- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Additional menu

Nine essential problem solving tools: The ultimate guide to finding a solution
October 26, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Problem solving may unfold differently depending on the industry, or even the department you work in. However, most agree that before you can fix any issue, you need to be clear on what it is, why it’s happening, and what your ideal long-term solution will achieve.
Understanding both the nature and the cause of a problem is the only way to figure out which actions will help you resolve it.
Given that most problem-solving processes are part inspiration and part perspiration, you’ll be more successful if you can reach for a problem solving tool that facilitates collaboration, encourages creative thinking, and makes it easier to implement the fix you devise.
The problem solving tools include three unique categories: problem solving diagrams, problem solving mind maps, and problem solving software solutions.
They include:
- Fishbone diagrams
- Strategy maps
- Mental maps
- Concept maps
- Layered process audit software
- Charting software
- MindManager
In this article, we’ve put together a roundup of versatile problem solving tools and software to help you and your team map out and repair workplace issues as efficiently as possible.
Let’s get started!
Problem solving diagrams
Mapping your way out of a problem is the simplest way to see where you are, and where you need to end up.
Not only do visual problem maps let you plot the most efficient route from Point A (dysfunctional situation) to Point B (flawless process), problem mapping diagrams make it easier to see:
- The root cause of a dilemma.
- The steps, resources, and personnel associated with each possible solution.
- The least time-consuming, most cost-effective options.
A visual problem solving process help to solidify understanding. Furthermore, it’s a great way for you and your team to transform abstract ideas into a practical, reconstructive plan.
Here are three examples of common problem mapping diagrams you can try with your team:
1. Fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams are a common problem solving tool so-named because, once complete, they resemble the skeleton of a fish.
With the possible root causes of an issue (the ribs) branching off from either side of a spine line attached to the head (the problem), dynamic fishbone diagrams let you:
- Lay out a related set of possible reasons for an existing problem
- Investigate each possibility by breaking it out into sub-causes
- See how contributing factors relate to one another
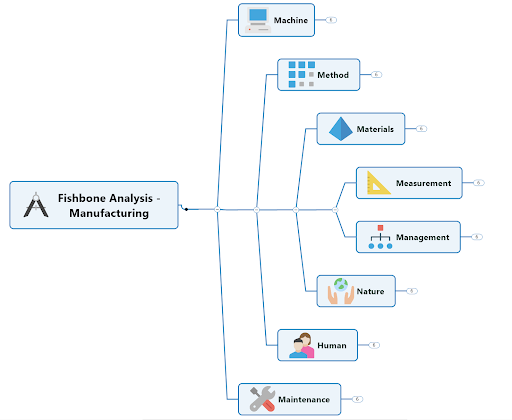
Fishbone diagrams are also known as cause and effect or Ishikawa diagrams.
2. Flowcharts
A flowchart is an easy-to-understand diagram with a variety of applications. But you can use it to outline and examine how the steps of a flawed process connect.
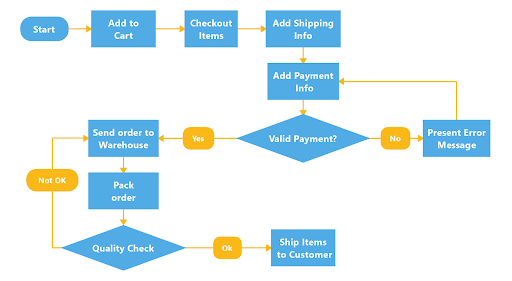
Made up of a few simple symbols linked with arrows indicating workflow direction, flowcharts clearly illustrate what happens at each stage of a process – and how each event impacts other events and decisions.
3. Strategy maps
Frequently used as a strategic planning tool, strategy maps also work well as problem mapping diagrams. Based on a hierarchal system, thoughts and ideas can be arranged on a single page to flesh out a potential resolution.
Once you’ve got a few tactics you feel are worth exploring as possible ways to overcome a challenge, a strategy map will help you establish the best route to your problem-solving goal.
Problem solving mind maps
Problem solving mind maps are especially valuable in visualization. Because they facilitate the brainstorming process that plays a key role in both root cause analysis and the identification of potential solutions, they help make problems more solvable.
Mind maps are diagrams that represent your thinking. Since many people struggle taking or working with hand-written or typed notes, mind maps were designed to let you lay out and structure your thoughts visually so you can play with ideas, concepts, and solutions the same way your brain does.
By starting with a single notion that branches out into greater detail, problem solving mind maps make it easy to:
- Explain unfamiliar problems or processes in less time
- Share and elaborate on novel ideas
- Achieve better group comprehension that can lead to more effective solutions
Mind maps are a valuable problem solving tool because they’re geared toward bringing out the flexible thinking that creative solutions require. Here are three types of problem solving mind maps you can use to facilitate the brainstorming process.
4. Mental maps
A mental map helps you get your thoughts about what might be causing a workplace issue out of your head and onto a shared digital space.
Because mental maps mirror the way our brains take in and analyze new information, using them to describe your theories visually will help you and your team work through and test those thought models.
5. Idea maps
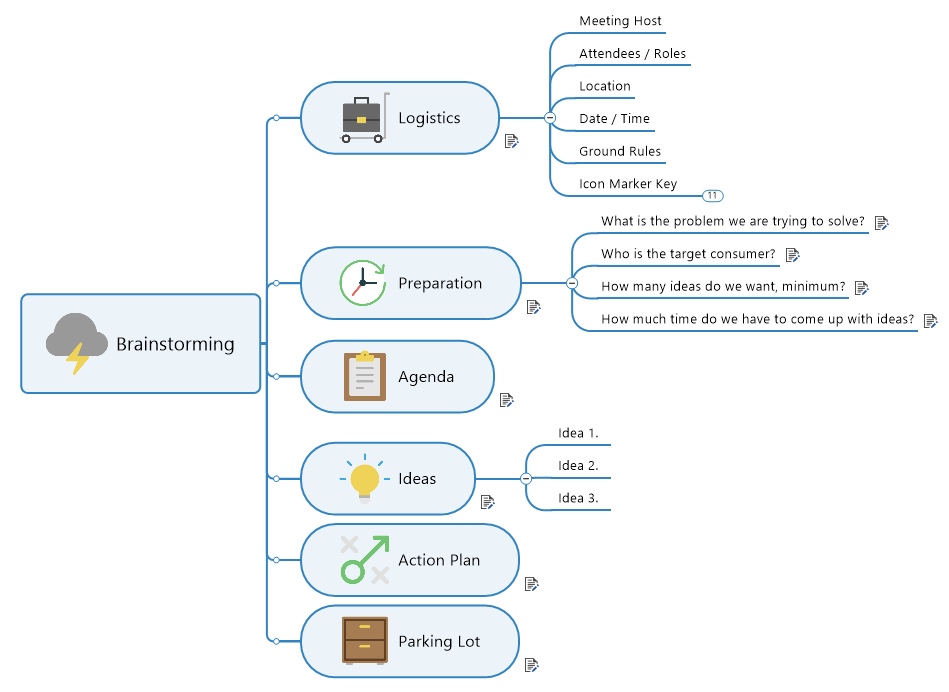
Idea maps let you take advantage of a wide assortment of colors and images to lay down and organize your scattered thought process. Idea maps are ideal brainstorming tools because they allow you to present and explore ideas about the best way to solve a problem collaboratively, and with a shared sense of enthusiasm for outside-the-box thinking.
6. Concept maps
Concept maps are one of the best ways to shape your thoughts around a potential solution because they let you create interlinked, visual representations of intricate concepts.
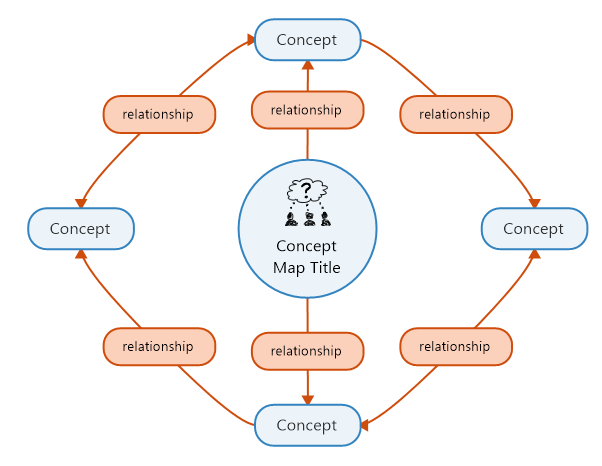
By laying out your suggested problem-solving process digitally – and using lines to form and define relationship connections – your group will be able to see how each piece of the solution puzzle connects with another.
Problem solving software solutions
Problem solving software is the best way to take advantage of multiple problem solving tools in one platform. While some software programs are geared toward specific industries or processes – like manufacturing or customer relationship management, for example – others, like MindManager , are purpose-built to work across multiple trades, departments, and teams.
Here are three problem-solving software examples.
7. Layered process audit software
Layered process audits (LPAs) help companies oversee production processes and keep an eye on the cost and quality of the goods they create. Dedicated LPA software makes problem solving easier for manufacturers because it helps them see where costly leaks are occurring and allows all levels of management to get involved in repairing those leaks.
8. Charting software
Charting software comes in all shapes and sizes to fit a variety of business sectors. Pareto charts, for example, combine bar charts with line graphs so companies can compare different problems or contributing factors to determine their frequency, cost, and significance. Charting software is often used in marketing, where a variety of bar charts and X-Y axis diagrams make it possible to display and examine competitor profiles, customer segmentation, and sales trends.
9. MindManager
No matter where you work, or what your problem-solving role looks like, MindManager is a problem solving software that will make your team more productive in figuring out why a process, plan, or project isn’t working the way it should.
Once you know why an obstruction, shortfall, or difficulty exists, you can use MindManager’s wide range of brainstorming and problem mapping diagrams to:
- Find the most promising way to correct the situation
- Activate your chosen solution, and
- Conduct regular checks to make sure your repair work is sustainable
MindManager is the ultimate problem solving software.
Not only is it versatile enough to use as your go-to system for puzzling out all types of workplace problems, MindManager’s built-in forecasting tools, timeline charts, and warning indicators let you plan, implement, and monitor your solutions.
By allowing your group to work together more effectively to break down problems, uncover solutions, and rebuild processes and workflows, MindManager’s versatile collection of problem solving tools will help make everyone on your team a more efficient problem solver.
Download a free trial today to get started!
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager

Ishikawa Fishbone Diagrams: A Proven Method for Problem-Solving
- October 25, 2024
- Lean Basics
Ishikawa fishbone diagrams, also known as cause-and-effect diagrams or fishbone charts, are powerful tools for problem-solving and quality management. Developed by Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, these diagrams help teams identify, organize, and analyze potential causes of problems in various processes. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, or service industries, fishbone diagrams facilitate root cause analysis, making them essential for continuous improvement initiatives.
What is a Fishbone Diagram?
Step 1: define the problem, step 2: draw the diagram, step 3: brainstorm causes, step 4: analyze the causes, step 5: develop action plans, best practices for effective fishbone diagrams, 👍 advantages, 👎 disadvantages, tools for creating fishbone diagrams, applications of ishikawa fishbone diagrams, implementation.
The fishbone diagram visually represents the relationship between a problem and its potential causes. Its structure resembles a fish skeleton, where:
- The head represents the main problem or effect.
- The bones branching off from the spine represent categories of causes.
- Smaller branches off the main bones detail specific causes within those categories.
This structured approach enables teams to explore the root causes of issues systematically and collaboratively.

How to Create an Ishikawa Fishbone Diagram
Creating a fishbone diagram is straightforward. Follow these steps to ensure an effective analysis:
Clearly articulate the problem or effect you want to analyze. This statement should be specific and measurable. For example, “Increased customer complaints about product quality” is a clear problem statement.
- Create the backbone : Draw a horizontal line (the spine) and write the problem statement at the head of the fish.
- Manpower: The people involved in the process.
- Method : The process steps involved to produce/deliver the product or service.
- Materials : The raw materials or consumables used to produce/deliver the product or service.
- Mother Nature : Both controllable and uncontrollable environmental conditions in the process area.
- Machine : The equipment used to produce/deliver the product or service.
- Measurement : Physical measurements or inspections involved in the process.

Gather your team and brainstorm potential causes for the problem under each category. Encourage open discussion and ensure that every idea is captured.
After brainstorming, prioritize the causes by their impact and likelihood. Focus on identifying root causes that, if addressed, will significantly reduce or eliminate the problem. The multi-voting technique can be used to narrow down the causes to the most critical ones.
Once the most critical root causes are identified, develop action plans to address them. Assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and establish metrics to evaluate progress.
- Involve the Right People: Ensure that team members with relevant knowledge and experience are involved in the brainstorming process. Diverse perspectives lead to more comprehensive cause identification.
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcomplicating the diagram. Focus on major categories and key causes to maintain clarity and effectiveness.
- Use Clear Language: When labeling categories and causes, use simple, clear language. This ensures that everyone involved understands the diagram without ambiguity.
- Regularly Review and Update: As processes and circumstances change, revisit the fishbone diagram to ensure its relevance. Regular updates can lead to continual improvement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fishbone Diagrams
While the fishbone diagram is definitely a powerful tool for root cause analysis, it also has its drawbacks. Here’s a closer look at both sides.
- Visual Clarity : The fishbone diagram provides a clear visual representation of the relationship between a problem and its potential causes. This visual format helps teams easily identify and understand complex relationships, making it easier to communicate findings to stakeholders.
- Structured Approach : The diagram organizes potential causes into categories, often referred to as the “bones” of the fish. This structured approach encourages comprehensive analysis and ensures that no potential cause is overlooked.
- Facilitates Team Collaboration : Creating a fishbone diagram is typically a group activity, promoting collaboration and brainstorming. Team members can contribute their perspectives, leading to a more thorough investigation of the issue. This collaborative effort fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to solving the problem.
- Encourages Comprehensive Thinking : By breaking down a problem into various categories, the fishbone diagram encourages teams to think critically about all possible factors that could contribute to the issue. This holistic view can reveal root causes that may not have been initially apparent.
- Simplicity and Accessibility : The fishbone diagram is straightforward to create and understand. It does not require advanced training, making it accessible to teams across various levels of expertise. This simplicity helps organizations adopt RCA practices without significant investment in time or resources.
- Versatile Applications : Ishikawa diagrams can be applied in various fields, including manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries. Their versatility makes them a valuable tool for any organization seeking to improve quality and resolve issues.
- Identification of Root Causes vs. Symptoms: Ishikawa diagrams help teams distinguish between symptoms and root causes. By diving deeper into each cause, teams can implement effective solutions rather than just addressing superficial issues.
- Facilitation of Continuous Improvement: Using fishbone diagrams aligns with continuous improvement methodologies like Six Sigma and Lean. They support the identification and elimination of waste , leading to improved processes and outcomes.
- Limited Depth : While the fishbone diagram helps identify potential causes, it may not provide enough depth for complex problems. It can sometimes oversimplify issues, leading teams to overlook underlying factors that require more in-depth analysis.
- Potential for Bias : The collaborative nature of creating a fishbone diagram can lead to groupthink, where dominant voices may overshadow others. This can result in biased conclusions or a focus on familiar causes rather than exploring all possibilities.
- Static Representation : The diagram represents a snapshot of the analysis at a particular point in time. As new information emerges or circumstances change, the diagram may quickly become outdated, necessitating continual revisions.
- Requires Follow-Up : Identifying potential causes is just the first step; the fishbone diagram does not provide solutions. Teams must follow up with further analysis and action plans to address the identified causes, which can sometimes lead to inaction if not properly managed.
- Over-reliance on the Tool : Organizations may become overly reliant on fishbone diagrams as a solution for all problems. This reliance can hinder the exploration of other effective RCA methodologies, limiting the team’s problem-solving toolkit.
- Time-Consuming : Depending on the complexity of the issue and the size of the team, creating a thorough fishbone diagram can be time-consuming. If not managed efficiently, this could detract from other critical tasks or deadlines.
While you can create fishbone diagrams using pen and paper or a whiteboard, various digital tools can streamline the process. Here are some popular options:
- Microsoft Visio : A robust diagramming tool that offers templates for fishbone diagrams.
- Lucidchart : An online diagramming application that allows for collaborative diagram creation.
- Miro : A digital whiteboard that facilitates real-time collaboration and brainstorming.
- Canva : Known for its design capabilities, Canva offers templates for creating visually appealing fishbone diagrams.
Fishbone diagrams are often associated with manufacturing processes, but they can be used in almost every sector of business.
Case Study: Using Fishbone Diagrams in a Manufacturing Environment
A manufacturing company experienced a significant increase in product defects, leading to customer complaints and returns. The management team decided to utilize an Ishikawa fishbone diagram to identify the root causes of the problem.
- Define the Problem : The team articulated the problem as “Increase in product defects exceeding 5%.”
- Draw the Diagram : They categorized potential causes into people, processes, materials, machinery, and environment.
- Manpower : Insufficient training, high turnover rates.
- Method : Lack of standardized procedures, inconsistent quality checks.
- Materials : Subpar raw materials, supply chain issues.
- Machine : Aging equipment, lack of maintenance.
- Measurement: Gage R&R shows measurement method is not repeatable, test equipment out of calibration.
- Mother Nature : Poor working conditions affecting morale, high humidity affecting product quality.
- Analysis and Action Plan : After prioritizing the causes, the team focused on training programs for employees and implementing standardized quality checks. They also established a maintenance schedule for machinery.

Within three months, the company saw a 50% reduction in product defects. The structured analysis facilitated by the fishbone diagram enabled the team to implement effective solutions quickly.
Ishikawa fishbone diagrams are invaluable tools for problem-solving and quality management across various industries. Their structured approach to identifying root causes fosters collaboration, enhances analysis, and supports continuous improvement initiatives. By following best practices and leveraging digital tools, organizations can effectively utilize fishbone diagrams to drive meaningful change and improve processes.
Incorporating fishbone diagrams into your problem-solving toolkit can lead to significant enhancements in quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Whether you’re in manufacturing, healthcare, or service industries, the power of the fishbone diagram can help you tackle challenges effectively and sustainably.
Lindsay Jordan
Hi there! My name is Lindsay Jordan, and I am an ASQ-certified Six Sigma Black Belt and a full-time Chemical Process Engineering Manager. That means I work with the principles of Lean methodology everyday. My goal is to help you develop the skills to use Lean methodology to improve every aspect of your daily life both in your career and at home!
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
I accept the Privacy Policy
Post Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Trending now

Ishikawa Diagram
Ishikawa diagram is a great tool to help you solve problems by identifying their root causes. Sometimes called also cause-and-effect or fishbone diagram, it was created by Japanese professor Kaoru Ishikawa. It's especially effective for tackling complex problems.
How to use it
Building out this diagram consists of few simple steps. This can be done in a group as a workshop but also just as well on your own.
1) Define the problem
Start with defining the problem and then drawing a line to the left or right of it (that's up to your preference).
The line will be for adding factors in the next step.
2) Identify contributing factors or categories
List out the factors/categories that could be contributing to the problem you're solving. Plot them along the main line.
You can come up with your own factors or you might use generic categories: People, Equipments, Methods, Measurement, Material and Environment.
Categorising is very helpful for breaking down complex problems and looking at them from different perspectives.
3) Find possible root causes related to each factor
Ask "Why is this happening?" Write down each idea as a line under the factor it relates to. First principles thinking is useful here including the "Five whys" method.
Keep in mind that the problem might not have just one root cause but multiple. So it's important to capture everything that might explain the problem, even if just partially.
At this point, you should have a complete diagram but no definitive answer yet.
4) Analyse the diagram
The most important step is looking at all the possible root causes and analysing them. The diagram now provides a structure for your most important thinking and next steps.
There are many possibilities what you can do at this point. Perhaps you can gather more data/evidence for each root cause candidate or immediately identify the most likely one and quickly try to solve it. This will depend on your specific problems and identified possible causes.
Now let's see how to apply this on a practical example.
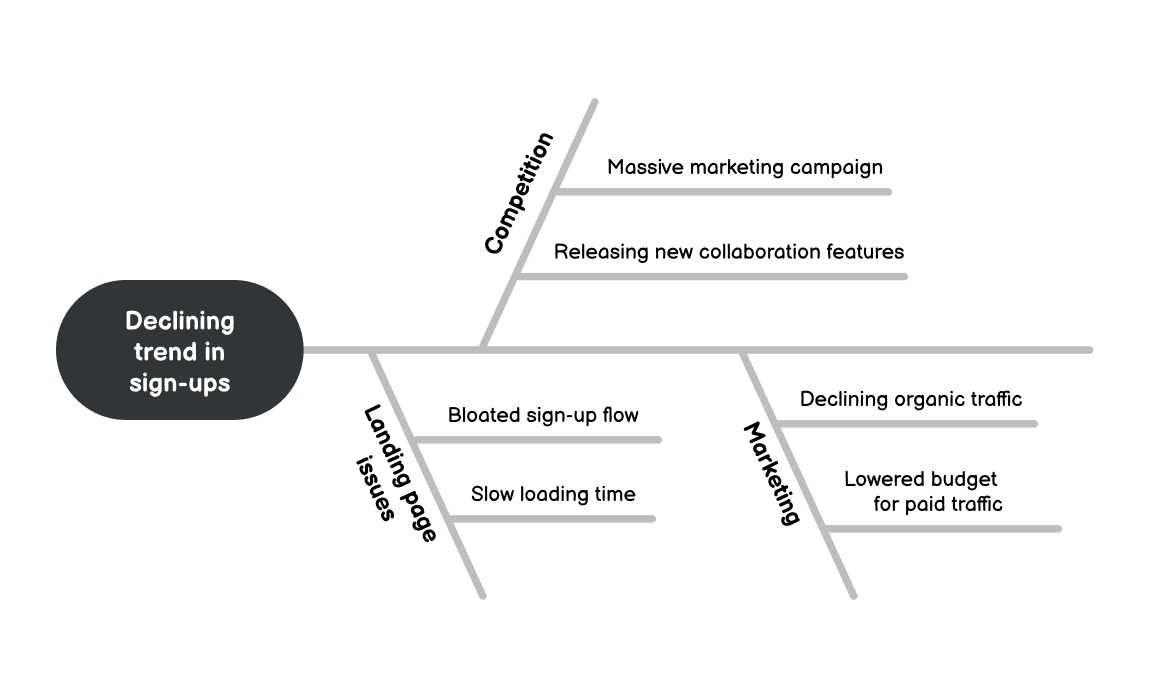
Suppose you're a product manager and have to solve a trend of getting less and less new sign-ups. You start with this definition and then identify contributing factors.
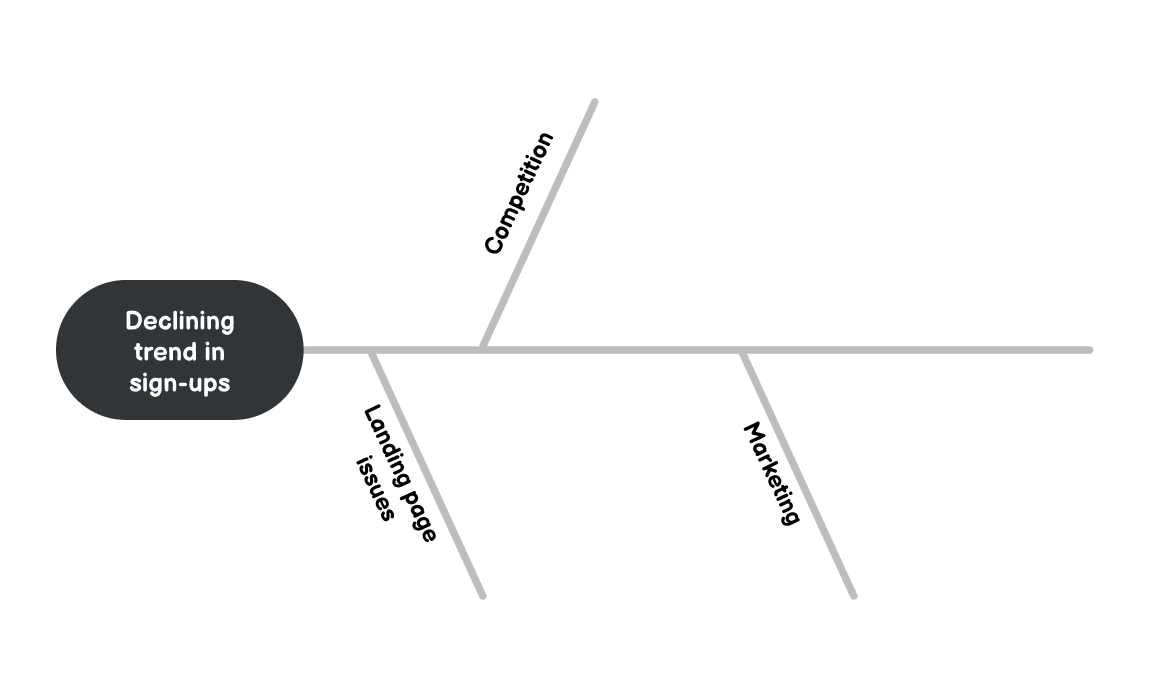
In this example, you identified landing page issues, competition and marketing as factors.
Now let's find specific possible root causes under each factor:
With all of these written down, you can begin to analyse where the problem originates. In this example, you might first verify if the conversion rate is steady despite lower traffic. Then you might audit your sign-up flow to find any leaks and possibly streamline it.
This is a simplified example but this diagram can be definitely used for much more complex problems.
Ishikawa diagram offers a simple framework for finding root causes of problems:
- Define the problem
- Identify contributing factors or categories
- Find possible root causes related to each factor
- Analyse the diagram
You'll create the diagram with the first three steps. It will then provide a structure for your analysis.
Share on Twitter
More problem solving tools
Iceberg Model
Uncover root causes of events by looking at hidden levels of abstractions.
Issue trees
Structure and solve problems in a systematic way.
EdrawMind – Free App
View and Edit Mind Maps with No PC
How to Use Fishbone Diagram for Problem Solving
Fishbone diagram is a problem-solving tool, used in literal terms like a fishbone. It is also known as a cause and effect diagram. The mechanism is to specifically identify the cause and effect of any business or project problem.
A fishbone diagram can help define potential reasons for an issue. This article will dive into understanding the core principles of the fishbone diagram problem solving as a tool.
In 1943 at Tokyo University, Kaoru Ishikawa created the "Fishbone Diagram." Fishbone diagrams can also be called diagrams of "cause and effect." The fishbone diagram problem solving tool is a perfect tool to dig through an issue when we try to assess the root cause and find a solution effectively.
It offers a mechanism for explicitly identifying the "effect" and then brings you to think about the potential triggers, based on typical manufacturing problems. The fishbone diagram problem solving is a basic model that makes it easy to grasp swift and efficient root causes to implement corrective behavior.
It reflects the question or impact at the fish's head or mouth. Possible contributing factors under separate causal groups are identified on the smaller "bones." A fishbone diagram can help define potential reasons for an issue that would otherwise not be discussed by encouraging the team to look through the definitions and discuss alternate reasons.
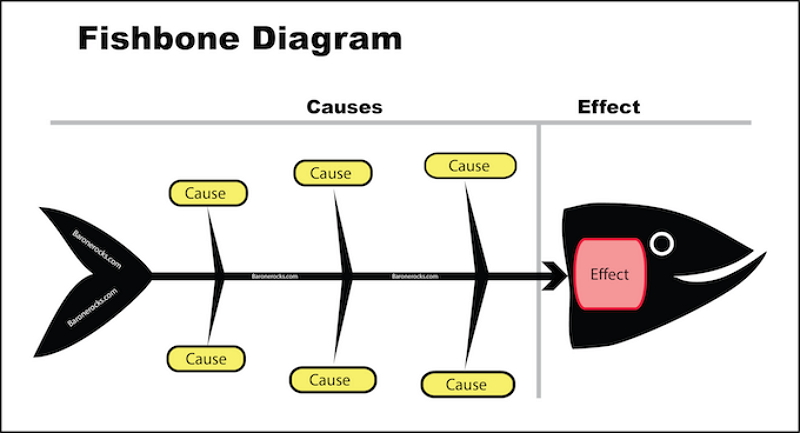
Source: EdrawMind
1.1 Why Use Fishbone Diagram for Problem Solving
The fishbone diagram makes you consider more when solving specific problems. During a brainstorming activity, various groups inspire thoughts from different areas.
The fishbone diagram brings order to the process of cause and effect . It's easy for participants to understand the main problems or issues and focus on the question across different potential triggers.
The fishbone diagram helps distinguish the causes and reasons for a problem and lets people intuitively figure out the solutions.
1.2 The Usage of Fishbone Diagram
The fishbone diagram problem solving method can be used when trying to fix problems or discover the root cause of an issue or problem, which helps you to see below the surface, and dive deeper into the real problem.
Here are several typical fishbone diagram problem solving applications:
- Manufacturing: ,nbsp;Uncover the root cause of a manufacturing problem by brainstorming and rating the likelihood and effect of all factors affecting the manufacturing cycle;
- Marketing or Product Marketing: ,nbsp;Identify the possible factors that may impede your company's popularity in the marketplace by investigating all the places that affect your product acceptance;
- Service: ,nbsp;Uncover the root cause of a business issue by brainstorming, and rate the probability and effect of all factors impacting the service delivery process.
There are 7 steps lead you to use fishbone diagram for problem solving:
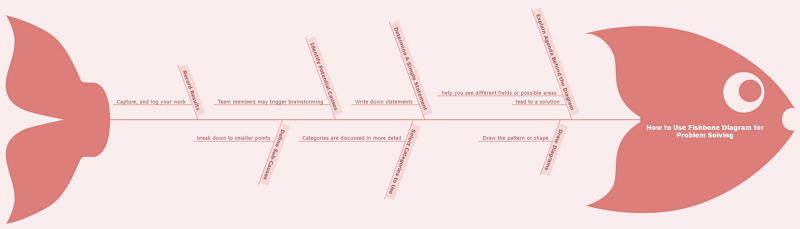
- Explain the agenda behind the diagram
Let your team members know that the diagram can help you see different fields or possible areas that might lead to a solution to your current business problem.
- Draw diagrams
Draw the pattern or shape on your whiteboard, or use a software diagramming tool to ease accessibility. If you need remote attendants to do this exercise, you can quickly build it in EdrawMind and display your computer.
- Determine a simple statement on an issue
Write down statements at the top of your page or above where you will build the diagram., which means everyone has the same idea of the issue you are concerned with.
- Select what categories to use
Categories are discussed in more detail below. For example, you can add Policies, Methods, Personnel, and Software categories.
- Identify potential causes within each category of your problem
Team members may trigger brainstorming or contribute factors that fall into this category. You can either go by category or only come up with ideas and determine which type they fit.
- Go a step deeper to define sub-causes for any cause in the category
If you decide whether something can or will break down to smaller points, build divisions from the critical point.
Team members study the diagram to determine the most relevant focus points. If you are trying to take this a step forward and fix the root cause, it helps define where you're trying to benefit your initiative. You can't solve all the root factors at once, and some can get more significant payoff than others. Check the diagram for an evaluation of where the concentration of the team is best.
- Record results
You bring the work in. Capture, and log your work. You will need to return to it later, so you don't want to miss the importance of the exercise that you got.
There are several tips that should be considered when using the fishbone diagram for solving problems:
- Using the fishbone diagram tool to keep the team focused not on signs, but the problem's causes;
- Make sure you leave ample room in the diagram between the main groups to add minor specific pointers later;
- Try making team members write every cause on sticky notes while you're brainstorming causes, moving around the community asking each person about a particular reason. Continue to go through the loops, have more pointers before all suggestions have been eliminated;
- Encourage each person to join in the brainstorming exercise and voice their own opinions;
- Remember that the strategy of "five-whys" is often used in combination with the fishbone diagram.
While it takes time to create a fishbone diagram , it will help you and your team define the real causes and encourage you to strengthen the process and make permanent improvements.
Regardless, whether you are using the graphical or indented fishbone hierarchy, this process optimization method will significantly help you understand the factors involved in a process. The root causes of the event are the underlying process and system issues, which allowed the contribution. Hence fishbone diagram , the problem-solving tool, is extremely crucial when discussing strategies to deal with problems.
EdrawMind is an easy-to-use, flexible mind mapping tool designed to help you generate modern, fresh visuals and mind maps. By combining the bullet points into a mind map on a project, EdrawMind lets you organize the thoughts or concepts and create essential strategies.

How to Be Productive at Home: 7 Work-from-Home Tips

How to Tell a Great Story: 6 Effective Storytelling Tips

How to Use Mind Maps for Studying Math

How to Make Good Use of Mind Map for Students

Complete Beginner's Guide to Project Planning

Meeting Management: How to Run a Meeting

Fishbone Diagrams for Consequential Problem-Solving

Visualize Processes and Improve
The most successful businesses are not perfect. They are resilient. Every business encounters problems; most encounter them frequently. The ones that thrive are developing a problem-solving culture and arm employees with the tools to find and resolve the root causes of issues effectively. When employees are effective, empowered problem-solvers, obstacles turn into opportunities. One powerful problem-solving tool is the Fishbone Diagram.
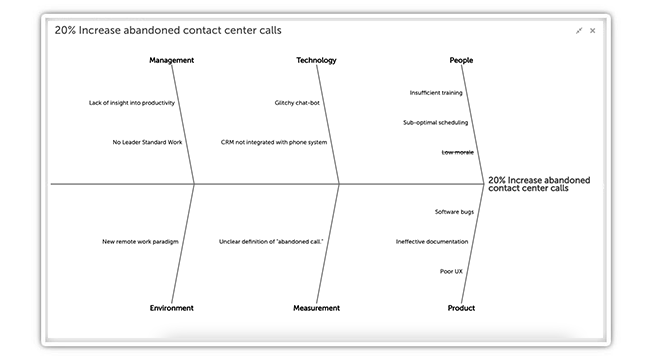
What is a Fishbone Diagram?
A Fishbone Diagram also called an Ishikawa diagram or cause and effect diagram is a visual management tool used to document all the potential causes of a problem to uncover the root causes. The Fishbone Diagram helps users group these causes into categories and provides a structure to display them. When used effectively, it ensures that teams address the actual cause of the problem and don’t just implement a Band-aid solution.
The Fishbone Diagram is called such due to its resemblance to a fish’s skeleton. It was developed by Kaoru Ishikawa and became popular in the 1960s. It is used within many modern quality management methodologies, including Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing.
When to Use a Fishbone Diagram
Although we refer to the Fishbone Diagram as a structured problem-solving tool, it has other uses. It is helpful in breaking down the contributors to any process or system. Some ways to use it to test a problem statement, conduct root cause analysis, predict the results of a new process, streamline an existing process, improve quality outcomes, and uncover bottlenecks.
How to Use a Fishbone Diagram
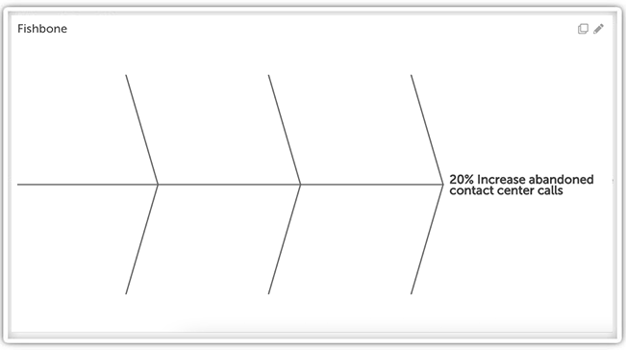
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in problem-solving, whether you use the Fishbone or not, is defining the problem correctly. Ideally, the problem statement will include an objective metric that can be used to determine success. For example, a problem statement such as, “The contact center abandon rate is too high,” will not be as helpful as a statement like, “The contact center abandon rate increased by 20% last month.”
In terms of the Diagram, the problem statement represents the “head” of the fish.
Keep in mind:
- If you are using a fishbone diagram to improve a process, instead of the problem, you will define your desired outcome in an objective and achievable way.
- Each of the “bones” in the diagram will represent a category of potential causes, but causes with the most significant impact should be closest to the “head.”
Step 2: Decide on Categories of Causes
The Fishbone tool forces you to think about the potential causes for the problem in several categories represented by the bones. The number will depend on the type and complexity of the problem. You can choose categories that make sense for your project, but in manufacturing, the 6 Ms are often used. They include:
- Man - the people involved in the process
- Methods - the Standard Work by which the process is performed
- Machines - the equipment and tools needed for the process
- Materials - the raw inputs, parts, consumables, and so forth
- Measurements - the data that is used to evaluate process results
- Mother Nature (Environment) - the conditions under which the process is performed.
Another commonly used structure is the McKinsey 7S Framework, which includes Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff. Marketers may go with the 4Ps of Marketing; Product, Place, Price, and Promotion. Non-manufacturing process may include additional categories such as:
In our software call center abandon rate example, we’ll choose the categories of :
- Measurement
- Environment
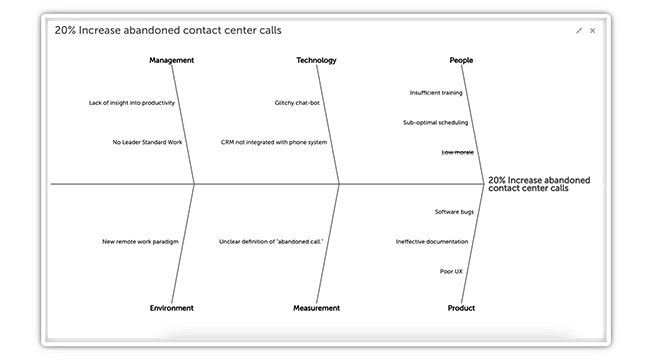
Step 3: Brainstorm Potential Causes and Identify Roots
Now that the categories are defined, the team can go through each one and try to determine all the individual influences that can affect our results. Look at each type and list everything that falls within it. If a potential cause sounds more like a symptom than the root of the matter, the 5 Whys technique can be used to ensure that bottom-line reasons are included. If a source cause supersedes a potential cause, it can be removed from the diagram, or you can use strikethrough to preserve it while moving on to the fundamental problem. In this example, I’ve struck through “Low morale” as a potential cause because it is most likely a symptom of the lack of training and scheduling problems.
Step 4: Analyze the Diagram and Determine Next Steps
The Fishbone Diagram does not direct you to the solution, but it gives you an idea about where to look. By identifying potential causes in this manner, the team can assess the impact of each and brainstorm possible solutions. As in the case of our example, you’ll probably find more opportunities for improvement than you can tackle at once, but the exercise will put the team in a better position to decide what to do next. The Fishbone Diagram also becomes a good starting point for the next improvement cycle once your most critical root causes are addressed.
See How it Works: Schedule a Demo
The benefits of digital fishbone diagrams.
Back in the 1960s when the Fishbone Diagram was introduced, teams used paper to visualize their problem statement and possible causes. While that approach is acceptable for small groups working in the same space for a short period, it is not ideal for the way people work today.
That’s why KaiNexus has incorporated Fishbone Diagrams into our continuous improvement software platform.
- The Fishbone Diagram is created and managed in the same platform you will use for implementing the changes once the analysis is complete.
- Information about your problem, the potential causes, and possible solutions are all collected for future review.
- Remote teams can be as effective as in-person ones.
- Roles and permissions can be applied to determine who can add access and edit Fishbones.
- Fishbone Diagrams can be used for Items, Projects, Improvements, Incidents, Tasks, and Charts.
- Set up to 6 custom categories per diagram or reuse existing categories
- Highlight or strikethrough items
Using digital Fishbone Diagrams that are integrated with your improvement management software will help your team solve problems faster and accelerate the pace of positive change.
Fishbone Diagram Tips
The Fishbone diagram approach is not complicated, but you can do a few things to get the most out of it. We recommend:
- Use category names that are meaningful for your business. If “Methods” isn’t quite right, maybe “Procedures” is a better fit, for example.
- Don’t overload the categories. Create a new one if necessary. Likewise, don’t overcomplicate it; there’s no need to use six categories if four will do.
- Be careful not to add causes that are actually solutions.
- Prioritize your causes by keeping the most impactful ones closest to the “head”
- Use Fishbone Diagrams along with, not instead of, other problem-solving techniques such as The 5 Whys, A3s, process maps, and control charts.
KaiNexus is delighted to put one more digital improvement tool in the hands of our customers. If you’d like to know more about the impact of KaiNexus, one of our experts is available to help.
Want to learn more about KaiNexus Fishbone Diagrams?
Check out our fishbone video or support.kainexus.com for more information..
Improvement Software Features
virtual visual management
IMPROVEMENTS & PROJECTS
whatever you do
CHARTS & DATA
track key metrics
KAINEXUS MOBILE
improve from anywhere
engagement, activity & impact
increase collaboration
SMART NOTIFICATIONS
knowledge sharing
see how it works
Why KaiNexus
- Collaboration
- Standardization
- Customer Success Manager
- Lean Strategy
- Solutions Engineering
- Customer Marketing
- Configuration
- Continuous Enhancements
- Employee Driven
- Leader Driven
- Strategy Development
- Process Driven
- Daily Huddles
- Idea Generation
- Standard Work
- Visual Management
- Advanced ROI
- Notifications
- Universal Badges
- Case Studies
- Education Videos
Copyright © 2024 Privacy Policy
- Activity Diagram (UML)
- Amazon Web Services
- Android Mockups
- Block Diagram
- Business Process Management
- Chemical Chart
- Cisco Network Diagram
- Class Diagram (UML)
- Collaboration Diagram (UML)
- Compare & Contrast Diagram
- Component Diagram (UML)
- Concept Diagram
- Cycle Diagram
- Data Flow Diagram
- Data Flow Diagrams (YC)
- Database Diagram
- Deployment Diagram (UML)
- Entity Relationship Diagram
- Family Tree
- Fishbone / Ishikawa Diagram
- Gantt Chart
- Infographics
- iOS Mockups
- Network Diagram
- Object Diagram (UML)
- Object Process Model
- Organizational Chart
- Sequence Diagram (UML)
- Spider Diagram
- State Chart Diagram (UML)
- Story Board
- SWOT Diagram
- TQM - Total Quality Management
- Use Case Diagram (UML)
- Value Stream Mapping
- Venn Diagram
- Web Mockups
- Work Breakdown Structure
Problem Solving Template
A Problem-Solving Diagram is a visual tool that illustrates the steps and processes involved in addressing and resolving a specific issue or challenge. It typically includes stages such as problem identification, analysis, solution generation, implementation, and evaluation. This diagram helps teams or individuals systematically approach problem-solving, fostering clarity and collaboration in finding effective solutions.
You can easily edit this template using Creately. You can export it in multiple formats like JPEG, PNG and SVG and easily add it to Word documents, Powerpoint (PPT) presentations, Excel or any other documents. You can export it as a PDF for high-quality printouts.
- Flowchart Templates
- Org Chart Templates
- Concept Map Templates
- Mind Mapping Templates
- WBS Templates
- Family Tree Templates
- VSM Templates
- Data Flow Diagram Templates
- Network Diagram Templates
- SWOT Analysis Templates
- Genogram Templates
- Business Model Canvas
- Pedigree Chart Templates
- Activity Diagram Templates
- Amazon Web Services Templates
- Android Mockups Templates
- Block Diagram Templates
- Business Process Management Templates
- Chemical Chart Templates
- Cisco Network Diagram Templates
- Class Diagram Templates
- Collaboration Diagram Templates
- Compare & Contrast Diagram Templates
- Component Diagram Templates
- Concept Diagram Templates
- Cycle Diagram Templates
- Data Flow Diagrams(YC) Templates
- Database Diagram Templates
- Deployment Diagram Templates
- Entity Relationship Diagram Templates
- Fishbone Diagram Templates
- Gantt Chart Templates
- Infographic Templates
- iOS Mockup Templates
- KWL Chart Templates
- Logic Gate Templates
- Mind Map Templates
- Object Diagram Templates
- Object Process Model Templates
- Organizational Chart Templates
- Other Templates
- PERT Chart Templates
- Sequence Diagram Templates
- Site Map Templates
- Spider Diagram Templates
- State Chart Diagram Templates
- Story Board Templates
- SWOT Diagram Templates
- T Chart Templates
- TQM - Total Quality Management Templates
- UI Mockup Templates
- Use Case Diagram Templates
- Value Stream Mapping Templates
- Venn Diagram Templates
- Web Mockup Templates
- Y Chart Templates
Related Templates

Strategy Peeps: Streamlining Processes, Maximizing Efficiency - Bringing Order to Chaos
Decoding the fishbone (ishikawa) diagram: a comprehensive guide to effective problem solving, introduction.
In the realm of problem-solving and continuous improvement, the Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Cause and Effect Diagram, is one of the most powerful visual tool. Fishbone offers a structured approach to identify and explore the root causes of problems. here is a detailed guide to the Fishbone (Ishikawa/Cause and Effect) Diagram, its components, benefits, and how to create one for your problem-solving endeavors.
What is a Fishbone Diagram?
The Fishbone Diagram is a graphical representation that helps visualize the many potential causes of a problem. Its distinctive shape resembles the skeleton of a fish, with the "head" representing the problem and the "bones" representing various contributing factors that lead to the problem.
Key Components of a Fishbone Diagram
Albeit the name, its a very basic tool which only has four components, namely:
Head : This is where you define the problem or the effect you want to analyze.
Main Bones : These represent the major categories or groups of potential causes that contribute to the problem. Common categories include "People," "Processes," "Equipment," "Materials," "Environment," and "Management."
Secondary Bones : These are the smaller branches extending from the main bones. They represent specific factors within each category that might be causing the problem.
Spines : These lines connect the bones to the head of the fish, creating a visual representation of the cause-and-effect relationships.

Benefits of Using a Fishbone Diagram
The Fishbone Diagram offers several key benefits in problem-solving:
Visual Clarity : The diagram provides a visual overview of all possible causes, making it easier to understand complex relationships.
Systematic Approach : It guides teams through a structured process to identify potential causes and explore their interactions.
Collaboration : The Fishbone Diagram encourages cross-functional teams to collaborate and share insights.
Root Cause Identification : It helps uncover the root causes of a problem rather than just addressing symptoms.
Data-Driven Decisions : The diagram is based on available data and evidence, supporting informed decision-making.
Steps to Create a Fishbone Diagram
Define the Problem : Clearly articulate the problem you want to analyze and write it in the "Head" section.
Identify Major Categories : Determine the main contributing categories or factors related to the problem (e.g., People, Process, Equipment).
Brainstorm Causes : Within each major category, brainstorm potential causes that might be contributing to the problem.
Connect Causes : Draw lines (spines) connecting each cause to its corresponding category.
Analyze Relationships : Discuss and analyze the relationships between different causes and how they might interact.
Identify Root Causes : Through analysis, identify the most likely root causes that contribute to the problem.
Implement Solutions : Develop and implement solutions to address the identified root causes.
Real-Life Application of a Fishbone Diagram
Let's consider a practical example: A manufacturing company is facing a high rate of defective products. The problem is defined as "High Defect Rate."
Main Categories : People, Process, Equipment, Materials, Environment
Secondary Causes : Inadequate Training (People), Improper Calibration (Equipment), Low-Quality Raw Materials (Materials), Inadequate Ventilation (Environment), Complex Assembly Process (Process)
By creating a Fishbone Diagram for this scenario, the team can visually map out the potential causes and pinpoint the root causes that need to be addressed.
The Fishbone Diagram is a versatile and insightful tool that empowers teams to systematically analyze complex problems and uncover their underlying causes. Whether you're in manufacturing, healthcare, IT, or any other field, the Fishbone Diagram can enhance your problem-solving capabilities and lead to more effective solutions. By visualizing the cause-and-effect relationships, you gain a clearer understanding of the problem landscape, enabling you to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement.
Use the blog linked below on our website for a step by step guide to Integrate the Fishbone Diagram ( Virtually ) into your problem-solving toolkit and embark on a journey of discovery and solution like never before!
Charting Success Remotely? - Tools for Collaborating on Fishbone Diagrams for Virtual Teams
Recent Posts
Unveiling Customer-Centric Success: Generate Value through Lean Project Management
What is Lean Project Management?
What is Value Stream Mapping (VSM)? - 6 Steps to Leverage VSM for Optimal Process Performance

Easy Problem Solving
Graphical - Visual Tools
" A picture is worth a thousand words"
Use the tools and techniques below to think and present your findings in a visual mode
Tree Diagram
Work with your team to breakdown a task, problem, produce counter-measures
Tree diagram
Cause & Effect
Identify the causes in a visual team activity , know Cause & Effect diagram
From trivial many , boil down to vital few via
Follow it via 5 whys to remove
Understand your process, and find ways to map it thru
Flow charting
Its a diagram that presents hierarchical view from the goal / question till a certain level.
A tree diagram is a great visual and thinking tool, and is used for variety of reasons - task mapping, decision, probability tree , to show logical break down of an argument.
It also is task mapping tool for implementation. You start with a goal and then break into detailed actions, that would be required for implementation
See examples and "how to" of tree diagrams here
Cause & Effect Diagram
Also known as fish bone, C&E, Ishikawa diagram
Fishbone shaped diagram with Effect (Y, output) being the head and Bones as the major causes (Xs). This is about cause and effect and not symptoms . It a great way to brainstorm on causes of a problem and finding root causes
It can have a fair amount of detail in a visual format, which is easy to read and relate to.
Removes personal biases - a team tool
Keeps focus on the problem
Read on about how to use Cause and effect diagram and see an example here
Pareto helps you prioritize and visually present it. Find the factors that are affecting your problem area most, follow it up with 5 why and improve your process.
Learn more about Pareto, download an excel template here
Flow Chart - Process Mapping
Mapping a process, is perhaps the most visual and easy way to understand and explain your process.
Once a map is there - immaterial to the level to which it is detailed - it is also easy to compare it against the what happens on the ground and what we thought it is. Also we can use the map to with more details, to find the bottle necks.
How to make flow charts and how to use them

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Oct 26, 2023 · Fishbone diagrams are a common problem solving tool so-named because, once complete, they resemble the skeleton of a fish. With the possible root causes of an issue (the ribs) branching off from either side of a spine line attached to the head (the problem), dynamic fishbone diagrams let you:
Oct 25, 2024 · Ishikawa fishbone diagrams, also known as cause-and-effect diagrams or fishbone charts, are powerful tools for problem-solving and quality management. Developed by Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, these diagrams help teams identify, organize, and analyze potential causes of problems in various processes.
Ishikawa diagram is a great tool to help you solve problems by identifying their root causes. Sometimes called also cause-and-effect or fishbone diagram, it was created by Japanese professor Kaoru Ishikawa. It's especially effective for tackling complex problems.
The fishbone diagram problem solving tool is a perfect tool to dig through an issue when we try to assess the root cause and find a solution effectively. It offers a mechanism for explicitly identifying the "effect" and then brings you to think about the potential triggers, based on typical manufacturing problems.
Ishikawa Diagrams are a powerful problem-solving tool, but they must be used correctly to produce the desired results. Some best practises for using Ishikawa Diagrams in problem-solving processes are as follows: Clearly define the problem: Before you create an Ishikawa Diagram, you must first define the problem you are attempting to solve. This ...
The fishbone diagram, also known as the cause and effect diagram or Ishikawa diagram, is a powerful tool for problem-solving and root cause analysis. It helps to identify the potential causes of a problem and visually organize them into categories, facilitating a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving.
The ones that thrive are developing a problem-solving culture and arm employees with the tools to find and resolve the root causes of issues effectively. When employees are effective, empowered problem-solvers, obstacles turn into opportunities. One powerful problem-solving tool is the Fishbone Diagram.
A Problem-Solving Diagram is a visual tool that illustrates the steps and processes involved in addressing and resolving a specific issue or challenge. It typically includes stages such as problem identification, analysis, solution generation, implementation, and evaluation. This diagram helps teams or individuals systematically approach problem-solving, fostering clarity and collaboration in ...
Aug 5, 2023 · IntroductionIn the realm of problem-solving and continuous improvement, the Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Cause and Effect Diagram, is one of the most powerful visual tool. Fishbone offers a structured approach to identify and explore the root causes of problems. here is a detailed guide to the Fishbone (Ishikawa/Cause and Effect) Diagram, its components, benefits ...
Its a diagram that presents hierarchical view from the goal / question till a certain level. A tree diagram is a great visual and thinking tool, and is used for variety of reasons - task mapping, decision, probability tree , to show logical break down of an argument. It also is task mapping tool for implementation.