Humanities in Class: Webinar Series

A History of Money in Nine Slides

Simon Middleton (Fellow, 2019–20; Associate Professor of History)
February 16, 2021
What is money and where does it come from? If asked, most people would likely respond to these questions by pointing to the notes and coins in their pockets—or maybe their debit and charge cards—and muse on some connection between the “government” and printed money. Concerning origins, most would probably add that money developed more or less spontaneously in the market in response to the inconveniences of barter exchange. Both answers are wide of the mark: most money—meaning credit and value—is created by the banks and the myth about money’s spontaneous market origins is traceable as far back as Aristotle. In this session we will survey the actual history of money, beginning from its origins in Iraq/Syria in 3000 BCE through to its latest reformulation as Bitcoin. We will also consider how changing understandings of monetary forms and functions have been linked to major political and economic developments, from the collapse of the monarchy in the early modern era to the rise of capitalism and its troubles in the nineteenth through twenty-first centuries. We will do this in nine, straightforward, and easy to follow powerpoint slides. To check on the accuracy of the assumptions above, here’s a challenge for you: Before you come to the session, ask a friend or family member what they think money is and where they think it originates.
History / Economics / Money / Economic History / World History / Monetary Systems / Banking / Material Culture /

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
The History of Money.
Published by Agnes Singleton Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "The History of Money."— Presentation transcript:

The History of Money October Why do we have money? Convenience It is often easier to use money than barter / trade Would you prefer to receive fish.

CIA4U0 Analyzing Current Economic Issues

Introduction to Macroeconomics

Money Module 23.

Unit 3 Understanding Money Unit 3. Learning Outcomes At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Understand the history of money Describe.

MONEY. One of the important function of a financial system is the monetary function. This is where the introduction of money into the economy enables.

1 of 32 © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. CHAPTER OUTLINE 10- Part 1 The Money Supply An Overview of Money What Is Money? Commodity and Fiat Monies Measuring.

Definition and Measurement of Money. Objectives: What is money and what are the functions of it? What are the various roles that money plays in the.

BuffDaniel Presents Money and Banking Chapter 2 Money.
Evolution of Money Chapter # 2. Evolution of Money. In the earlier stages of human civilization, to satisfy man needs, barter system took place. In the.

Money, Banking, and the Federal Reserve

Money Objectives Describe the three uses for money

Presentation on Dollar Based Gold Standard By Group-09.

Money and Banking Chapter 10. Three Uses of Money Medium of Exchange – anything used to determine value during the exchange of goods and services. Unit.

Mississippi Bubble In the early 18th century the economy of France was depressed. The government was deeply in debt and taxes were high. In addition, the.

Germany After WWI. Why Is This Important? To analyse how Hitler came to power and why World War II broke out, it helps to understand the conditions in.

Money!. Money Medium of Exchange = anything that is used to determine value during the exchange of a good or service. Money = anything that serves as.

Barter System.

By: Miranda Crowl EDCI 270 Project 3 November 8, 2013.

Chapter 14 Money and Banking. MONEY Money must be durable enough to withstand repeated use. Money must be easily divisible into smaller units of value.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

A brief history of money
Nov 30, 2011
651 likes | 1.85k Views
A brief history of money. Where all begins.
Share Presentation
- public hoards silver coins
- inferior bronze ones
- natural resources nature doesn
- space research
- money creation

Presentation Transcript
Where all begins 1792 - 1750 BC: Money and banking originates in Babyloniaout of the activities of temples and palaces which provided safe places for the storage of valuables. Initially deposits of grain are accepted and later other goods including cattle, agricultural implements, and precious metals.
The Code of Hammurabi includes laws governing banking operations - all carved in stone! 640 - 630 BC The earliest coins made in Lydia, Asia Minor, consisted of electrum, a naturally occurring amalgam of gold and silver.
640 - 630 BC: Athens issues bronze and silver coins. The Athenian public hoards silver coins which, as a result, quickly disappear from circulation, leaving only the inferior bronze ones According to Demosthenes 10% is the normal rate of interest for run-of-the-mill business. For risky business such as lending for shipping rates of between 20% and 30% are normal.
390 BC The Gauls attack Rome The cackling of geese in the capitol, where the city's reserves of money are kept, alerts the defenders. The grateful Romans build a shrine to Moneta, the goddess of warning, and from Moneta the words money and mint are derived.
1095-1270: The Crusades The need to transfer large sums of money to finance the Crusades provides a stimulus to the re-emergence of banking in western Europe.
The functions of money • measure of value • medium of exchange • store of value
Money throughout the history of the world Shells Live stock Precious stones Skulls Pearls Wheat Feathers Brass Silver Gold Paper money
Gold as money • widely accepted • divisible • easy to measure • easy to carry • non-perishable (although it wears out) • impossible to forge
Macro-economic equilibrium Requires that the demand for money equals the supply of money
Demand for monetary gold • is a function of economic needs • an expanding economy needs extra money • the demand for monetary gold competes with the demand from the industry (i.e., electronics, medical equipment, space research etc.)
Supply of gold Is a function of natural resources Nature doesn’t care if the PM wants to increase the money supply
Why would governments want to issue more and more money? To keep up with demand Seignorage means more wealth for the issuer Seignorage = face value of money - cost of issuing money
250 AD: Nero debases the gold and silver coinages.Twenty years later, the silver content of Roman coins has fallen to only 4%
270 AD: Aurelian issues new, nearly pure coins, using gold from his eastern conquests • He raises the coins’ nominal value by 2½ times hoping in this way to stay ahead of inflation. • This "reform" sends inflation soaring.
1542-1551 The Great Debasement Henry VIII debases the coinage of England as a means of raising revenue.
1560 Elizabeth I begins the reform of England's debased coinage • Thomas Gresham, after whom Gresham's law ("bad money drives out good") is named, is an influential adviser. • The debased coins are recalled and melted down and the base and precious metals separated.
Gold as money: A summary When debasing of coins is prohibited: • Very little incentive for governments to "fudge" with the money supply • Gold is even deflationary
Paper money • c. 960- Issues of Chinese paper money start to become regular
Paper money 1659 The earliest British cheque is issued This is an order to the London goldsmiths Morris and Clayton to pay a Mr Delboe £ 400. Because notes are accepted as evidence of ability to pay they are a convenient alternative to handling coins or bullion.
1690 - The Massachusetts Bay Colony issued the first paper money in the colonies which would later form the United States.
Paper money 1698 Coins form less than half the English money supply Davenant, a contemporary writer, estimates that the total value of coins in circulation is less than that of tallies, bills, banknotes etc. Increasingly the power of money creation is passing from the King, in charge of the mint, to the London money market and provincial banks. Political and constitutional power is also affected by this transfer of financial power. 1704 Promissory Notes Act This confirms the legality in England of goldsmith's notes as negotiable, i.e. payable to the bearer rather than to a named person.
Paper money 1832 Capital punishment for forging banknotes abolished in Britain The maximum penalty for forgery is reduced from death to transportation for life (e.g. exile to Australia). 1848 Bank of France is given a nationwide monopoly of note issues The national bank is given a monopoly of note issuing to fill the gap left by the failure of numerous local banks. The Bank of France also begins to develop a large network of branches in different parts of the country.
Paper money • was initially a claim on gold • has no natural (intrinsic value), hence acceptance is backed by guarantees from a central authority • during tumultuous economic periods, drove gold out of circulation
- More by User

A History of Money!
A History of Money!. Banking & Credit Mr. Yates. What did we do before money?. In the beginning, people bartered . Barter is the exchange of a good or service for another good or service bag of rice for a bag of beans. . Barter. Commodity Money.
7.88k views • 27 slides

A Brief History of Money
A Brief History of Money. What is Money?. We normally think of currency when we think of money. However, more generally speaking, money is any commodity which satisfies the following: Unit of account Store of Value Medium of exchange. Early Commodity Money.
821 views • 25 slides


A Brief History Of
A Brief History Of . History Independent Data Structures. Credit: South China Morning Post. Oblivious Data Structures. [Mic97]. Daniele Micciancio Oblivious data structures: Applications to cryptography - STOC 1997. An attempt to solve the privacy problem in incremental cryptography.
1.26k views • 76 slides

A Brief History
1818: Founded in Amsterdam by Johann Peter Bunge 1884 : Bunge y Born established in Argentina by grandson, Ernest Bunge 1905 : Bunge y Born expanded into Brazil 1923 : Bunge North American Grain Corporation founded in New York City to trade raw agricultural commodities
529 views • 19 slides

A brief history
A brief history. 1602 – Dutch East India Company becomes dominant power in the area that is modern day Indonesia At this time, Indonesia is actually a creation of the Dutch and the Dutch East Indian Company
530 views • 20 slides

A Brief History of
A Brief History of . The First 48 Years: 1962 to 2010. 1960s… . W. K. H. Panofsky. “Pief”. 1970s …. SPEAR under construction. 1970s …. November Revolution 11/11/1974. Burton Richter and Sam Ting shared Nobel Prize in Physics, 1976. 1970s …. Martin Perl at
977 views • 21 slides

A Brief History. Early Beginnings. Today’s music originally developed from what was known as African township jive Instead of instruments, these artists used their mouth, lips, and tongues to create a variety of sounds, later duplicated by instrumentation . Early Beginnings.
325 views • 16 slides

A BRIEF History
The Evolution of the Doctor of Nursing Practice Degree. A BRIEF History. What sparked the DNP movement The focus on clinical practice vs. pure research Evidence-based practice – required research knowledge Other health professionals – Pharm. D., DPT
448 views • 33 slides

A brief history …
A history of the CACG, EUGridPMA, and the IGTF (and some next steps) First APGridPMA Face-to-Face Meeting Beijing David Groep, 2005-11-29. A brief history …. From the CACG to EUGridPMA to IGTF … The EU DataGrid CACG The EUGridPMA: charter and growth IGTF Foundation on October 5 th , 2005
462 views • 34 slides

A brief history. Challenge for grammar school kids 14-15y Competition: Take over control of the enemy bot You know the system, when you know the leaks Deadline: May 2011 / School Centennial. 60% of Berlin would vanish, if c-base starts right now…. reconstructioneering the future.
295 views • 17 slides
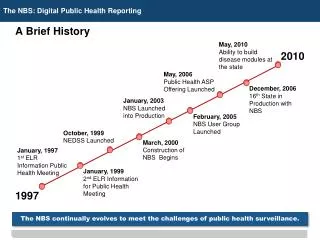
A Brief History. May, 2010 Ability to build disease modules at the state. 2010. May, 2006 Public Health ASP Offering Launched. December, 2006 16 th State in Production with NBS. January, 2003 NBS Launched into Production. February, 2005 NBS User Group Launched. October, 1999
408 views • 23 slides

____________________________________ ____________________________________ A BRIEF HISTORY OF
____________________________________ ____________________________________ A BRIEF HISTORY OF DISABILITY RIGHTS IN CANADA * October 21, 2013
375 views • 18 slides

a brief history of
a brief history of. andreas müller theory group max camenzind lsw heidelberg http://www.lsw.uni-heidelberg.de/users/amueller. student seminar mpia & lsw january 2004. talk organisation. basics J standard knowledge advanced knowledge edge of knowledge and verifiability N. mind map.
991 views • 44 slides

A Brief History of History
A Brief History of History. Herodotus (484-425 BCE) – “Father of History”. Statue of Herodotus. Persian Empire. Persia had the largest empire in the world at the time (late 500s/early 400s BCE) Persia ruled land in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia
993 views • 10 slides

A Brief History Of. History Independent Data Structures. Credit: South China Morning Post. Oblivious Data Structures. [Mic97]. Daniele Micciancio Oblivious data structures: Applications to cryptography - STOC 1997. An attempt to solve the privacy problem in incremental cryptography.
1.03k views • 76 slides

A Brief History. of. Organic Chemistry. The Phlogiston Theory. metal + heat = calx of metal + Ø. e.g., zinc = zinc oxide + Ø. phlogiston (Ø) is lost. calx + charcoal(Ø) + heat = metal + (fixed air). phlogiston (Ø) is gained. Problem:. phlogiston has a negative mass!.
500 views • 30 slides

A Brief History. In 1933, NRCS (then the Soil Erosion Service), started working with farmers to reduce erosion and conserve soil 1935 – Soil Conservation Act 1937 – establishment of first Conservation District
319 views • 7 slides

341 views • 25 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Money needs to serve as a medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account. King Croesus created the first coins of gold and silver in 561 BC. Paper currency was first issued in China in 806 AD but led to inflation. Various commodities served as forms of money throughout history.
Just as humans have evolved - money has evolved. First it was Barter Then shells Then mental Then silver Then leather money Most money today is paper money 4. Barter is when people trade or exchange (swap) goods for other goods without the use of money, like for instance trading seeds for apples.
Presentation on theme: "A Brief History of Money"— Presentation transcript: 1 A Brief History of Money. 2 What is Money? We normally think of currency when we think of money. However, more generally ... History of American Money The History of U.S. Paper Money In the early days of the nation, before and just after the revolution, Americans ...
This document provides a history of the development of money. It begins with bartering and the use of shells as early forms of currency. It then discusses the introduction of coinage in Lydia in 600 BC and the later development of paper money in China in the 9th century. It also briefly outlines the gold standard, development of credit cards ...
In this session we will survey the actual history of money, beginning from its origins in Iraq/Syria in 3000 BCE through to its latest reformulation as Bitcoin. We will also consider how changing understandings of monetary forms and functions have been linked to major political and economic developments, from the collapse of the monarchy in the ...
14 Currency Debasement in China Initially, the paper money was fine, because it was exchangeable for gold, silver, or silk Eventually, inflation began to take hold, as China was funding an ongoing war with the Mongols, which it eventually lost. In the end, the best families in the empire were ruined, a new set of men came into the control of public affairs, and the country became the scene of ...
The History of Money - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. 1) The document traces the history of money from barter systems to modern forms like mobile payments and virtual currency. It discusses the move from commodity money to fiat money and the development of coinage and banking.
The presentation offers interactive activities, such as discussion points, reflections, and turn-and-talk questions to encourage active participation and engagement from your students. The History of Money PowerPoint and Google Slides presentation is visually engaging and easy to follow for your students. It features vivid images and graphics ...
Bring history to life in your classroom with this engaging and informative PowerPoint on the history of money. From ancient civilizations and their forms of currency, to the rise of coinage in the Middle Ages, this presentation covers all the key points in the evolution of money. It also delves into...
A brief history of money. Where all begins 1792 - 1750 BC: Money and banking originates in Babyloniaout of the activities of temples and palaces which provided safe places for the storage of valuables. Initially deposits of grain are accepted and later other goods including cattle, agricultural implements, and precious metals.