Experimental Research Design — 6 mistakes you should never make!
Since school days’ students perform scientific experiments that provide results that define and prove the laws and theorems in science. These experiments are laid on a strong foundation of experimental research designs.
An experimental research design helps researchers execute their research objectives with more clarity and transparency.
In this article, we will not only discuss the key aspects of experimental research designs but also the issues to avoid and problems to resolve while designing your research study.
Table of Contents
What Is Experimental Research Design?
Experimental research design is a framework of protocols and procedures created to conduct experimental research with a scientific approach using two sets of variables. Herein, the first set of variables acts as a constant, used to measure the differences of the second set. The best example of experimental research methods is quantitative research .
Experimental research helps a researcher gather the necessary data for making better research decisions and determining the facts of a research study.
When Can a Researcher Conduct Experimental Research?
A researcher can conduct experimental research in the following situations —
- When time is an important factor in establishing a relationship between the cause and effect.
- When there is an invariable or never-changing behavior between the cause and effect.
- Finally, when the researcher wishes to understand the importance of the cause and effect.
Importance of Experimental Research Design
To publish significant results, choosing a quality research design forms the foundation to build the research study. Moreover, effective research design helps establish quality decision-making procedures, structures the research to lead to easier data analysis, and addresses the main research question. Therefore, it is essential to cater undivided attention and time to create an experimental research design before beginning the practical experiment.
By creating a research design, a researcher is also giving oneself time to organize the research, set up relevant boundaries for the study, and increase the reliability of the results. Through all these efforts, one could also avoid inconclusive results. If any part of the research design is flawed, it will reflect on the quality of the results derived.
Types of Experimental Research Designs
Based on the methods used to collect data in experimental studies, the experimental research designs are of three primary types:
1. Pre-experimental Research Design
A research study could conduct pre-experimental research design when a group or many groups are under observation after implementing factors of cause and effect of the research. The pre-experimental design will help researchers understand whether further investigation is necessary for the groups under observation.
Pre-experimental research is of three types —
- One-shot Case Study Research Design
- One-group Pretest-posttest Research Design
- Static-group Comparison
2. True Experimental Research Design
A true experimental research design relies on statistical analysis to prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis. It is one of the most accurate forms of research because it provides specific scientific evidence. Furthermore, out of all the types of experimental designs, only a true experimental design can establish a cause-effect relationship within a group. However, in a true experiment, a researcher must satisfy these three factors —
- There is a control group that is not subjected to changes and an experimental group that will experience the changed variables
- A variable that can be manipulated by the researcher
- Random distribution of the variables
This type of experimental research is commonly observed in the physical sciences.
3. Quasi-experimental Research Design
The word “Quasi” means similarity. A quasi-experimental design is similar to a true experimental design. However, the difference between the two is the assignment of the control group. In this research design, an independent variable is manipulated, but the participants of a group are not randomly assigned. This type of research design is used in field settings where random assignment is either irrelevant or not required.
The classification of the research subjects, conditions, or groups determines the type of research design to be used.
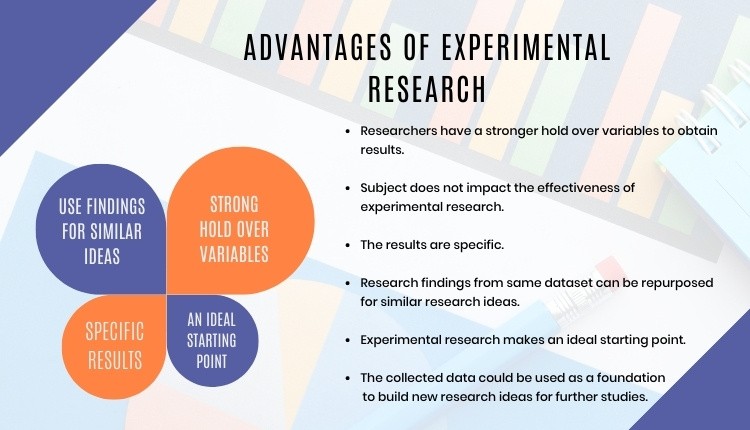
Advantages of Experimental Research
Experimental research allows you to test your idea in a controlled environment before taking the research to clinical trials. Moreover, it provides the best method to test your theory because of the following advantages:
- Researchers have firm control over variables to obtain results.
- The subject does not impact the effectiveness of experimental research. Anyone can implement it for research purposes.
- The results are specific.
- Post results analysis, research findings from the same dataset can be repurposed for similar research ideas.
- Researchers can identify the cause and effect of the hypothesis and further analyze this relationship to determine in-depth ideas.
- Experimental research makes an ideal starting point. The collected data could be used as a foundation to build new research ideas for further studies.
6 Mistakes to Avoid While Designing Your Research
There is no order to this list, and any one of these issues can seriously compromise the quality of your research. You could refer to the list as a checklist of what to avoid while designing your research.
1. Invalid Theoretical Framework
Usually, researchers miss out on checking if their hypothesis is logical to be tested. If your research design does not have basic assumptions or postulates, then it is fundamentally flawed and you need to rework on your research framework.
2. Inadequate Literature Study
Without a comprehensive research literature review , it is difficult to identify and fill the knowledge and information gaps. Furthermore, you need to clearly state how your research will contribute to the research field, either by adding value to the pertinent literature or challenging previous findings and assumptions.
3. Insufficient or Incorrect Statistical Analysis
Statistical results are one of the most trusted scientific evidence. The ultimate goal of a research experiment is to gain valid and sustainable evidence. Therefore, incorrect statistical analysis could affect the quality of any quantitative research.
4. Undefined Research Problem
This is one of the most basic aspects of research design. The research problem statement must be clear and to do that, you must set the framework for the development of research questions that address the core problems.
5. Research Limitations
Every study has some type of limitations . You should anticipate and incorporate those limitations into your conclusion, as well as the basic research design. Include a statement in your manuscript about any perceived limitations, and how you considered them while designing your experiment and drawing the conclusion.
6. Ethical Implications
The most important yet less talked about topic is the ethical issue. Your research design must include ways to minimize any risk for your participants and also address the research problem or question at hand. If you cannot manage the ethical norms along with your research study, your research objectives and validity could be questioned.
Experimental Research Design Example
In an experimental design, a researcher gathers plant samples and then randomly assigns half the samples to photosynthesize in sunlight and the other half to be kept in a dark box without sunlight, while controlling all the other variables (nutrients, water, soil, etc.)
By comparing their outcomes in biochemical tests, the researcher can confirm that the changes in the plants were due to the sunlight and not the other variables.
Experimental research is often the final form of a study conducted in the research process which is considered to provide conclusive and specific results. But it is not meant for every research. It involves a lot of resources, time, and money and is not easy to conduct, unless a foundation of research is built. Yet it is widely used in research institutes and commercial industries, for its most conclusive results in the scientific approach.
Have you worked on research designs? How was your experience creating an experimental design? What difficulties did you face? Do write to us or comment below and share your insights on experimental research designs!

Frequently Asked Questions
Randomization is important in an experimental research because it ensures unbiased results of the experiment. It also measures the cause-effect relationship on a particular group of interest.
Experimental research design lay the foundation of a research and structures the research to establish quality decision making process.
There are 3 types of experimental research designs. These are pre-experimental research design, true experimental research design, and quasi experimental research design.
The difference between an experimental and a quasi-experimental design are: 1. The assignment of the control group in quasi experimental research is non-random, unlike true experimental design, which is randomly assigned. 2. Experimental research group always has a control group; on the other hand, it may not be always present in quasi experimental research.
Experimental research establishes a cause-effect relationship by testing a theory or hypothesis using experimental groups or control variables. In contrast, descriptive research describes a study or a topic by defining the variables under it and answering the questions related to the same.
good and valuable
Very very good
Good presentation.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
Graphical Abstracts Vs. Infographics: Best practices for using visual illustrations for increased research impact
Dr. Sarah Chen stared at her computer screen, her eyes staring at her recently published…

- Publishing Research
10 Tips to Prevent Research Papers From Being Retracted
Research paper retractions represent a critical event in the scientific community. When a published article…

- Industry News
Google Releases 2024 Scholar Metrics, Evaluates Impact of Scholarly Articles
Google has released its 2024 Scholar Metrics, assessing scholarly articles from 2019 to 2023. This…
![the difference between descriptive and experimental research design What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- AI in Academia
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Open Access Week 2024
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Publication Integrity Week 2024
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

Which among these would you prefer the most for improving research integrity?
The Four Types of Research Design — Everything You Need to Know
Updated: October 07, 2024
Published: December 23, 2022
When you conduct research, you need to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve and how to accomplish it. A good research design enables you to collect accurate and reliable data to draw valid conclusions.

In this blog post, we'll outline the key features of the four common types of research design with real-life examples from UnderArmor, Carmex, and more. Then, you can easily choose the right approach for your project.
Table of Contents
What is research design?
The four types of research design, research design examples.
Research design is the process of planning and executing a study to answer specific questions. This process allows you to test hypotheses in the business or scientific fields.
Research design involves choosing the right methodology, selecting the most appropriate data collection methods, and devising a plan (or framework) for analyzing the data. In short, a good research design helps us to structure our research.
Marketers use different types of research design when conducting research .
There are four common types of research design — descriptive, correlational, experimental, and diagnostic designs. Let’s take a look at each in more detail.
Researchers use different designs to accomplish different research objectives. Here, we'll discuss how to choose the right type, the benefits of each, and use cases.
Research can also be classified as quantitative or qualitative at a higher level. Some experiments exhibit both qualitative and quantitative characteristics.
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Experimental
An experimental design is used when the researcher wants to examine how variables interact with each other. The researcher manipulates one variable (the independent variable) and observes the effect on another variable (the dependent variable).
In other words, the researcher wants to test a causal relationship between two or more variables.
In marketing, an example of experimental research would be comparing the effects of a television commercial versus an online advertisement conducted in a controlled environment (e.g. a lab). The objective of the research is to test which advertisement gets more attention among people of different age groups, gender, etc.
Another example is a study of the effect of music on productivity. A researcher assigns participants to one of two groups — those who listen to music while working and those who don't — and measure their productivity.
The main benefit of an experimental design is that it allows the researcher to draw causal relationships between variables.
One limitation: This research requires a great deal of control over the environment and participants, making it difficult to replicate in the real world. In addition, it’s quite costly.
Best for: Testing a cause-and-effect relationship (i.e., the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable).
Correlational
A correlational design examines the relationship between two or more variables without intervening in the process.
Correlational design allows the analyst to observe natural relationships between variables. This results in data being more reflective of real-world situations.
For example, marketers can use correlational design to examine the relationship between brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. In particular, the researcher would look for patterns or trends in the data to see if there is a relationship between these two entities.
Similarly, you can study the relationship between physical activity and mental health. The analyst here would ask participants to complete surveys about their physical activity levels and mental health status. Data would show how the two variables are related.
Best for: Understanding the extent to which two or more variables are associated with each other in the real world.
Descriptive
Descriptive research refers to a systematic process of observing and describing what a subject does without influencing them.
Methods include surveys, interviews, case studies, and observations. Descriptive research aims to gather an in-depth understanding of a phenomenon and answers when/what/where.
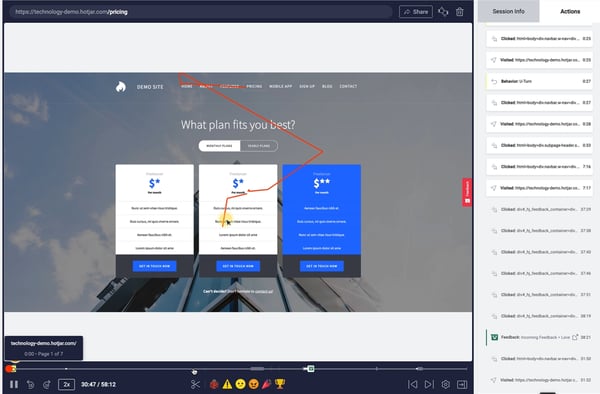
SaaS companies use descriptive design to understand how customers interact with specific features. Findings can be used to spot patterns and roadblocks.
For instance, product managers can use screen recordings by Hotjar to observe in-app user behavior. This way, the team can precisely understand what is happening at a certain stage of the user journey and act accordingly.
Brand24, a social listening tool, tripled its sign-up conversion rate from 2.56% to 7.42%, thanks to locating friction points in the sign-up form through screen recordings.
Carma Laboratories worked with research company MMR to measure customers’ reactions to the lip-care company’s packaging and product . The goal was to find the cause of low sales for a recently launched line extension in Europe.
The team moderated a live, online focus group. Participants were shown w product samples, while AI and NLP natural language processing identified key themes in customer feedback.
This helped uncover key reasons for poor performance and guided changes in packaging.