methods Categorised by Activity
Teaching: Elementary Concepts • What is a Variable? • Scales of Measurement • Qualitative -v- Quantitative • Continuous -v- Categorical / Dichotomous • Independence -v- Dependence
Teaching: Selecting Statistics
William Gossett - nicknamed ‘Student’ was a chemist at the Guinness brewery in Dublin and developed the student t-test in 1908 to ensure that each batch of Guinness was as similar as possible to every other batch! The t-test is used to compare two groups and comes in at least 3 flavours.
Teaching: Software • Spreadsheets • EXCEL • Statistical Software • SPSS (http://www.spss.com/) • MINITAB (http://www.minitab.com/) • SAS (http://www.sas.com/)
Resources http://trochim.human.cornell.edu/
Resources http://www.socsciresearch.com/
Assessment • Written – a report, research proposal or evaluation • Group Work – interdisciplinary groups • VLE – internet • Peer Tuition • Peer Assessment • Multiple Choice – maybe online • Exam – written or using computer • CAA, QTI
Conclusion What matters is that the methods used fit the intended purposes of the research!
- More by User

The complementarity of qualitative and quantitative research methods
The complementarity of qualitative and quantitative research methods. IN5000, April 25, 2019 Asbjørn Følstad, SINTEF. Quick quiz: What will be the format of this lecture ? Lecturing . Group discussions and presentations . None of the above. Content. Research process
509 views • 13 slides

Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative Research Methods. Ryan Cannon Adriana Cantu. Focus Groups. A focus group is a form of qualitative research in which a group of people are asked about their attitude towards a product, service, concept, advertisement, idea, or packaging.
631 views • 20 slides

Ergonomics: Qualitative and Quantitative Methods
Ergonomics: Qualitative and Quantitative Methods. Every Method Has Both Qualitative and Quantitative Aspects There is No Clear Distinction Between Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches Professional Judgment is Required With Any Methodology. Methods. Walk-Through and Observation Checklists
369 views • 6 slides

QUALITATIVE VS. QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
QUALITATIVE VS. QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH. QUAntiTATIVE RESEARCH. The goal is scientific objectivity, the focus is on data that can be measured numerically. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH.
1.36k views • 5 slides

Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Methods
Integrating Quantitative and Qualitative Methods. Roger Pulwarty, NOAA and Mary Hayden, University of Colorado WAS*IS/Climate and Health July 20, 2006. Points to ponder: What’s quantitative? What’s qualitative? Who uses these approaches, why and what do they think of each other? .
518 views • 23 slides


Options for Blending Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods
Options for Blending Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methods. Ian McDowell (Based on a seminar presentation in 1997). Overview. Epidemiologic research methods are gradually evolving in recognition of inadequacies in current methods
622 views • 15 slides

Qualitative vs. Quantitative research methods
Qualitative vs. Quantitative research methods. PART I – THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH METHODS PART II – EVALUATION OF QUALITATIVE METHODS INCLUDING CONCEPTS LIKE CREDIBILITY, RESEARCHER BIAS, GERNERALIZATION, TRIANGULATION AND REFLEXIVITY.
1.33k views • 30 slides

Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research. Qualitative Research is an umbrella covering several forms of inquiry that help us understand and explain the meaning of social phenomena with as little disruption to the natural setting as possible.
1.36k views • 76 slides

Narrative methods in qualitative and quantitative research
Narrative methods in qualitative and quantitative research. 22 nd February 2006 Combining social research methods, data and analyses Jane Elliott Centre for Longitudinal Studies Institute of Education. Main themes of workshop session.
563 views • 19 slides

Quantitative and Qualitative methods in Library Research
Quantitative and Qualitative methods in Library Research. Amy Catalano, Ed.D ., MLS, MALS Associate Professor of Library Services, Hofstra University. Library Research. Library research tends to be rather poor.
665 views • 31 slides

Quantitative and Qualitative research
Quantitative and Qualitative research. Quantitative Research. Qualitative Research?. A type of educational research in which the researcher decides what to study. A type of educational research in which the researcher relies on the views of the participants.
1.53k views • 25 slides

Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research. AMA Collegiate Marketing Research Certificate Program. Module Objectives. Qualitative and quantitative data offer different problem solving opportunities
806 views • 26 slides

Qualitative vs Quantitative research & Multilevel methods
Qualitative vs Quantitative research & Multilevel methods. How to include context in your research April 2005 Marjolein Deunk. Content. What is qualitative analysis and how does it differ from quantitative analysis? How to combine qualitative and quantitative research?
840 views • 38 slides

Qualitative and Quantitative Research Designs
Qualitative and Quantitative Research Designs. Social Research Methods 2117 & 6501 Fall, 2006 October 25-30, 2006. Overview of Research Design. Research Purposes Exploration ( 探索 ), Description ( 描述 ), Explanation ( 解釋 ) Units of Analysis ( 研究單位 ): possibly individuals ( 個人 )
707 views • 18 slides

Quantitative and Qualitative Research
Quantitative and Qualitative Research. Learning Objectives Explore the differences between quantitative and qualitative data. Outcomes C and below (Knowledge only) Explain the differences between quantitative and qualitative data Explain what an observational study is
1.79k views • 9 slides

Qualitative Research Methods. Mary H. Hayden, PhD NCAR Summer WAS*IS July 20, 2006. Presentation Outline. Distinguishing qualitative and quantitative approaches Qualitative methods – Types of qualitative methods Advantages vs. Disadvantages Real World Examples.
853 views • 39 slides

Sampling Methods in Quantitative and Qualitative Research
Sampling Methods in Quantitative and Qualitative Research. Sampling. Sampling in Quantitative Research. Sampling in Quantitative Research. Population The entire aggregation of cases that meets a specified set of criteria Eligibility criteria determines the attributes of the target population
436 views • 30 slides

RESEARCH DESIGN: Qualitative and quantITATIVE
RESEARCH DESIGN: Qualitative and quantITATIVE. BUSN 364 – Week 6 Özge Can. Research Activities:. Read article: “Bilim Ortamı Olmadan Bilim Olmaz” by Dogan Kuban Available at Course webpage – Reading Materials Read article: “Science in America: Decline and Fall”
503 views • 39 slides

Quantitative and Qualitative Methods
Quantitative and Qualitative Methods. Sebastian M. Rasinger Research Methods in Linguistics. An Introduction. Second Edition London: Bloomsbury. Agenda. Pros and cons of questionnaire use Design Coding. Questionnaires - Basics.
383 views • 22 slides

Quantitative Deductive: transforms general theory into hypothesis suitable for testing Objective Sample represents the whole population so that results can be generalized. Qualitative Inductive: inductive thought which transforms specific observations into general theory Subjective
2.04k views • 5 slides

Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Qualitative And Quantitative Research Methods | Simplilearn
This presentation will help you learn the significant differences between qualitative and quantitative research. You will understand what they are and when to use qualitative and quantitative research methods. You will get an idea about their research approach and the scientific methods used. Finally, we'll look at how to analyze data using these methods and see the final report. 1. What is it? 2. When to Use? 3. Data Collection 4. Research Approach 5. Research Samples 6. Role of Researcher 7. Scientific Method 8. Analyzing Data 9. Final Report What are the learning objectives? Simplilearnu2019s Data Analyst Master's Program developed in collaboration with IBM will provide you with extensive expertise in the booming data analytics field. This data analytics certification training course will teach you how to master descriptive and inferential statistics, hypothesis testing, regression analysis, data blending, data extracts, and forecasting. Through this course, you will also gain expertise in data visualization techniques using Tableau and Power BI, learning how to organize data and design dashboards. In this data analyst certification online course, a special emphasis is placed on those currently employed in the non-technical workforce. Through this Data Analytics course, those with a basic understanding of mathematical concepts will be able to complete the course and become an expert in data analytics. This learning experience melds the knowledge of Data Analytics with hands-on demos and projects via CloudLab. Upon completing this course, you will have all the skills required to become a successful data analyst. Why become Data Analyst? By 2020, the World Economic Forum forecasts that data analysts will be in demand due to increasing data collection and usage. Organizations view data analysis as one of the most crucial future specialties due to the value that can be derived from data. Data is more abundant and accessible than ever in todayu2019s business environment. In fact, 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created each day. With an ever-increasing skill gap in data analytics, the value of data analysts is continuing to grow, creating a new job and career advancement opportunities. The facts are that professionals who enter the Data Science field will have their pick of jobs and enjoy lucrative salaries. According to an IBM report, data and analytics jobs are predicted to increase by 15 percent to 2.72 million jobs by 2020, with the most significant demand for data analysts in finance, insurance, and information technology. Data analysts earn an average pay of $67,377 in 2019 according to Glassdoor. Who should take up this course? Aspiring professionals of any educational background with an analytical frame of mind are best suited to pursue the Data Analyst Masteru2019s Program, including: 1. IT professionals 2. Banking and finance professionals 3. Marketing managers 4. Sales professionals 5. Supply chain network managers 6. Beginners in the data analytics domain 7. Students in UG/ PG programs ud83dudc49Learn more at: https://bit.ly/2SECA5r
648 views • 14 slides
![methods of quantitative research slideshare [PDF DOWNLOAD] Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods](https://cdn5.slideserve.com/10147803/welcome-to-my-slide-now-you-read-research-design-dt.jpg)
[PDF DOWNLOAD] Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods
"Free P.D.F e_Book D.ownload and Rea.d Online Author : John W. Creswell Format : ===>Ebook magazine downloads<==== Click This Link To Download : https://wemblee1234.blogspot.com/?book=1506386709 (Works on PC, iPad, Android, iOS, Tablet, MAC) Synopsis: This bestselling text pioneered the comparison of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research design. For all three approaches, John W. Creswell and new co-author J. David Creswell include a preliminary consideration of philosophical assumptions; key elements of the research process; a review of the literature; an assessment of the use of theory in research applications, and reflections about the importance of writing and ethics in scholarly inquiry. New to this EditionUpdated discussion on designing a proposal for a research project and on the steps in designing a research study. Additional content on epistemological and ontological positioning in relation to the research question and chosen methodology and method. Additional updates on the transformative worldview. Expanded coverage on specific approaches such as case studies, participatory action research, and visual methods. Additional information about social media, online qualitative methods, and mentoring and "
252 views • 19 slides

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jan 11, 2016 · 10. Data Gathering Instrument – Quantitative Research makes use of tools such as questionnaires, surveys, measurements and other equipment to collect numerical or measurable data. Type of Data – if you are conducting a Quantitative Research, what will most likely appear in your discussion are tables containing data in the form of numbers and statistics. Approach – In Quantitative ...
May 12, 2015 · 8. From Research Methodology to Hypothesis Difference Between Research Methods and Research Methodology Research Methodology Research Methods explains the methods by which you may proceed with your research. the methods by which you conduct research into a subject or a topic. involves the learning of the various techniques that can be used in conducting research, tests, experiments, surveys ...
Nov 13, 2020 · 25. Data analysis is less time-consuming and can often be done using statistical software. Results can be generalized if the data are based on random samples and the sample size was sufficient. Data collection methods can be relatively quick, depending on the type of data being collected. Numerical quantitative data may be viewed as more credible and reliable, especially to policy makers ...
4 Research Hypotheses for Quantitative Research Educated guess ... Validity, and Threats to Validity Graziano and Raulin Research Methods: Chapter 8 This multimedia.
Quantitative Research Formal, objective, rigorous, systematic process for generating information Describes new situations, events, or concepts Examines relationships among variables Determines the effectiveness of treatments
Nov 9, 2014 · Quantitative Research Methods. Quantitative Research Methods. ‘Modelling data’: from source to essay. Data Modelling. Historical source material offers much potential for analysis but also many challenges… Unstructured source material Missing data Complications with numbers and dates Data comes from more than one source. 294 views • 13 ...
Qualitative Research Quantitative Research Ask broad, general Qs. Collects data consisting largely of words (text) or image (picture). Descriptions and analysis of words for themes. Conducts inquiry in subjective, biased manner. Ask specific narrow Qs. Collects data from participants generally in numerical form. Analyzes numbers using statistics.
Apr 7, 2019 · Quantitative Research Methods. Quantitative Research Methods. ‘Modelling data’: from source to essay. Data Modelling. Historical source material offers much potential for analysis but also many challenges… Unstructured source material Missing data Complications with numbers and dates Data comes from more than one source. 294 views • 13 ...
Jan 5, 2021 · This document discusses quantitative and qualitative research methods. Quantitative research involves systematic procedures like questionnaires and scales to measure variables and test relationships between variables statistically. It generally requires large sample sizes to generalize findings to populations.
Apr 19, 2012 · Qualitative vs. Quantitative research methods. Qualitative vs. Quantitative research methods. PART I – THE DISTINCTION BETWEEN QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH METHODS PART II – EVALUATION OF QUALITATIVE METHODS INCLUDING CONCEPTS LIKE CREDIBILITY, RESEARCHER BIAS, GERNERALIZATION, TRIANGULATION AND REFLEXIVITY. 1.33k views • 30 slides