
Literary Analysis–How To
Written by Ali Pineo

What is a Literary Analysis?
A literary analysis is a common assignment in first-year writing and English courses. Despite how ubiquitous they are, literary analyses can sometimes feel confusing or maybe even a little intimidating. This type of analytical essay requires you to zoom into a text to unpack and wrestle with deeper meaning (through exploring diction, syntax, structure—just to name a few elements) and then zoom out to illuminate how those elements contribute to the “big picture,” whether that be a central idea, theme, or social commentary.
Central to the literary analysis is the “why.” You should not aim to merely explain, describe, or interpret—you must do all three in addition to answering bigger questions like, “Why does this interpretation matter?” and “How is this perspective significant?” These questions are at the heart of analysis, which aims to examine complex ideas by studying their individual parts, characteristics, and features.
Your job, then, is to put on your detective cap, search for major ideas, and identify patterns in how those ideas connect. In doing so, you’ll work to bring the implicit to the surface and develop (and evolve!) your questions and interpretations to explore the text. Cultivating this detective state of mind will allow you to conquer your next major task: writing the literary analysis.
Table of Contents:
How to Find Your Topic
Writing Your Intro
Moving beyond the 5 paragraph structure, the importance of transitions, writing your conclusion, 3 ways to find a topic, notice what catches your attention.
Is it a symbol that continues to reappear? Is it the power struggle between two characters? Is it a nagging question you can’t shake? Investigating something that stands out to you is a good starting place. You may not end up writing on that particular topic, but it could lead you to a compelling idea worthy of unpacking.
Don’t take class for granted
check your notes! Your professors often leave a really clear trail of themes and ideas you can explore in your essay. If you think this will preclude you from having a novel or unique idea, think again. There are many ways to approach previously made arguments. Picking up on your professor’s bread crumbs is precisely why you go to class—to learn from an expert and to practice your analytical skills under their guidance. Following their lead can often guide you toward the richest ideas to explore and unpack.
Talk to a friend and have them keep track of the words and themes that keep popping up for you
Do you continue circling back to the theme of power? Or perhaps you keep repeating the same three words—like “education, socio-economic status, and success” (you might then ask yourself how those three things are connected). Saying your ideas out loud and having them repeated back to you can help you to develop clarity and understanding of your potential topic(s).
Once you’ve chosen a topic, you’re ready to explore significant quotes, passages, and themes that will make up your evidence. Rereading key sections of the text will help you to elevate your understanding of the ideas and evidence you are considering and aid in the tedious narrowing of your topic. This prep work is crucial to constructing your main argument, A.K.A. your thesis, which consists of a narrowed topic + the “so what.” When you’re ready, head over to this guide on How to Write a Strong Argument to build an outstanding thesis statement for your essay.
Your introduction is like a map—it should orient your reader to the main argument (your thesis). Your map should be inviting, clear, and useful, as well as capture your reader’s attention. If your map had a shape, it would be an upside down triangle, starting general and narrowing to its most specific point—your thesis.
[action_item]
Pro tip: Although the intro comes first in the essay, that doesn’t mean you actually have to write it first. It’s hard to introduce something that doesn't exist yet! Instead, you could start by writing a simple place-holder introduction and come back to revise and refine it after you’ve finished drafting the body paragraphs. (This is how many of your professors write.)
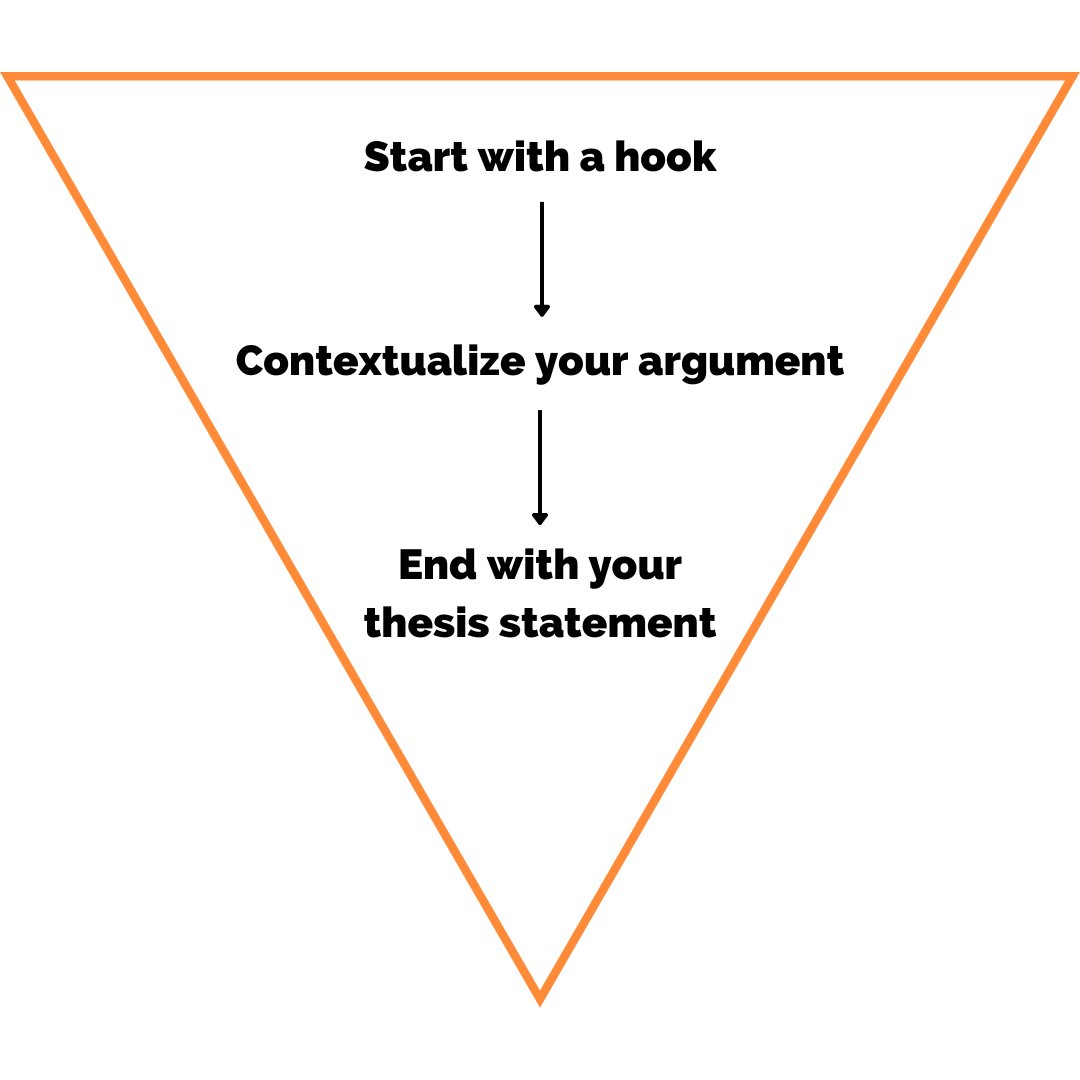
Top of the funnel: Start with a hook (remember, enticing)
An interesting rhetorical question like “Is Heathcliff worthy of sympathy?” or a bold statement(s) (think newspaper headlines) like “He tortured his newphew and son. He abused women. He crafted a master plan to seek revenge on his enemies'' will catch your reader’s attention.
Middle of the funnel: Contextualize your argument
At first, writing an intro can feel like navigating murky waters? “Put the stuff a reader needs to know to understand your paper in the intro” is the advice often given to students. But how do you know exactly what to include and what to leave out? The easiest way to construct your intro is to reverse engineer it from your thesis statement and/or topic sentences.
3 Ways to Reverse Engineer:
Divide your thesis into parts and provide context that sequentially elaborates on those individual parts.
Think about your thesis statement as a set of key terms—define those terms so the reader is able to understand the specifics of your argument.
After you’re done writing the essay, compile every first and last sentence of your body paragraphs. Paraphrase those sentences into an introduction.
BOTTOM OF THE FUNNEL: end with your thesis statement
In high school, you were likely taught the 5 paragraph structure for an essay: intro, 3 body paragraphs, conclusion. While the 5-paragraph structure can be a helpful beginner’s tool for understanding argumentation and organizing your ideas, it can be constraining in certain situations. It’s highly likely you’ll want to move beyond the 5-paragraph essay, for example, when your ideas or argument demand it, as is often the case for a literary analysis (and probably most if not all of your college essays).
One pitfall I often see in literary analyses that attempt to adhere to the five-paragraph structure is the tendency to prove the same point, “my thesis is true,” for every body paragraph. Your analysis should add up to more than proving that your thesis is true or valid—it should also question, complicate, and most importantly, evolve your main argument. One way to do this is through David Rosenwasser’s “10-1” method, which aims to cultivate freedom of thought and hopefully, deeper analysis.
The 10-1 Method (in a nutshell)
Your first job is to find the best representative example to use as your evidence for a point you’ll want to make in your analysis (that stands for the “1”). You can do this by collecting quotes that support or illustrate the same idea and then selecting the quote that most overtly represents your claim.
Next, you’ll want to unpack 10 points of analysis for each piece of evidence. This will likely feel difficult—but that’s the point! You can dig into the details, identify patterns, wrestle with meaning, highlight implications, point out significance, and more. By doing so, you’ll stretch your thinking and make connections you might have otherwise overlooked. This part of the exercise will also help you generate ideas and content for your body paragraphs, which you can use when outlining or drafting. You don’t have to necessarily use all 10 points you generate—you can narrow them down to the points that best support that paragraph’s claim. What will result is deeper analysis and a more nuanced argument.
As you continue to formulate your body paragraphs, you can repeat the first two steps with new evidence that further extends and qualifies your argument. This will help you to avoid a static argument and help your main argument gain complexity and relevancy.
The 10-1 method will help to free up your thinking through the selection of strong, representative evidence and the unfolding of insightful, detailed analysis. When you shift from outline to draft, you’ll have ensured that your arguments have movement to them, reminiscent of a visual spectacle—evolving and changing shape from beginning to end.
Transitions may seem like an accessory, a nice embellishment. But imagine you’re following that map we discussed earlier, and it leads you through scenic waterfalls and mountains by way of an extremely bumpy road. You’ll probably miss the view because you’re focusing so hard on keeping the steering wheel straight! Similarly, your transitions allow for a smooth ride, taking your reader from idea to idea without ejecting them from their seat. More importantly, good transitions will allow for your arguments and ideas to shine.
In your essay, you will utilize two main types of transitions:
Transitions between different ideas in your argument (sentence level)
Transitions between arguments (paragraph/section level)
Whether you are transitioning from one idea to the next or introducing a totally new argument, you want to show how the thing you’re saying connects and leads to the next thing you’d like to say, or how something links back to a piece you spent time exploring earlier.
So, how do you do that?
On a sentence level: start your sentences by referring back to the main idea or subject of the sentence before it, and end your sentences with the new information. This way, you create a smooth ramp into your next idea.
On a paragraph level: start by either summarizing or referring back to the “so what” of the paragraph before it and use a strong transition word or phrase to connect it to your next argument.
Examples of great transition words
As a result
Accordingly
In contrast
First, second, third, next, finally
Additionally/in addition
Furthermore
For greater detail and further examples, check out this guide to transitions from the University of Melbourne .
To evaluate your transitions, ask yourself:
Are there smooth transitions and/or topic sentences at the beginning of each paragraph? Underlining or circling those transitions will help you to visually map whether you're providing adequate anchors and links for your readers.
Can I define or explain the relationship a transition is trying to convey between each new idea (e.g. are they similar? do they contrast? are they chronological?). If you’re struggling to answer that question, you probably a) don’t have a transition yet or b) need a stronger, more specific transition.
Feel free to check out this guide on How to Edit a College Essay for more tips on how to up-level the focus, clarity, and style of your essay with strong transitions.
Let’s begin with what the conclusion is not: it is not strictly a summary of your main points and thesis. While the conclusion frequently does start with a look back at previously made arguments, the majority of the conclusion should be forward looking. It should focus on the “so what” and aim for a feeling of resolution with an openness to possibilities.
Here’s one way to think about it: In your essay, we don’t mean “conclusion” as in “to end”; we mean it more along the lines of “to draw conclusions,” as in “to make judgements, often about the greater meaning or importance of a thing.”
So, how do you achieve this?
Introduce your evolved thesis by circling back to reevaluate and establish connections between previously made arguments. Using keywords to guide this “summary” will help you to avoid redundancy while still communicating the important evolution of your ideas throughout the essay.
Connect to Implications and/or Larger Themes
Broaden your focus to larger issues or themes brought forth by the text. A few different moves you can make include:
stating the author’s implied warning to the reader
identifying and connecting the significance of your thesis to a larger theme
commenting on the cultural currency of your argument
Example conclusion from a comparative analysis of Intimate Apparel by Lynn Nottage and Sassafrass, Cypress & Indigo by Ntozake Shange:
Female protagonists Esther and Indigo were ahead of their time in their ability to exemplify powerful, independent women. They used their creativity to retain their sense of self and make unique contributions to the world around them. As a result, they did not need to rely on men or societal acceptance to formulate strong identities. By creating strong female characters grounded in their “domestic” creative art, Nottage and Shange reframe female domesticity as more than just a role women should play—it’s a tool that women can wield to generate fuller, more empowered lives for themselves.
Notice that the underlined section does link back to and in effect summarizes some of the major points made in the essay (and notice that even without having read the whole essay, you have a clear sense of what was likely discussed). But the section in italics draws conclusions by examining the wider meaning or importance and by discussing its possible social implications and applications.
Final Thoughts
Let me normalize something for you—writing is hard.
For basically everybody. If you don’t believe me, read Anne Lamott’s “Shitty First Drafts.”
But IMO, knowing how to analyze and write a textual analysis is one of the best tools you can have in your writer’s toolbox. You’ll have learned to cultivate a critical lens, which sets a solid foundation for all types of analytical writing, including writing on research, government policies, historical events, works of art, and much more. And though writing may sometimes feel like what I once heard someone else describe as a “glorious frustration,” I hope this guide helps you find your “glory” (or at least eases the frustration a bit).
Special thanks to Ali Pineo for writing this post and contributing to other College Writing Center resources

Ali is a college essay specialist with her BA in English from Stanford University and MFA from UC Irvine. She has spent thousands of hours coaching admissions essays and helping students to build their confidence in the writing process. In addition to essay coaching, she is a former professional ballerina and current co-artistic director for Maui’s contemporary dance company Adaptations Dance Theater. She is a hybrid writer-dancer who enjoys the power of storytelling.
How to Write a Literature Review
How to Write a History Essay
College Writing Center
First-Year Writing Essentials
College-Level Writing
Unpacking Academic Writing Prompts
What Makes a Good Argument?
How to Use Sources in College Essays
Evaluating Sources: A Guide for the Online Generation
What Are Citations?
Avoiding Plagiarism
US Academic Writing for College: 10 Features of Style
Applying Writing Feedback
How to Edit a College Essay
Asking for Help in College & Using Your Resources
What Is Academic Research + How To Do It
Subject or Context Specific Guides
How to Write A History Essay
A Sophomore or Junior’s Guide to the Senior Thesis

Literary Analysis Essay
Literary Analysis Essay Writing
Last updated on: May 21, 2023
Literary Analysis Essay - Ultimate Guide By Professionals
By: Cordon J.
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Dec 3, 2019

A literary analysis essay specifically examines and evaluates a piece of literature or a literary work. It also understands and explains the links between the small parts to their whole information.
It is important for students to understand the meaning and the true essence of literature to write a literary essay.
One of the most difficult assignments for students is writing a literary analysis essay. It can be hard to come up with an original idea or find enough material to write about. You might think you need years of experience in order to create a good paper, but that's not true.
This blog post will show you how easy it can be when you follow the steps given here.Writing such an essay involves the breakdown of a book into small parts and understanding each part separately. It seems easy, right?
Trust us, it is not as hard as good book reports but it may also not be extremely easy. You will have to take into account different approaches and explain them in relation with the chosen literary work.
It is a common high school and college assignment and you can learn everything in this blog.
Continue reading for some useful tips with an example to write a literary analysis essay that will be on point. You can also explore our detailed article on writing an analytical essay .

On this Page
What is a Literary Analysis Essay?
A literary analysis essay is an important kind of essay that focuses on the detailed analysis of the work of literature.
The purpose of a literary analysis essay is to explain why the author has used a specific theme for his work. Or examine the characters, themes, literary devices , figurative language, and settings in the story.
This type of essay encourages students to think about how the book or the short story has been written. And why the author has created this work.
The method used in the literary analysis essay differs from other types of essays. It primarily focuses on the type of work and literature that is being analyzed.
Mostly, you will be going to break down the work into various parts. In order to develop a better understanding of the idea being discussed, each part will be discussed separately.
The essay should explain the choices of the author and point of view along with your answers and personal analysis.
How To Write A Literary Analysis Essay
So how to start a literary analysis essay? The answer to this question is quite simple.
The following sections are required to write an effective literary analysis essay. By following the guidelines given in the following sections, you will be able to craft a winning literary analysis essay.
Introduction
The aim of the introduction is to establish a context for readers. You have to give a brief on the background of the selected topic.
It should contain the name of the author of the literary work along with its title. The introduction should be effective enough to grab the reader’s attention.
In the body section, you have to retell the story that the writer has narrated. It is a good idea to create a summary as it is one of the important tips of literary analysis.
Other than that, you are required to develop ideas and disclose the observed information related to the issue. The ideal length of the body section is around 1000 words.
To write the body section, your observation should be based on evidence and your own style of writing.
It would be great if the body of your essay is divided into three paragraphs. Make a strong argument with facts related to the thesis statement in all of the paragraphs in the body section.
Start writing each paragraph with a topic sentence and use transition words when moving to the next paragraph.
Summarize the important points of your literary analysis essay in this section. It is important to compose a short and strong conclusion to help you make a final impression of your essay.
Pay attention that this section does not contain any new information. It should provide a sense of completion by restating the main idea with a short description of your arguments. End the conclusion with your supporting details.
You have to explain why the book is important. Also, elaborate on the means that the authors used to convey her/his opinion regarding the issue.
For further understanding, here is a downloadable literary analysis essay outline. This outline will help you structure and format your essay properly and earn an A easily.
DOWNLOADABLE LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY OUTLINE (PDF)
Types of Literary Analysis Essay
- Close reading - This method involves attentive reading and detailed analysis. No need for a lot of knowledge and inspiration to write an essay that shows your creative skills.
- Theoretical - In this type, you will rely on theories related to the selected topic.
- Historical - This type of essay concerns the discipline of history. Sometimes historical analysis is required to explain events in detail.
- Applied - This type involves analysis of a specific issue from a practical perspective.
- Comparative - This type of writing is based on when two or more alternatives are compared
Examples of Literary Analysis Essay
Examples are great to understand any concept, especially if it is related to writing. Below are some great literary analysis essay examples that showcase how this type of essay is written.
A ROSE FOR EMILY LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
THE GREAT GATSBY LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
THE YELLOW WALLPAPER LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
If you do not have experience in writing essays, this will be a very chaotic process for you. In that case, it is very important for you to conduct good research on the topic before writing.
There are two important points that you should keep in mind when writing a literary analysis essay.
First, remember that it is very important to select a topic in which you are interested. Choose something that really inspires you. This will help you to catch the attention of a reader.
The selected topic should reflect the main idea of writing. In addition to that, it should also express your point of view as well.
Another important thing is to draft a good outline for your literary analysis essay. It will help you to define a central point and division of this into parts for further discussion.
Literary Analysis Essay Topics
Literary analysis essays are mostly based on artistic works like books, movies, paintings, and other forms of art. However, generally, students choose novels and books to write their literary essays.
Some cool, fresh, and good topics and ideas are listed below:
- Role of the Three Witches in flaming Macbeth’s ambition.
- Analyze the themes of the Play Antigone,
- Discuss Ajax as a tragic hero.
- The Judgement of Paris: Analyze the Reasons and their Consequences.
- Oedipus Rex: A Doomed Son or a Conqueror?
- Describe the Oedipus complex and Electra complex in relation to their respective myths.
- Betrayal is a common theme of Shakespearean tragedies. Discuss
- Identify and analyze the traits of history in T.S Eliot’s ‘Gerontion’.
- Analyze the theme of identity crisis in The Great Gatsby.
- Analyze the writing style of Emily Dickinson.
If you are still in doubt then there is nothing bad in getting professional writers’ help.
We at 5StarEssays.com can help you get a custom paper as per your specified requirements with our do essay for me service.
Our essay writers will help you write outstanding literary essays or any other type of essay. Such as compare and contrast essays, descriptive essays, rhetorical essays. We cover all of these.
So don’t waste your time browsing the internet and place your order now to get your well-written custom paper.

Frequently Asked Questions
What should a literary analysis essay include.
A good literary analysis essay must include a proper and in-depth explanation of your ideas. They must be backed with examples and evidence from the text. Textual evidence includes summaries, paraphrased text, original work details, and direct quotes.
What are the 4 components of literary analysis?
Here are the 4 essential parts of a literary analysis essay;
No literary work is explained properly without discussing and explaining these 4 things.
How do you start a literary analysis essay?
Start your literary analysis essay with the name of the work and the title. Hook your readers by introducing the main ideas that you will discuss in your essay and engage them from the start.
How do you do a literary analysis?
In a literary analysis essay, you study the text closely, understand and interpret its meanings. And try to find out the reasons behind why the author has used certain symbols, themes, and objects in the work.
Why is literary analysis important?
It encourages the students to think beyond their existing knowledge, experiences, and belief and build empathy. This helps in improving the writing skills also.
What is the fundamental characteristic of a literary analysis essay?
Interpretation is the fundamental and important feature of a literary analysis essay. The essay is based on how well the writer explains and interprets the work.

Law, Finance Essay
Cordon. is a published author and writing specialist. He has worked in the publishing industry for many years, providing writing services and digital content. His own writing career began with a focus on literature and linguistics, which he continues to pursue. Cordon is an engaging and professional individual, always looking to help others achieve their goals.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Interesting Literary Analysis Essay Topics for Students

- Write a Perfect Literary Analysis Essay Outline

Say Goodbye to Academic Stress!
With FREE AI report, Turnitin report, bibliography, title page, and a lot more!
LIMITED TIME ONLY
People Also Read
- literary analysis essay outline
- types of qualitative research
- types of autobiography
- writing narrative essay
- analytical essay example
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
OFFER EXPIRES SOON!
© 2024 - All rights reserved
How to Write a Literary Analysis: 6 Tips for the Perfect Essay
by Kaelyn Barron | 2 comments

Sometimes, you’ll want to read a book just for the pleasure of being entertained and taken to a different time or place, and see the world through the eyes of another.
Other times, however, like when you’re in your English Literature class or reading a classic, you’ll have to dig past the surface and look beyond the words on the page to understand the author’s message.
To do this, you can conduct your own literary analysis, and examine how the author uses various literary devices and techniques to artfully tell their story while delivering a larger message.
What Is a Literary Analysis?
The purpose of a literary analysis is to examine and deconstruct a work of literature to evaluate how the writer uses literary components to convey ideas.
A literary analysis is not a summary; it reaches past basic comprehension and facts. Often, this type of analysis will argue the theme, message, or purpose of a work by analyzing the writer’s use of literary devices and narrative techniques.
How to Write a Literary Analysis
These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics.
1. Read the text and identify literary devices.
As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as clues to larger, underlying themes.
The following is a checklist of the literary and narrative devices you should take note of while reading. (If possible, marking the text with a pencil can be very helpful.)
- Point of view: First, examine the point of view from which the story is told. Who is the narrator? Is it a character from the story, or an unknown, all-knowing figure? Do they have something at stake? Do you find them to be a reliable narrator? The answers to these questions can help shape your argument.
- Recurring symbols : Things like colors, rivers, and seasons may not seem significant at first glance, but together, and especially if they appear more than once, they can signify a deeper message. (Just look at this analysis of Hemingway’s “Hills Like White Elephants” as an example.) Our guide to symbolism explains some of the most common symbols in literature. If you come across these in a text, highlight or circle them. These symbols can also be part of an extended metaphors, so it’s helpful to keep track of them and look for any possible connections.
- Character motivation : The main character’s motivation is extremely important when it comes to advancing the plot. Ask yourself what the character wants, and what’s keeping them from getting it. Why is that thing important to them? Could it carry any deeper significance that its face value?
- Tone : Evaluate the writer’s tone . Do the words convey an anxious, ominous, or hopeful tone? Is it sad, witty, or whimsical? There are lots of ways to describe tone, and your assessment of this literary device can add important insight to your overall analysis.
- Diction : The author’s word choice, or diction , can also influence the piece’s tone. Do any words seem peculiar? Do you think the author chose that word over other synonyms for a reason? When a word stands out to you, ask yourself why it matters that this particular word was chosen over others.
- Imagery: What types of images does the author paint? This can be done explicitly through vivid descriptions, or implicitly through sensory details, or words that evoke the feelings of a place, emotion, or idea.
- Story structure : How is the story structured, and what impact does this have on the story? Is it told in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? What about the characters, setting, and their relation to the narrative?
- Themes : As you’re taking note of the literary elements outlined above, you’ll likely see certain patterns start to emerge. These patterns represent underlying themes . For example, in The Great Gatsby , recurring images, symbols, and even character motivations point to themes of excess, material wealth, and lost values.
- Characters : Your entire essay might actually be a character analysis, depending on your topic. However, you can also cite characterization as a supporting element to your main argument. For example, a specific character, major or minor, might embody an ideal, which contributes to a larger theme.
2. Develop your thesis.
If you’re writing an essay for your literature class, you’ll likely be given a prompt or question to answer with your essay.
If you’re not assigned a topic, you’ll have to think of one yourself. You may find it helpful to develop questions in order to get started.
The answer to this question is known as your thesis . In order to serve as the foundation for your analysis, your thesis needs to meet several conditions. It must be:
- Arguable : Your thesis should reflect your opinion or interpretation, not a fact. For example, “ The Grapes of Wrath is about a family’s migration from the Oklahoma Dust Bowl to California” is not a good thesis, because that’s a simple fact. However, “ Frankenstein is actually a feminist novel that rejects patriarchy” is an arguable interpretation, and we can argue for or against that statement with supporting evidence.
- Supported through textual evidence : While your thesis shouldn’t be an objective fact, you should still be able to support it with textual evidence and details.
3. Create an outline.
Once you have your thesis, it’s time to make a plan for how you’ll prove your argument. Look back at your notes about the literary and narrative devices above. These will serve as your supporting evidence.
Which elements will help you make the most compelling argument for your thesis? You might choose, for example, to build your argument around imagery, symbolism, and diction.
You can dedicate a section to each of these elements and cite evidence directly from the text to explain why and how they support your thesis.
Create an outline to organize your thoughts, so when it’s time to start writing, you won’t forget where you were going with those points.
4. Cite the evidence.
When you’re making your argument, it’s important that you have concrete evidence from the text to support your claims.
When you can, provide direct quotes and other concrete details. For example, if you’re using symbolism as supporting evidence for why Frankenstein is a feminist text, you should be able to cite passages that illustrate the claim.
5. Write your body paragraphs.
Using your outline and notes from the text, you can now start writing your literary analysis. However, may find it helpful to leave room for your introduction and start by writing the body paragraphs, which contain your main arguments.
You’ll already have all the points and supporting details you need in your outline, so you can jump right in, rather than trying to think of the perfect opening line to your essay.
This strategy can also be beneficial because as you develop your arguments, you may generate new ideas or slightly adjust your thesis.
6. Write your introduction and conclusion.
Once you’ve fleshed out your body paragraphs and written a compelling argument, you can write your introductory paragraph (using the thesis statement you developed earlier), as well as your conclusion, which should neatly tie up your argument and leave your readers with some final insights.
Types of Literary Criticism
When you’re analyzing literature, there are numerous lenses through which you can examine the work. For example, common types of literary criticism include ethical, feminist, historic, and social criticism.
This means that your analysis, interpretation, and evaluation of the work will be through one of those lenses.
Analyzing Literature
The best works of literature are filled with hints that will lead you to a bigger picture, and discovering those clues and how they fit together is what makes reading so fun.
Whether you want to ace your next English essay or refine your critical thinking skills, understanding how to analyze literature will lead you to a more fulfilling reading experience.
Did you find this post helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- Symbolism: Common Examples in Life and Literature
- The Last Line of The Great Gatsby, Explained
- Extended Metaphors Explained: Definition, Purpose, and Examples from Literature
- 17 of the Most Common Literary Devices Every Reader and Writer Should Know
As a blog writer for TCK Publishing, Kaelyn loves crafting fun and helpful content for writers, readers, and creative minds alike. She has a degree in International Affairs with a minor in Italian Studies, but her true passion has always been writing. Working remotely allows her to do even more of the things she loves, like traveling, cooking, and spending time with her family.
We read a critic generously when they tackle a difficult topic, so one doesn’t judge Barron overly harshly for a seemingly shallow understanding of the subject. The article is useful as a starting point, giving us a chance to consider why so much of the content is ultimately indefensible. This blog has proven a genuinely valuable teaching resource. My students learn a great deal by exploring how this article manages to fall so far short of the promise in its title. Were her approach more thoughtful and erudite, such a rich opportunity to critically engage with literary theory would be denied Barron’s audience.
Hi Gregory, I’m sorry you found the article shallow. I intended it to be an overview for students, to walk them through the process of writing a solid literary analysis essay. What about the content do you find indefensible?

Learn More About
- Fiction (225)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (47)
- Book Promotion (29)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (71)
- Traditional Publishing (54)
- How to Find an Editor (12)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (121)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (75)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (50)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (3)
- Publishing News (9)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (18)
- Technology (18)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (66)
- Word Choice (75)
- Writing a Book (86)
- Writing Fiction (197)
- Writing Nonfiction (85)

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jan 30, 2020 · A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis, nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Literary Analysis–How To. Written by Ali Pineo. What is a Literary Analysis? A literary analysis is a common assignment in first-year writing and English courses. Despite how ubiquitous they are, literary analyses can sometimes feel confusing or maybe even a little intimidating.
Types of Literary Essays Compare and contrast. Compare and contrast the characters of Huck and Jim in The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn. Chances are you’ve written this kind of essay before. In an academic literary context, you’ll organize your arguments the same way you would in any other class.
Dec 3, 2019 · How To Write A Literary Analysis Essay. So how to start a literary analysis essay? The answer to this question is quite simple. The following sections are required to write an effective literary analysis essay. By following the guidelines given in the following sections, you will be able to craft a winning literary analysis essay. Introduction
The term regularly used for the development of the central idea of a literary analysis essay is the body. In this section you present the paragraphs (at least 3 paragraphs for a 500-750 word essay) that support your thesis statement. Good literary analysis essays contain an explanation of your ideas and evidence from the text (short story,
Often, this type of analysis will argue the theme, message, or purpose of a work by analyzing the writer’s use of literary devices and narrative techniques. How to Write a Literary Analysis. These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and ...