
Experimental Psychology: 10 Examples & Definition

Dave Cornell (PhD)
Dr. Cornell has worked in education for more than 20 years. His work has involved designing teacher certification for Trinity College in London and in-service training for state governments in the United States. He has trained kindergarten teachers in 8 countries and helped businessmen and women open baby centers and kindergartens in 3 countries.
Learn about our Editorial Process

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.

Experimental psychology refers to studying psychological phenomena using scientific methods. Originally, the primary scientific method involved manipulating one variable and observing systematic changes in another variable.
Today, psychologists utilize several types of scientific methodologies.
Experimental psychology examines a wide range of psychological phenomena, including: memory, sensation and perception, cognitive processes, motivation, emotion, developmental processes, in addition to the neurophysiological concomitants of each of these subjects.
Studies are conducted on both animal and human participants, and must comply with stringent requirements and controls regarding the ethical treatment of both.
Definition of Experimental Psychology
Experimental psychology is a branch of psychology that utilizes scientific methods to investigate the mind and behavior.
It involves the systematic and controlled study of human and animal behavior through observation and experimentation .
Experimental psychologists design and conduct experiments to understand cognitive processes, perception, learning, memory, emotion, and many other aspects of psychology. They often manipulate variables ( independent variables ) to see how this affects behavior or mental processes (dependent variables).
The findings from experimental psychology research are often used to better understand human behavior and can be applied in a range of contexts, such as education, health, business, and more.
Experimental Psychology Examples
1. The Puzzle Box Studies (Thorndike, 1898) Placing different cats in a box that can only be escaped by pulling a cord, and then taking detailed notes on how long it took for them to escape allowed Edward Thorndike to derive the Law of Effect: actions followed by positive consequences are more likely to occur again, and actions followed by negative consequences are less likely to occur again (Thorndike, 1898).
2. Reinforcement Schedules (Skinner, 1956) By placing rats in a Skinner Box and changing when and how often the rats are rewarded for pressing a lever, it is possible to identify how each schedule results in different behavior patterns (Skinner, 1956). This led to a wide range of theoretical ideas around how rewards and consequences can shape the behaviors of both animals and humans.
3. Observational Learning (Bandura, 1980) Some children watch a video of an adult punching and kicking a Bobo doll. Other children watch a video in which the adult plays nicely with the doll. By carefully observing the children’s behavior later when in a room with a Bobo doll, researchers can determine if television violence affects children’s behavior (Bandura, 1980).
4. The Fallibility of Memory (Loftus & Palmer, 1974) A group of participants watch the same video of two cars having an accident. Two weeks later, some are asked to estimate the rate of speed the cars were going when they “smashed” into each other. Some participants are asked to estimate the rate of speed the cars were going when they “bumped” into each other. Changing the phrasing of the question changes the memory of the eyewitness.
5. Intrinsic Motivation in the Classroom (Dweck, 1990) To investigate the role of autonomy on intrinsic motivation, half of the students are told they are “free to choose” which tasks to complete. The other half of the students are told they “must choose” some of the tasks. Researchers then carefully observe how long the students engage in the tasks and later ask them some questions about if they enjoyed doing the tasks or not.
6. Systematic Desensitization (Wolpe, 1958) A clinical psychologist carefully documents his treatment of a patient’s social phobia with progressive relaxation. At first, the patient is trained to monitor, tense, and relax various muscle groups while viewing photos of parties. Weeks later, they approach a stranger to ask for directions, initiate a conversation on a crowded bus, and attend a small social gathering. The therapist’s notes are transcribed into a scientific report and published in a peer-reviewed journal.
7. Study of Remembering (Bartlett, 1932) Bartlett’s work is a seminal study in the field of memory, where he used the concept of “schema” to describe an organized pattern of thought or behavior. He conducted a series of experiments using folk tales to show that memory recall is influenced by cultural schemas and personal experiences.
8. Study of Obedience (Milgram, 1963) This famous study explored the conflict between obedience to authority and personal conscience. Milgram found that a majority of participants were willing to administer what they believed were harmful electric shocks to a stranger when instructed by an authority figure, highlighting the power of authority and situational factors in driving behavior.
9. Pavlov’s Dog Study (Pavlov, 1927) Ivan Pavlov, a Russian physiologist, conducted a series of experiments that became a cornerstone in the field of experimental psychology. Pavlov noticed that dogs would salivate when they saw food. He then began to ring a bell each time he presented the food to the dogs. After a while, the dogs began to salivate merely at the sound of the bell. This experiment demonstrated the principle of “classical conditioning.”
10, Piaget’s Stages of Development (Piaget, 1958) Jean Piaget proposed a theory of cognitive development in children that consists of four distinct stages: the sensorimotor stage (birth to 2 years), where children learn about the world through their senses and motor activities, through to the the formal operational stage (12 years and beyond), where abstract reasoning and hypothetical thinking develop. Piaget’s theory is an example of experimental psychology as it was developed through systematic observation and experimentation on children’s problem-solving behaviors .
Types of Research Methodologies in Experimental Psychology
Researchers utilize several different types of research methodologies since the early days of Wundt (1832-1920).
1. The Experiment
The experiment involves the researcher manipulating the level of one variable, called the Independent Variable (IV), and then observing changes in another variable, called the Dependent Variable (DV).
The researcher is interested in determining if the IV causes changes in the DV. For example, does television violence make children more aggressive?
So, some children in the study, called research participants, will watch a show with TV violence, called the treatment group. Others will watch a show with no TV violence, called the control group.
So, there are two levels of the IV: violence and no violence. Next, children will be observed to see if they act more aggressively. This is the DV.
If TV violence makes children more aggressive, then the children that watched the violent show will me more aggressive than the children that watched the non-violent show.
A key requirement of the experiment is random assignment . Each research participant is assigned to one of the two groups in a way that makes it a completely random process. This means that each group will have a mix of children: different personality types, diverse family backgrounds, and range of intelligence levels.
2. The Longitudinal Study
A longitudinal study involves selecting a sample of participants and then following them for years, or decades, periodically collecting data on the variables of interest.
For example, a researcher might be interested in determining if parenting style affects academic performance of children. Parenting style is called the predictor variable , and academic performance is called the outcome variable .
Researchers will begin by randomly selecting a group of children to be in the study. Then, they will identify the type of parenting practices used when the children are 4 and 5 years old.
A few years later, perhaps when the children are 8 and 9, the researchers will collect data on their grades. This process can be repeated over the next 10 years, including through college.
If parenting style has an effect on academic performance, then the researchers will see a connection between the predictor variable and outcome variable.
Children raised with parenting style X will have higher grades than children raised with parenting style Y.
3. The Case Study
The case study is an in-depth study of one individual. This is a research methodology often used early in the examination of a psychological phenomenon or therapeutic treatment.
For example, in the early days of treating phobias, a clinical psychologist may try teaching one of their patients how to relax every time they see the object that creates so much fear and anxiety, such as a large spider.
The therapist would take very detailed notes on how the teaching process was implemented and the reactions of the patient. When the treatment had been completed, those notes would be written in a scientific form and submitted for publication in a scientific journal for other therapists to learn from.
There are several other types of methodologies available which vary different aspects of the three described above. The researcher will select a methodology that is most appropriate to the phenomenon they want to examine.
They also must take into account various practical considerations such as how much time and resources are needed to complete the study. Conducting research always costs money.
People and equipment are needed to carry-out every study, so researchers often try to obtain funding from their university or a government agency.
Origins and Key Developments in Experimental Psychology
Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt (1832-1920) is considered one of the fathers of modern psychology. He was a physiologist and philosopher and helped establish psychology as a distinct discipline (Khaleefa, 1999).
In 1879 he established the world’s first psychology research lab at the University of Leipzig. This is considered a key milestone for establishing psychology as a scientific discipline. In addition to being the first person to use the term “psychologist,” to describe himself, he also founded the discipline’s first scientific journal Philosphische Studien in 1883.
Another notable figure in the development of experimental psychology is Ernest Weber . Trained as a physician, Weber studied sensation and perception and created the first quantitative law in psychology.
The equation denotes how judgments of sensory differences are relative to previous levels of sensation, referred to as the just-noticeable difference (jnd). This is known today as Weber’s Law (Hergenhahn, 2009).
Gustav Fechner , one of Weber’s students, published the first book on experimental psychology in 1860, titled Elemente der Psychophysik. His worked centered on the measurement of psychophysical facets of sensation and perception, with many of his methods still in use today.
The first American textbook on experimental psychology was Elements of Physiological Psychology, published in 1887 by George Trumball Ladd .
Ladd also established a psychology lab at Yale University, while Stanley Hall and Charles Sanders continued Wundt’s work at a lab at Johns Hopkins University.
In the late 1800s, Charles Pierce’s contribution to experimental psychology is especially noteworthy because he invented the concept of random assignment (Stigler, 1992; Dehue, 1997).
Go Deeper: 15 Random Assignment Examples
This procedure ensures that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any of the experimental groups (e.g., treatment or control group). This eliminates the influence of confounding factors related to inherent characteristics of the participants.
Random assignment is a fundamental criterion for a study to be considered a valid experiment.
From there, experimental psychology flourished in the 20th century as a science and transformed into an approach utilized in cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, and social psychology .
Today, the term experimental psychology refers to the study of a wide range of phenomena and involves methodologies not limited to the manipulation of variables.
The Scientific Process and Experimental Psychology
The one thing that makes psychology a science and distinguishes it from its roots in philosophy is the reliance upon the scientific process to answer questions. This makes psychology a science was the main goal of its earliest founders such as Wilhelm Wundt.
There are numerous steps in the scientific process, outlined in the graphic below.
1. Observation
First, the scientist observes an interesting phenomenon that sparks a question. For example, are the memories of eyewitnesses really reliable, or are they subject to bias or unintentional manipulation?
2. Hypothesize
Next, this question is converted into a testable hypothesis. For instance: the words used to question a witness can influence what they think they remember.
3. Devise a Study
Then the researcher(s) select a methodology that will allow them to test that hypothesis. In this case, the researchers choose the experiment, which will involve randomly assigning some participants to different conditions.
In one condition, participants are asked a question that implies a certain memory (treatment group), while other participants are asked a question which is phrased neutrally and does not imply a certain memory (control group).
The researchers then write a proposal that describes in detail the procedures they want to use, how participants will be selected, and the safeguards they will employ to ensure the rights of the participants.
That proposal is submitted to an Institutional Review Board (IRB). The IRB is comprised of a panel of researchers, community representatives, and other professionals that are responsible for reviewing all studies involving human participants.
4. Conduct the Study
If the IRB accepts the proposal, then the researchers may begin collecting data. After the data has been collected, it is analyzed using a software program such as SPSS.
Those analyses will either support or reject the hypothesis. That is, either the participants’ memories were affected by the wording of the question, or not.
5. Publish the study
Finally, the researchers write a paper detailing their procedures and results of the statistical analyses. That paper is then submitted to a scientific journal.
The lead editor of that journal will then send copies of the paper to 3-5 experts in that subject. Each of those experts will read the paper and basically try to find as many things wrong with it as possible. Because they are experts, they are very good at this task.
After reading those critiques, most likely, the editor will send the paper back to the researchers and require that they respond to the criticisms, collect more data, or reject the paper outright.
In some cases, the study was so well-done that the criticisms were minimal and the editor accepts the paper. It then gets published in the scientific journal several months later.
That entire process can easily take 2 years, usually more. But, the findings of that study went through a very rigorous process. This means that we can have substantial confidence that the conclusions of the study are valid.
Experimental psychology refers to utilizing a scientific process to investigate psychological phenomenon.
There are a variety of methods employed today. They are used to study a wide range of subjects, including memory, cognitive processes, emotions and the neurophysiological basis of each.
The history of psychology as a science began in the 1800s primarily in Germany. As interest grew, the field expanded to the United States where several influential research labs were established.
As more methodologies were developed, the field of psychology as a science evolved into a prolific scientific discipline that has provided invaluable insights into human behavior.
Bartlett, F. C., & Bartlett, F. C. (1995). Remembering: A study in experimental and social psychology . Cambridge university press.
Dehue, T. (1997). Deception, efficiency, and random groups: Psychology and the gradual origination of the random group design. Isis , 88 (4), 653-673.
Ebbinghaus, H. (2013). Memory: A contribution to experimental psychology. Annals of neurosciences , 20 (4), 155.
Hergenhahn, B. R. (2009). An introduction to the history of psychology. Belmont. CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning .
Khaleefa, O. (1999). Who is the founder of psychophysics and experimental psychology? American Journal of Islam and Society , 16 (2), 1-26.
Loftus, E. F., & Palmer, J. C. (1974). Reconstruction of auto-mobile destruction : An example of the interaction between language and memory. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal behavior , 13, 585-589.
Pavlov, I.P. (1927). Conditioned reflexes . Dover, New York.
Piaget, J. (1959). The language and thought of the child (Vol. 5). Psychology Press.
Piaget, J., Fraisse, P., & Reuchlin, M. (2014). Experimental psychology its scope and method: Volume I (Psychology Revivals): History and method . Psychology Press.
Skinner, B. F. (1956). A case history in scientlfic method. American Psychologist, 11 , 221-233
Stigler, S. M. (1992). A historical view of statistical concepts in psychology and educational research. American Journal of Education , 101 (1), 60-70.
Thorndike, E. L. (1898). Animal intelligence: An experimental study of the associative processes in animals. Psychological Review Monograph Supplement 2 .
Wolpe, J. (1958). Psychotherapy by reciprocal inhibition. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Appendix: Images reproduced as Text
Definition: Experimental psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on conducting systematic and controlled experiments to study human behavior and cognition.
Overview: Experimental psychology aims to gather empirical evidence and explore cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Experimental psychologists utilize various research methods, including laboratory experiments, surveys, and observations, to investigate topics such as perception, memory, learning, motivation, and social behavior .
Example: The Pavlov’s Dog experimental psychology experiment used scientific methods to develop a theory about how learning and association occur in animals. The same concepts were subsequently used in the study of humans, wherein psychology-based ideas about learning were developed. Pavlov’s use of the empirical evidence was foundational to the study’s success.
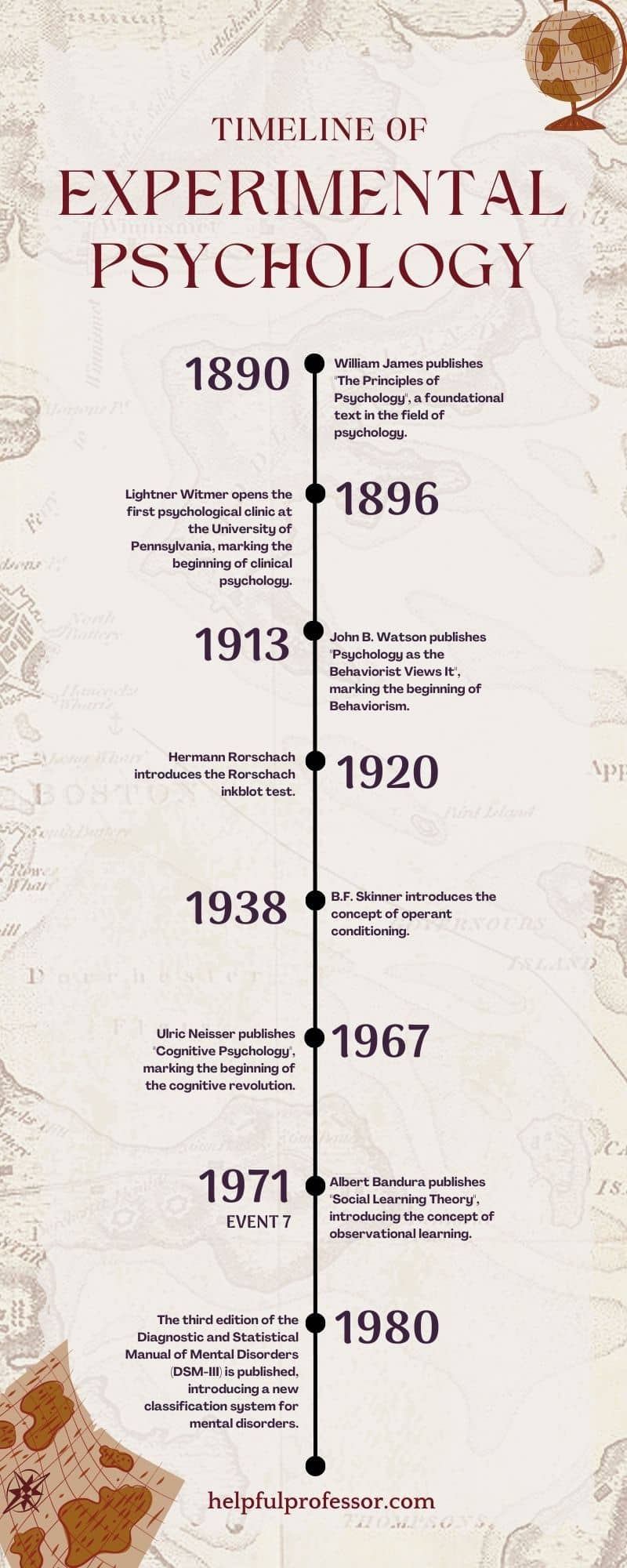
Experimental Psychology Milestones:
1890: William James publishes “The Principles of Psychology”, a foundational text in the field of psychology.
1896: Lightner Witmer opens the first psychological clinic at the University of Pennsylvania, marking the beginning of clinical psychology.
1913: John B. Watson publishes “Psychology as the Behaviorist Views It”, marking the beginning of Behaviorism.
1920: Hermann Rorschach introduces the Rorschach inkblot test.
1938: B.F. Skinner introduces the concept of operant conditioning .
1967: Ulric Neisser publishes “Cognitive Psychology” , marking the beginning of the cognitive revolution.
1980: The third edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-III) is published, introducing a new classification system for mental disorders.
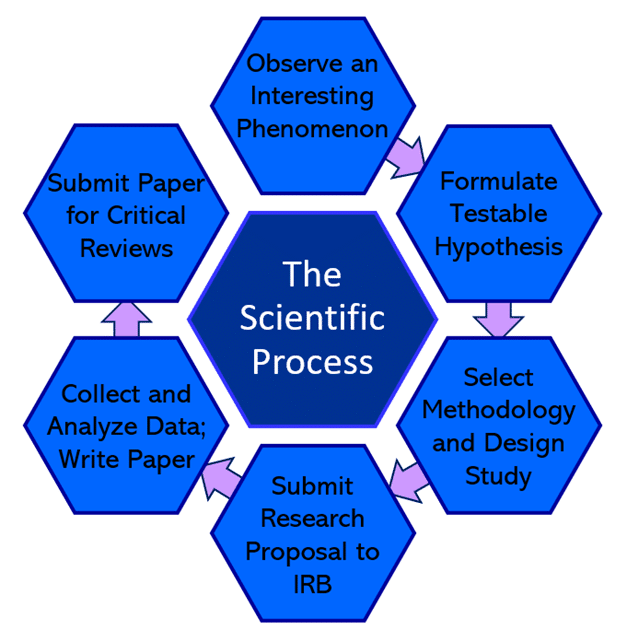
The Scientific Process
- Observe an interesting phenomenon
- Formulate testable hypothesis
- Select methodology and design study
- Submit research proposal to IRB
- Collect and analyzed data; write paper
- Submit paper for critical reviews

- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 23 Achieved Status Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 25 Defense Mechanisms Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Theory of Planned Behavior Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 18 Adaptive Behavior Examples

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 23 Achieved Status Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Ableism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Defense Mechanisms Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Theory of Planned Behavior Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- General Categories
- Mental Health
- IQ and Intelligence
- Bipolar Disorder

Experimental Method in Psychology: Principles, Applications, and Limitations
As the cornerstone of psychological research, the experimental method has revolutionized our understanding of the human mind, behavior, and the intricate workings of the brain. This powerful approach has paved the way for countless breakthroughs in our quest to unravel the mysteries of human cognition and behavior. From the early days of Wilhelm Wundt’s pioneering work to the cutting-edge neuroscience experiments of today, the experimental method has been the driving force behind our ever-expanding knowledge of psychology.
But what exactly is the experimental method, and why is it so crucial to psychological research? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of experimental psychology and explore its principles, applications, and limitations.
The Birth of Experimental Psychology: A Journey Through Time
Picture this: It’s the late 19th century, and psychology is still in its infancy. Enter Wilhelm Wundt, a German physiologist with a burning curiosity about the human mind. In 1879, Wundt established the first psychology laboratory at the University of Leipzig, marking the birth of experimental psychology as we know it today.
Wundt’s groundbreaking work laid the foundation for a more scientific approach to studying the mind. He believed that mental processes could be measured and analyzed systematically, just like physical phenomena. This radical idea sparked a revolution in psychological research, inspiring generations of scientists to explore the depths of human cognition and behavior through carefully controlled experiments.
As the field of psychology evolved, so did the experimental method. Researchers refined their techniques, developed new tools, and tackled increasingly complex questions about the human mind. Today, laboratory experiments in psychology are sophisticated endeavors that employ cutting-edge technology and rigorous methodologies to unveil the science of human behavior.
The Building Blocks of Experimental Design: A Recipe for Scientific Discovery
At its core, the experimental method in psychology is all about uncovering cause-and-effect relationships. But how do researchers go about designing experiments that can reliably answer their questions? Let’s break down the key components of an experiment in psychology :
1. Variables: The stars of the show in any experiment are the variables. These are the factors that researchers manipulate or measure to test their hypotheses. There are three main types of variables:
– Independent variables: These are the factors that researchers deliberately manipulate to observe their effects on behavior or cognition. – Dependent variables: These are the outcomes or behaviors that researchers measure in response to changes in the independent variables. – Control variables: These are factors that researchers keep constant to ensure that they don’t interfere with the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
2. Hypothesis: Every good experiment starts with a clear, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. This hypothesis serves as the guiding light for the entire research process.
3. Experimental design: Researchers must carefully plan how they’ll manipulate variables, assign participants to groups, and collect data. This step is crucial for ensuring that the experiment can reliably answer the research question.
4. Participants: The people (or animals) who take part in the experiment are the lifeblood of psychological research. Careful selection and assignment of participants help ensure that the results are generalizable to the broader population.
5. Procedure: This is the step-by-step plan for conducting the experiment, including instructions for participants, data collection methods, and any necessary equipment or materials.
6. Data analysis: Once the experiment is complete, researchers use statistical techniques to make sense of their findings and determine whether their hypothesis was supported.
By carefully considering each of these components, researchers can design experiments that shed light on the complexities of human behavior and cognition.
The Art and Science of Experimental Design: Crafting the Perfect Study
Designing a psychological experiment is both an art and a science. It requires creativity, critical thinking, and a deep understanding of scientific principles. Let’s explore some of the key considerations that researchers must keep in mind when designing their studies:
1. Establishing cause-and-effect relationships: The holy grail of experimental psychology is uncovering causal relationships between variables. To do this, researchers must carefully manipulate independent variables while controlling for potential confounds.
2. Controlling for confounding variables: In the messy world of human behavior, countless factors can influence our thoughts and actions. Researchers must be vigilant in identifying and controlling for these potential confounds to ensure that their results are valid.
3. Randomization: This powerful technique helps reduce bias by ensuring that participants have an equal chance of being assigned to different experimental conditions. It’s like shuffling a deck of cards before dealing – it helps level the playing field.
4. Types of experimental designs: Researchers can choose from various experimental designs, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The two main categories are:
– Between-subjects designs: Different groups of participants are exposed to different conditions. – Within-subjects designs: The same participants are exposed to multiple conditions.
The choice of design depends on the research question, practical considerations, and the nature of the variables being studied.
From Hypothesis to Discovery: The Journey of a Psychological Experiment
Now that we’ve explored the building blocks of experimental design, let’s walk through the steps of conducting a psychological experiment. It’s a journey filled with excitement, challenges, and the potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
1. Formulating a research question and hypothesis: Every great experiment starts with curiosity. Researchers identify a gap in our understanding of human behavior or cognition and develop a specific, testable hypothesis to address it.
2. Designing the experimental procedure: This is where the rubber meets the road. Researchers must carefully plan every aspect of their study, from the precise wording of instructions to the timing of each task.
3. Selecting and assigning participants: Finding the right participants is crucial for ensuring that the results are meaningful and generalizable. Researchers must consider factors like sample size, demographic characteristics, and recruitment methods.
4. Collecting and analyzing data: With everything in place, it’s time to run the experiment and gather data. This process can range from simple pencil-and-paper surveys to complex neuroimaging studies.
5. Drawing conclusions and reporting results: Once the data is collected, researchers use statistical analyses to determine whether their hypothesis was supported. They then interpret their findings in the context of existing theories and previous research.
This journey from hypothesis to discovery is at the heart of scientific progress in psychology. Each experiment, no matter how small, contributes to our growing understanding of the human mind and behavior.
Experiments in Action: Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Psychological Research
The experimental method is a versatile tool that can be applied to a wide range of psychological phenomena. Let’s take a whirlwind tour of some fascinating experiments across different areas of psychology:
1. Cognitive psychology: Researchers in this field use experiments to explore mental processes like memory, attention, and decision-making. For example, the famous “cocktail party effect” experiments revealed our remarkable ability to focus on a single conversation in a noisy room.
2. Social psychology: Experiments in this area shed light on how our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by others. The classic Milgram obedience experiments, while ethically controversial, revealed startling insights into human compliance with authority.
3. Developmental psychology: Researchers use clever experimental designs to study how children’s minds grow and change over time. Jean Piaget’s conservation tasks, for instance, revealed fascinating insights into children’s understanding of quantity and volume.
4. Clinical psychology: Experiments in this field help us understand mental health disorders and develop effective treatments. For example, studies on exposure therapy have shown its effectiveness in treating phobias and anxiety disorders.
5. Neuroscience and behavioral experiments: By combining behavioral tasks with brain imaging techniques, researchers can explore the neural basis of psychological phenomena. The famous “split-brain” experiments, for instance, revealed fascinating insights into how the two hemispheres of the brain work together.
These examples barely scratch the surface of the diverse and exciting world of psychological experiments. Each study contributes to our growing understanding of the human mind and behavior, piece by piece.
The Power and Promise of Experimental Psychology
The experimental method has numerous advantages that make it a cornerstone of psychological research:
1. High internal validity: By carefully controlling variables, experiments allow researchers to draw strong conclusions about cause-and-effect relationships.
2. Ability to establish causality: This is perhaps the most significant advantage of experiments. They allow us to move beyond mere correlation and identify true causal relationships.
3. Replicability and generalizability: Well-designed experiments can be replicated by other researchers, helping to confirm and extend findings. This is crucial for building a solid foundation of scientific knowledge.
4. Precision in measuring variables: Experiments allow for precise manipulation and measurement of variables, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
5. Contribution to theory development and testing: Experiments play a crucial role in testing and refining psychological theories, driving the field forward.
The experimental effects in psychology have had a profound impact on our understanding of human behavior and cognition. From uncovering the basic principles of learning and memory to revealing the complexities of social influence, experiments have been at the forefront of psychological discovery.
Navigating the Challenges: Limitations and Ethical Considerations
While the experimental method is incredibly powerful, it’s not without its limitations and ethical challenges. As researchers, we must be aware of these issues and work to address them:
1. Potential for artificial settings: Laboratory experiments may create environments that don’t accurately reflect real-world situations, potentially limiting the experimental realism in psychology .
2. Ethical concerns: Experiments involving human participants must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to protect participants’ well-being and rights. The infamous Stanford Prison Experiment serves as a cautionary tale about the potential for ethical breaches in psychological research.
3. Challenges in studying complex phenomena: Some aspects of human behavior and cognition are difficult to study in controlled laboratory settings, requiring researchers to be creative in their experimental designs.
4. Potential researcher bias and demand characteristics: Experimenters must be careful not to inadvertently influence participants’ behavior through subtle cues or expectations.
5. Time and resource constraints: Well-designed experiments can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially limiting the scope of research questions that can be addressed.
These disadvantages of experiments in psychology highlight the need for researchers to be thoughtful and creative in their approach to studying human behavior and cognition.
The Future of Experimental Psychology: Pushing the Boundaries of Discovery
As we look to the future, the experimental method in psychology continues to evolve and adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Emerging technologies, such as virtual reality and advanced brain imaging techniques, are opening up exciting new avenues for research.
Researchers are also working to address some of the limitations of traditional experiments by developing innovative methodologies. For example, ecological momentary assessment allows researchers to study behavior in real-world settings, bridging the gap between laboratory experiments and naturalistic observation.
The future of experimental psychology lies in striking a balance between rigorous scientific methodology and real-world applicability. By combining the strengths of experimental designs with other research approaches, psychologists can continue to push the boundaries of our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
In conclusion, the experimental method remains a powerful and indispensable tool in psychological research. From its humble beginnings in Wilhelm Wundt’s laboratory to the cutting-edge neuroscience experiments of today, this approach has revolutionized our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of human cognition and behavior, the experimental method will undoubtedly play a crucial role. By embracing new technologies, addressing ethical concerns, and pushing the boundaries of experimental design, researchers can ensure that this cornerstone of psychological research remains as relevant and impactful as ever.
So, the next time you hear about a fascinating psychological study, take a moment to appreciate the careful planning, creativity, and scientific rigor that went into its design. Who knows? Maybe you’ll be inspired to design your own experiment and contribute to our ever-growing understanding of the human mind.
References:
1. Coolican, H. (2018). Research methods and statistics in psychology. Routledge.
2. Goodwin, C. J., & Goodwin, K. A. (2016). Research in psychology: Methods and design. John Wiley & Sons.
3. Kantowitz, B. H., Roediger III, H. L., & Elmes, D. G. (2014). Experimental psychology. Cengage Learning.
4. Leary, M. R. (2011). Introduction to behavioral research methods. Pearson.
5. Martin, D. W. (2007). Doing psychology experiments. Cengage Learning.
6. Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Houghton Mifflin.
7. Shaughnessy, J. J., Zechmeister, E. B., & Zechmeister, J. S. (2015). Research methods in psychology. McGraw-Hill Education.
8. Smith, R. A., & Davis, S. F. (2012). The psychologist as detective: An introduction to conducting research in psychology. Pearson.
9. Stanovich, K. E. (2013). How to think straight about psychology. Pearson.
10. Weiten, W. (2016). Psychology: Themes and variations. Cengage Learning.
Was this article helpful?
Would you like to add any comments (optional), leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Related Resources
Brain Samples: Unlocking the Secrets of Neuroscience

Discover Psychology Impact Factor: Exploring the Journal’s Influence and Significance

Confidence Intervals in Psychology: Enhancing Statistical Interpretation and Research Validity

Control Condition in Psychology: Definition, Purpose, and Applications

Dependent Variables in Psychology: Definition, Examples, and Importance

Debriefing in Psychology: Definition, Purpose, and Techniques

Correlation in Psychology: Definition, Types, and Applications

Data Collection Methods in Psychology: Essential Techniques for Researchers
Histogram in Psychology: Definition, Applications, and Significance

Dimensional vs Categorical Approach in Psychology: Comparing Methods of Classification

Experimental Design: Types, Examples & Methods
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to different groups in an experiment. Types of design include repeated measures, independent groups, and matched pairs designs.
Probably the most common way to design an experiment in psychology is to divide the participants into two groups, the experimental group and the control group, and then introduce a change to the experimental group, not the control group.
The researcher must decide how he/she will allocate their sample to the different experimental groups. For example, if there are 10 participants, will all 10 participants participate in both groups (e.g., repeated measures), or will the participants be split in half and take part in only one group each?
Three types of experimental designs are commonly used:
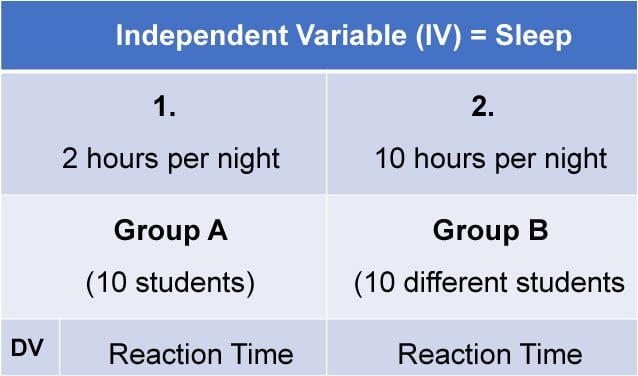
1. Independent Measures
Independent measures design, also known as between-groups , is an experimental design where different participants are used in each condition of the independent variable. This means that each condition of the experiment includes a different group of participants.
This should be done by random allocation, ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to one group.
Independent measures involve using two separate groups of participants, one in each condition. For example:
- Con : More people are needed than with the repeated measures design (i.e., more time-consuming).
- Pro : Avoids order effects (such as practice or fatigue) as people participate in one condition only. If a person is involved in several conditions, they may become bored, tired, and fed up by the time they come to the second condition or become wise to the requirements of the experiment!
- Con : Differences between participants in the groups may affect results, for example, variations in age, gender, or social background. These differences are known as participant variables (i.e., a type of extraneous variable ).
- Control : After the participants have been recruited, they should be randomly assigned to their groups. This should ensure the groups are similar, on average (reducing participant variables).
2. Repeated Measures Design
Repeated Measures design is an experimental design where the same participants participate in each independent variable condition. This means that each experiment condition includes the same group of participants.
Repeated Measures design is also known as within-groups or within-subjects design .
- Pro : As the same participants are used in each condition, participant variables (i.e., individual differences) are reduced.
- Con : There may be order effects. Order effects refer to the order of the conditions affecting the participants’ behavior. Performance in the second condition may be better because the participants know what to do (i.e., practice effect). Or their performance might be worse in the second condition because they are tired (i.e., fatigue effect). This limitation can be controlled using counterbalancing.
- Pro : Fewer people are needed as they participate in all conditions (i.e., saves time).
- Control : To combat order effects, the researcher counter-balances the order of the conditions for the participants. Alternating the order in which participants perform in different conditions of an experiment.
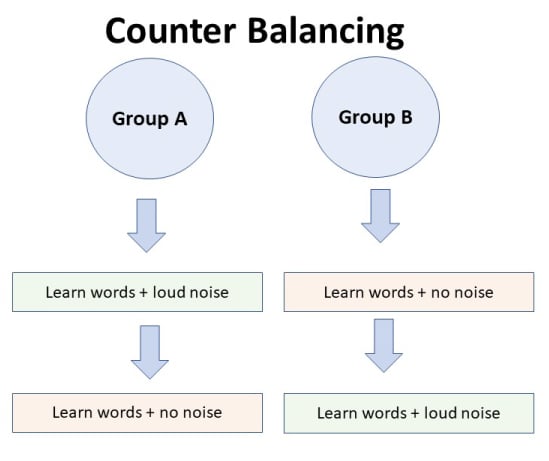
Counterbalancing
Suppose we used a repeated measures design in which all of the participants first learned words in “loud noise” and then learned them in “no noise.”
We expect the participants to learn better in “no noise” because of order effects, such as practice. However, a researcher can control for order effects using counterbalancing.
The sample would be split into two groups: experimental (A) and control (B). For example, group 1 does ‘A’ then ‘B,’ and group 2 does ‘B’ then ‘A.’ This is to eliminate order effects.
Although order effects occur for each participant, they balance each other out in the results because they occur equally in both groups.
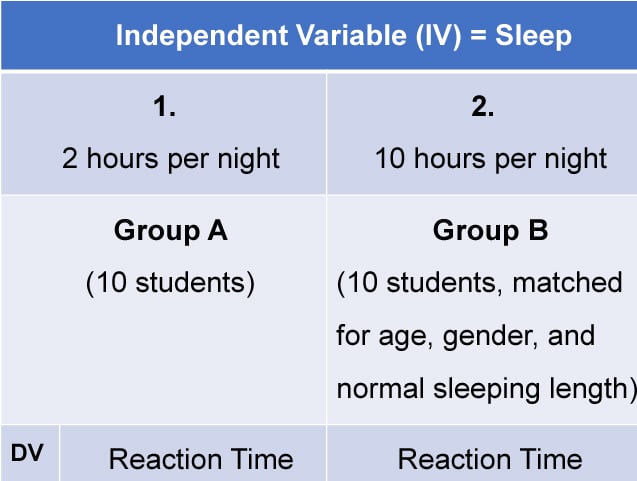
3. Matched Pairs Design
A matched pairs design is an experimental design where pairs of participants are matched in terms of key variables, such as age or socioeconomic status. One member of each pair is then placed into the experimental group and the other member into the control group .
One member of each matched pair must be randomly assigned to the experimental group and the other to the control group.
- Con : If one participant drops out, you lose 2 PPs’ data.
- Pro : Reduces participant variables because the researcher has tried to pair up the participants so that each condition has people with similar abilities and characteristics.
- Con : Very time-consuming trying to find closely matched pairs.
- Pro : It avoids order effects, so counterbalancing is not necessary.
- Con : Impossible to match people exactly unless they are identical twins!
- Control : Members of each pair should be randomly assigned to conditions. However, this does not solve all these problems.
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to an experiment’s different conditions (or IV levels). There are three types:
1. Independent measures / between-groups : Different participants are used in each condition of the independent variable.
2. Repeated measures /within groups : The same participants take part in each condition of the independent variable.
3. Matched pairs : Each condition uses different participants, but they are matched in terms of important characteristics, e.g., gender, age, intelligence, etc.
Learning Check
Read about each of the experiments below. For each experiment, identify (1) which experimental design was used; and (2) why the researcher might have used that design.
1 . To compare the effectiveness of two different types of therapy for depression, depressed patients were assigned to receive either cognitive therapy or behavior therapy for a 12-week period.
The researchers attempted to ensure that the patients in the two groups had similar severity of depressed symptoms by administering a standardized test of depression to each participant, then pairing them according to the severity of their symptoms.
2 . To assess the difference in reading comprehension between 7 and 9-year-olds, a researcher recruited each group from a local primary school. They were given the same passage of text to read and then asked a series of questions to assess their understanding.
3 . To assess the effectiveness of two different ways of teaching reading, a group of 5-year-olds was recruited from a primary school. Their level of reading ability was assessed, and then they were taught using scheme one for 20 weeks.
At the end of this period, their reading was reassessed, and a reading improvement score was calculated. They were then taught using scheme two for a further 20 weeks, and another reading improvement score for this period was calculated. The reading improvement scores for each child were then compared.
4 . To assess the effect of the organization on recall, a researcher randomly assigned student volunteers to two conditions.
Condition one attempted to recall a list of words that were organized into meaningful categories; condition two attempted to recall the same words, randomly grouped on the page.
Experiment Terminology
Ecological validity.
The degree to which an investigation represents real-life experiences.
Experimenter effects
These are the ways that the experimenter can accidentally influence the participant through their appearance or behavior.
Demand characteristics
The clues in an experiment lead the participants to think they know what the researcher is looking for (e.g., the experimenter’s body language).
Independent variable (IV)
The variable the experimenter manipulates (i.e., changes) is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
Dependent variable (DV)
Variable the experimenter measures. This is the outcome (i.e., the result) of a study.
Extraneous variables (EV)
All variables which are not independent variables but could affect the results (DV) of the experiment. Extraneous variables should be controlled where possible.
Confounding variables
Variable(s) that have affected the results (DV), apart from the IV. A confounding variable could be an extraneous variable that has not been controlled.
Random Allocation
Randomly allocating participants to independent variable conditions means that all participants should have an equal chance of taking part in each condition.
The principle of random allocation is to avoid bias in how the experiment is carried out and limit the effects of participant variables.
Order effects
Changes in participants’ performance due to their repeating the same or similar test more than once. Examples of order effects include:
(i) practice effect: an improvement in performance on a task due to repetition, for example, because of familiarity with the task;
(ii) fatigue effect: a decrease in performance of a task due to repetition, for example, because of boredom or tiredness.

Experimental Methods In Psychology
March 7, 2021 - paper 2 psychology in context | research methods.
- Back to Paper 2 - Research Methods
There are three experimental methods in the field of psychology; Laboratory, Field and Natural Experiments. Each of the experimental methods holds different characteristics in relation to; the manipulation of the IV, the control of the EVs and the ability to accurately replicate the study in exactly the same way.
When conducting research, it is important to create an aim and a hypothesis, click here to learn more about the formation of aims and hypotheses.
- Psychopathology
- Social Psychology
- Approaches To Human Behaviour
- Biopsychology
- Research Methods
- Issues & Debates
- Teacher Hub
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- [email protected]
- www.psychologyhub.co.uk
We're not around right now. But you can send us an email and we'll get back to you, asap.
Start typing and press Enter to search
Cookie Policy - Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How Does Experimental Psychology Study Behavior?
Purpose, methods, and history
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
- Why It Matters
What factors influence people's behaviors and thoughts? Experimental psychology utilizes scientific methods to answer these questions by researching the mind and behavior. Experimental psychologists conduct experiments to learn more about why people do certain things.
Overview of Experimental Psychology
Why do people do the things they do? What factors influence how personality develops? And how do our behaviors and experiences shape our character?
These are just a few of the questions that psychologists explore, and experimental methods allow researchers to create and empirically test hypotheses. By studying such questions, researchers can also develop theories that enable them to describe, explain, predict, and even change human behaviors.
For example, researchers might utilize experimental methods to investigate why people engage in unhealthy behaviors. By learning more about the underlying reasons why these behaviors occur, researchers can then search for effective ways to help people avoid such actions or replace unhealthy choices with more beneficial ones.
Why Experimental Psychology Matters
While students are often required to take experimental psychology courses during undergraduate and graduate school , think about this subject as a methodology rather than a singular area within psychology. People in many subfields of psychology use these techniques to conduct research on everything from childhood development to social issues.
Experimental psychology is important because the findings play a vital role in our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
By better understanding exactly what makes people tick, psychologists and other mental health professionals can explore new approaches to treating psychological distress and mental illness. These are often topics of experimental psychology research.
Experimental Psychology Methods
So how exactly do researchers investigate the human mind and behavior? Because the mind is so complex, it seems like a challenging task to explore the many factors that contribute to how we think, act, and feel.
Experimental psychologists use a variety of different research methods and tools to investigate human behavior. Methods in the experimental psychology category include experiments, case studies, correlational research, and naturalistic observations.
Experiments
Experimentation remains the primary standard in psychological research. In some cases, psychologists can perform experiments to determine if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between different variables.
The basics of conducting a psychology experiment involve:
- Randomly assigning participants to groups
- Operationally defining variables
- Developing a hypothesis
- Manipulating independent variables
- Measuring dependent variables
One experimental psychology research example would be to perform a study to look at whether sleep deprivation impairs performance on a driving test. The experimenter could control other variables that might influence the outcome, varying the amount of sleep participants get the night before.
All of the participants would then take the same driving test via a simulator or on a controlled course. By analyzing the results, researchers can determine if changes in the independent variable (amount of sleep) led to differences in the dependent variable (performance on a driving test).
Case Studies
Case studies allow researchers to study an individual or group of people in great depth. When performing a case study, the researcher collects every single piece of data possible, often observing the person or group over a period of time and in a variety of situations. They also collect detailed information about their subject's background—including family history, education, work, and social life—is also collected.
Such studies are often performed in instances where experimentation is not possible. For example, a scientist might conduct a case study when the person of interest has had a unique or rare experience that could not be replicated in a lab.
Correlational Research
Correlational studies are an experimental psychology method that makes it possible for researchers to look at relationships between different variables. For example, a psychologist might note that as one variable increases, another tends to decrease.
While such studies can look at relationships, they cannot be used to imply causal relationships. The golden rule is that correlation does not equal causation.
Naturalistic Observations
Naturalistic observation gives researchers the opportunity to watch people in their natural environments. This experimental psychology method can be particularly useful in cases where the investigators believe that a lab setting might have an undue influence on participant behaviors.
What Experimental Psychologists Do
Experimental psychologists work in a wide variety of settings, including colleges, universities, research centers, government, and private businesses. Some of these professionals teach experimental methods to students while others conduct research on cognitive processes, animal behavior, neuroscience, personality, and other subject areas.
Those who work in academic settings often teach psychology courses in addition to performing research and publishing their findings in professional journals. Other experimental psychologists work with businesses to discover ways to make employees more productive or to create a safer workplace—a specialty area known as human factors psychology .
Experimental Psychology Research Examples
Some topics that might be explored in experimental psychology research include how music affects motivation, the impact social media has on mental health , and whether a certain color changes one's thoughts or perceptions.
History of Experimental Psychology
To understand how experimental psychology got where it is today, it can be helpful to look at how it originated. Psychology is a relatively young discipline, emerging in the late 1800s. While it started as part of philosophy and biology, it officially became its own field of study when early psychologist Wilhelm Wundt founded the first laboratory devoted to the study of experimental psychology.
Some of the important events that helped shape the field of experimental psychology include:
- 1874 - Wilhelm Wundt published the first experimental psychology textbook, "Grundzüge der physiologischen Psychologie" ("Principles of Physiological Psychology").
- 1875 - William James opened a psychology lab in the United States. The lab was created for the purpose of class demonstrations rather than to perform original experimental research.
- 1879 - The first experimental psychology lab was founded in Leipzig, Germany. Modern experimental psychology dates back to the establishment of the very first psychology lab by pioneering psychologist Wilhelm Wundt during the late nineteenth century.
- 1883 - G. Stanley Hall opened the first experimental psychology lab in the United States at John Hopkins University.
- 1885 - Herman Ebbinghaus published his famous "Über das Gedächtnis" ("On Memory"), which was later translated to English as "Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology." In the work, Ebbinghaus described learning and memory experiments that he conducted on himself.
- 1887 - George Truball Ladd published his textbook "Elements of Physiological Psychology," the first American book to include a significant amount of information on experimental psychology.
- 1887 - James McKeen Cattell established the world's third experimental psychology lab at the University of Pennsylvania.
- 1890 - William James published his classic textbook, "The Principles of Psychology."
- 1891 - Mary Whiton Calkins established an experimental psychology lab at Wellesley College, becoming the first woman to form a psychology lab.
- 1893 - G. Stanley Hall founded the American Psychological Association , the largest professional and scientific organization of psychologists in the United States.
- 1920 - John B. Watson and Rosalie Rayner conducted their now-famous Little Albert Experiment , in which they demonstrated that emotional reactions could be classically conditioned in people.
- 1929 - Edwin Boring's book "A History of Experimental Psychology" was published. Boring was an influential experimental psychologist who was devoted to the use of experimental methods in psychology research.
- 1955 - Lee Cronbach published "Construct Validity in Psychological Tests," which popularized the use of construct validity in psychological studies.
- 1958 - Harry Harlow published "The Nature of Love," which described his experiments with rhesus monkeys on attachment and love.
- 1961 - Albert Bandura conducted his famous Bobo doll experiment, which demonstrated the effects of observation on aggressive behavior.
Experimental Psychology Uses
While experimental psychology is sometimes thought of as a separate branch or subfield of psychology, experimental methods are widely used throughout all areas of psychology.
- Developmental psychologists use experimental methods to study how people grow through childhood and over the course of a lifetime.
- Social psychologists use experimental techniques to study how people are influenced by groups.
- Health psychologists rely on experimentation and research to better understand the factors that contribute to wellness and disease.
A Word From Verywell
The experimental method in psychology helps us learn more about how people think and why they behave the way they do. Experimental psychologists can research a variety of topics using many different experimental methods. Each one contributes to what we know about the mind and human behavior.
Shaughnessy JJ, Zechmeister EB, Zechmeister JS. Research Methods in Psychology . McGraw-Hill.
Heale R, Twycross A. What is a case study? . Evid Based Nurs. 2018;21(1):7-8. doi:10.1136/eb-2017-102845
Chiang IA, Jhangiani RS, Price PC. Correlational research . In: Research Methods in Psychology, 2nd Canadian edition. BCcampus Open Education.
Pierce T. Naturalistic observation . Radford University.
Kantowitz BH, Roediger HL, Elmes DG. Experimental Psychology . Cengage Learning.
Weiner IB, Healy AF, Proctor RW. Handbook of Psychology: Volume 4, Experimental Psychology . John Wiley & Sons.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6.1 Experiment Basics
Learning objectives.
- Explain what an experiment is and recognize examples of studies that are experiments and studies that are not experiments.
- Explain what internal validity is and why experiments are considered to be high in internal validity.
- Explain what external validity is and evaluate studies in terms of their external validity.
- Distinguish between the manipulation of the independent variable and control of extraneous variables and explain the importance of each.
- Recognize examples of confounding variables and explain how they affect the internal validity of a study.
What Is an Experiment?
As we saw earlier in the book, an experiment is a type of study designed specifically to answer the question of whether there is a causal relationship between two variables. Do changes in an independent variable cause changes in a dependent variable? Experiments have two fundamental features. The first is that the researchers manipulate, or systematically vary, the level of the independent variable. The different levels of the independent variable are called conditions. For example, in Darley and Latané’s experiment, the independent variable was the number of witnesses that participants believed to be present. The researchers manipulated this independent variable by telling participants that there were either one, two, or five other students involved in the discussion, thereby creating three conditions. The second fundamental feature of an experiment is that the researcher controls, or minimizes the variability in, variables other than the independent and dependent variable. These other variables are called extraneous variables. Darley and Latané tested all their participants in the same room, exposed them to the same emergency situation, and so on. They also randomly assigned their participants to conditions so that the three groups would be similar to each other to begin with. Notice that although the words manipulation and control have similar meanings in everyday language, researchers make a clear distinction between them. They manipulate the independent variable by systematically changing its levels and control other variables by holding them constant.
Internal and External Validity
Internal validity.
Recall that the fact that two variables are statistically related does not necessarily mean that one causes the other. “Correlation does not imply causation.” For example, if it were the case that people who exercise regularly are happier than people who do not exercise regularly, this would not necessarily mean that exercising increases people’s happiness. It could mean instead that greater happiness causes people to exercise (the directionality problem) or that something like better physical health causes people to exercise and be happier (the third-variable problem).
The purpose of an experiment, however, is to show that two variables are statistically related and to do so in a way that supports the conclusion that the independent variable caused any observed differences in the dependent variable. The basic logic is this: If the researcher creates two or more highly similar conditions and then manipulates the independent variable to produce just one difference between them, then any later difference between the conditions must have been caused by the independent variable. For example, because the only difference between Darley and Latané’s conditions was the number of students that participants believed to be involved in the discussion, this must have been responsible for differences in helping between the conditions.
An empirical study is said to be high in internal validity if the way it was conducted supports the conclusion that the independent variable caused any observed differences in the dependent variable. Thus experiments are high in internal validity because the way they are conducted—with the manipulation of the independent variable and the control of extraneous variables—provides strong support for causal conclusions.
External Validity
At the same time, the way that experiments are conducted sometimes leads to a different kind of criticism. Specifically, the need to manipulate the independent variable and control extraneous variables means that experiments are often conducted under conditions that seem artificial or unlike “real life” (Stanovich, 2010). In many psychology experiments, the participants are all college undergraduates and come to a classroom or laboratory to fill out a series of paper-and-pencil questionnaires or to perform a carefully designed computerized task. Consider, for example, an experiment in which researcher Barbara Fredrickson and her colleagues had college students come to a laboratory on campus and complete a math test while wearing a swimsuit (Fredrickson, Roberts, Noll, Quinn, & Twenge, 1998). At first, this might seem silly. When will college students ever have to complete math tests in their swimsuits outside of this experiment?
The issue we are confronting is that of external validity. An empirical study is high in external validity if the way it was conducted supports generalizing the results to people and situations beyond those actually studied. As a general rule, studies are higher in external validity when the participants and the situation studied are similar to those that the researchers want to generalize to. Imagine, for example, that a group of researchers is interested in how shoppers in large grocery stores are affected by whether breakfast cereal is packaged in yellow or purple boxes. Their study would be high in external validity if they studied the decisions of ordinary people doing their weekly shopping in a real grocery store. If the shoppers bought much more cereal in purple boxes, the researchers would be fairly confident that this would be true for other shoppers in other stores. Their study would be relatively low in external validity, however, if they studied a sample of college students in a laboratory at a selective college who merely judged the appeal of various colors presented on a computer screen. If the students judged purple to be more appealing than yellow, the researchers would not be very confident that this is relevant to grocery shoppers’ cereal-buying decisions.
We should be careful, however, not to draw the blanket conclusion that experiments are low in external validity. One reason is that experiments need not seem artificial. Consider that Darley and Latané’s experiment provided a reasonably good simulation of a real emergency situation. Or consider field experiments that are conducted entirely outside the laboratory. In one such experiment, Robert Cialdini and his colleagues studied whether hotel guests choose to reuse their towels for a second day as opposed to having them washed as a way of conserving water and energy (Cialdini, 2005). These researchers manipulated the message on a card left in a large sample of hotel rooms. One version of the message emphasized showing respect for the environment, another emphasized that the hotel would donate a portion of their savings to an environmental cause, and a third emphasized that most hotel guests choose to reuse their towels. The result was that guests who received the message that most hotel guests choose to reuse their towels reused their own towels substantially more often than guests receiving either of the other two messages. Given the way they conducted their study, it seems very likely that their result would hold true for other guests in other hotels.
A second reason not to draw the blanket conclusion that experiments are low in external validity is that they are often conducted to learn about psychological processes that are likely to operate in a variety of people and situations. Let us return to the experiment by Fredrickson and colleagues. They found that the women in their study, but not the men, performed worse on the math test when they were wearing swimsuits. They argued that this was due to women’s greater tendency to objectify themselves—to think about themselves from the perspective of an outside observer—which diverts their attention away from other tasks. They argued, furthermore, that this process of self-objectification and its effect on attention is likely to operate in a variety of women and situations—even if none of them ever finds herself taking a math test in her swimsuit.
Manipulation of the Independent Variable
Again, to manipulate an independent variable means to change its level systematically so that different groups of participants are exposed to different levels of that variable, or the same group of participants is exposed to different levels at different times. For example, to see whether expressive writing affects people’s health, a researcher might instruct some participants to write about traumatic experiences and others to write about neutral experiences. The different levels of the independent variable are referred to as conditions , and researchers often give the conditions short descriptive names to make it easy to talk and write about them. In this case, the conditions might be called the “traumatic condition” and the “neutral condition.”
Notice that the manipulation of an independent variable must involve the active intervention of the researcher. Comparing groups of people who differ on the independent variable before the study begins is not the same as manipulating that variable. For example, a researcher who compares the health of people who already keep a journal with the health of people who do not keep a journal has not manipulated this variable and therefore not conducted an experiment. This is important because groups that already differ in one way at the beginning of a study are likely to differ in other ways too. For example, people who choose to keep journals might also be more conscientious, more introverted, or less stressed than people who do not. Therefore, any observed difference between the two groups in terms of their health might have been caused by whether or not they keep a journal, or it might have been caused by any of the other differences between people who do and do not keep journals. Thus the active manipulation of the independent variable is crucial for eliminating the third-variable problem.
Of course, there are many situations in which the independent variable cannot be manipulated for practical or ethical reasons and therefore an experiment is not possible. For example, whether or not people have a significant early illness experience cannot be manipulated, making it impossible to do an experiment on the effect of early illness experiences on the development of hypochondriasis. This does not mean it is impossible to study the relationship between early illness experiences and hypochondriasis—only that it must be done using nonexperimental approaches. We will discuss this in detail later in the book.
In many experiments, the independent variable is a construct that can only be manipulated indirectly. For example, a researcher might try to manipulate participants’ stress levels indirectly by telling some of them that they have five minutes to prepare a short speech that they will then have to give to an audience of other participants. In such situations, researchers often include a manipulation check in their procedure. A manipulation check is a separate measure of the construct the researcher is trying to manipulate. For example, researchers trying to manipulate participants’ stress levels might give them a paper-and-pencil stress questionnaire or take their blood pressure—perhaps right after the manipulation or at the end of the procedure—to verify that they successfully manipulated this variable.
Control of Extraneous Variables
An extraneous variable is anything that varies in the context of a study other than the independent and dependent variables. In an experiment on the effect of expressive writing on health, for example, extraneous variables would include participant variables (individual differences) such as their writing ability, their diet, and their shoe size. They would also include situation or task variables such as the time of day when participants write, whether they write by hand or on a computer, and the weather. Extraneous variables pose a problem because many of them are likely to have some effect on the dependent variable. For example, participants’ health will be affected by many things other than whether or not they engage in expressive writing. This can make it difficult to separate the effect of the independent variable from the effects of the extraneous variables, which is why it is important to control extraneous variables by holding them constant.
Extraneous Variables as “Noise”
Extraneous variables make it difficult to detect the effect of the independent variable in two ways. One is by adding variability or “noise” to the data. Imagine a simple experiment on the effect of mood (happy vs. sad) on the number of happy childhood events people are able to recall. Participants are put into a negative or positive mood (by showing them a happy or sad video clip) and then asked to recall as many happy childhood events as they can. The two leftmost columns of Table 6.1 “Hypothetical Noiseless Data and Realistic Noisy Data” show what the data might look like if there were no extraneous variables and the number of happy childhood events participants recalled was affected only by their moods. Every participant in the happy mood condition recalled exactly four happy childhood events, and every participant in the sad mood condition recalled exactly three. The effect of mood here is quite obvious. In reality, however, the data would probably look more like those in the two rightmost columns of Table 6.1 “Hypothetical Noiseless Data and Realistic Noisy Data” . Even in the happy mood condition, some participants would recall fewer happy memories because they have fewer to draw on, use less effective strategies, or are less motivated. And even in the sad mood condition, some participants would recall more happy childhood memories because they have more happy memories to draw on, they use more effective recall strategies, or they are more motivated. Although the mean difference between the two groups is the same as in the idealized data, this difference is much less obvious in the context of the greater variability in the data. Thus one reason researchers try to control extraneous variables is so their data look more like the idealized data in Table 6.1 “Hypothetical Noiseless Data and Realistic Noisy Data” , which makes the effect of the independent variable is easier to detect (although real data never look quite that good).
Table 6.1 Hypothetical Noiseless Data and Realistic Noisy Data
One way to control extraneous variables is to hold them constant. This can mean holding situation or task variables constant by testing all participants in the same location, giving them identical instructions, treating them in the same way, and so on. It can also mean holding participant variables constant. For example, many studies of language limit participants to right-handed people, who generally have their language areas isolated in their left cerebral hemispheres. Left-handed people are more likely to have their language areas isolated in their right cerebral hemispheres or distributed across both hemispheres, which can change the way they process language and thereby add noise to the data.
In principle, researchers can control extraneous variables by limiting participants to one very specific category of person, such as 20-year-old, straight, female, right-handed, sophomore psychology majors. The obvious downside to this approach is that it would lower the external validity of the study—in particular, the extent to which the results can be generalized beyond the people actually studied. For example, it might be unclear whether results obtained with a sample of younger straight women would apply to older gay men. In many situations, the advantages of a diverse sample outweigh the reduction in noise achieved by a homogeneous one.
Extraneous Variables as Confounding Variables
The second way that extraneous variables can make it difficult to detect the effect of the independent variable is by becoming confounding variables. A confounding variable is an extraneous variable that differs on average across levels of the independent variable. For example, in almost all experiments, participants’ intelligence quotients (IQs) will be an extraneous variable. But as long as there are participants with lower and higher IQs at each level of the independent variable so that the average IQ is roughly equal, then this variation is probably acceptable (and may even be desirable). What would be bad, however, would be for participants at one level of the independent variable to have substantially lower IQs on average and participants at another level to have substantially higher IQs on average. In this case, IQ would be a confounding variable.
To confound means to confuse, and this is exactly what confounding variables do. Because they differ across conditions—just like the independent variable—they provide an alternative explanation for any observed difference in the dependent variable. Figure 6.1 “Hypothetical Results From a Study on the Effect of Mood on Memory” shows the results of a hypothetical study, in which participants in a positive mood condition scored higher on a memory task than participants in a negative mood condition. But if IQ is a confounding variable—with participants in the positive mood condition having higher IQs on average than participants in the negative mood condition—then it is unclear whether it was the positive moods or the higher IQs that caused participants in the first condition to score higher. One way to avoid confounding variables is by holding extraneous variables constant. For example, one could prevent IQ from becoming a confounding variable by limiting participants only to those with IQs of exactly 100. But this approach is not always desirable for reasons we have already discussed. A second and much more general approach—random assignment to conditions—will be discussed in detail shortly.
Figure 6.1 Hypothetical Results From a Study on the Effect of Mood on Memory

Because IQ also differs across conditions, it is a confounding variable.
Key Takeaways
- An experiment is a type of empirical study that features the manipulation of an independent variable, the measurement of a dependent variable, and control of extraneous variables.
- Studies are high in internal validity to the extent that the way they are conducted supports the conclusion that the independent variable caused any observed differences in the dependent variable. Experiments are generally high in internal validity because of the manipulation of the independent variable and control of extraneous variables.
- Studies are high in external validity to the extent that the result can be generalized to people and situations beyond those actually studied. Although experiments can seem “artificial”—and low in external validity—it is important to consider whether the psychological processes under study are likely to operate in other people and situations.
- Practice: List five variables that can be manipulated by the researcher in an experiment. List five variables that cannot be manipulated by the researcher in an experiment.
Practice: For each of the following topics, decide whether that topic could be studied using an experimental research design and explain why or why not.
- Effect of parietal lobe damage on people’s ability to do basic arithmetic.
- Effect of being clinically depressed on the number of close friendships people have.
- Effect of group training on the social skills of teenagers with Asperger’s syndrome.
- Effect of paying people to take an IQ test on their performance on that test.
Cialdini, R. (2005, April). Don’t throw in the towel: Use social influence research. APS Observer . Retrieved from http://www.psychologicalscience.org/observer/getArticle.cfm?id=1762 .
Fredrickson, B. L., Roberts, T.-A., Noll, S. M., Quinn, D. M., & Twenge, J. M. (1998). The swimsuit becomes you: Sex differences in self-objectification, restrained eating, and math performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75 , 269–284.
Stanovich, K. E. (2010). How to think straight about psychology (9th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Sep 25, 2023 · A field experiment is a research method in psychology that takes place in a natural, real-world setting. It is similar to a laboratory experiment in that the experimenter manipulates one or more independent variables and measures the effects on the dependent variable.
Nov 20, 2023 · The experimental method can provide insight into human thoughts and behaviors, Researchers use experiments to study many aspects of psychology. Attention A 2019 study investigated whether splitting attention between electronic devices and classroom lectures had an effect on college students' learning abilities.
May 24, 2024 · Experimental psychology its scope and method: Volume I (Psychology Revivals): History and method. Psychology Press. Skinner, B. F. (1956). A case history in scientlfic method. American Psychologist, 11, 221-233. Stigler, S. M. (1992). A historical view of statistical concepts in psychology and educational research.
Sep 14, 2024 · At its core, the experimental method in psychology is all about uncovering cause-and-effect relationships. But how do researchers go about designing experiments that can reliably answer their questions? Let’s break down the key components of an experiment in psychology: 1.
Jul 31, 2023 · Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology . BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester. Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Mar 7, 2021 · There are three experimental methods in the field of psychology; Laboratory, Field and Natural Experiments. Each of the experimental methods holds different characteristics in relation to; the manipulation of the IV, the control of the EVs and the ability to accurately replicate the study in exactly the same way.
experimental psychology, a method of studying psychological phenomena and processes.The experimental method in psychology attempts to account for the activities of animals (including humans) and the functional organization of mental processes by manipulating variables that may give rise to behaviour; it is primarily concerned with discovering laws that describe manipulable relationships.
Jan 4, 2024 · While experimental psychology is sometimes thought of as a separate branch or subfield of psychology, experimental methods are widely used throughout all areas of psychology. Developmental psychologists use experimental methods to study how people grow through childhood and over the course of a lifetime.
Random sampling is a method for selecting a sample from a population, and it is rarely used in psychological research. Random assignment is a method for assigning participants in a sample to the different conditions, and it is an important element of all experimental research in psychology and other fields too.
An experiment is a type of empirical study that features the manipulation of an independent variable, the measurement of a dependent variable, and control of extraneous variables. Studies are high in internal validity to the extent that the way they are conducted supports the conclusion that the independent variable caused any observed ...