- QUICK LINKS
- How to enroll
- Career services
- Go to MyPhoenix
- Return to my application
- My saved programs

How to Identify an Appropriate Research Problem

By Mansureh Kebritchi, Ph.D.
A research problem is the heart of the study. It is a clear, definite statement of the area of concern or investigation and is backed by evidence (Bryman, 2007). It drives the research questions and processes and provides the framework for understanding the research findings. To begin, you will need to know where to look for your research problem and how to evaluate when a research problem for success.
Where to Find a Research Problem
Ideas for research problems tend to come from two sources: real life and the scholarly arena. First, identifying a research problem can be as simple as observing the complications and issues in your local workplace. You may encounter ongoing issues on a daily basis in your workplace or observe your colleagues struggle with major issues or questions in your field. These ongoing obstacles and issues in the workplace can be the catalyst for developing a research problem.
Alternatively, research problems can be identified by reviewing recent literature, reports, or databases in your field. Often the section on “recommendations for future studies” provided at the end of journal articles or doctoral dissertations suggests potential research problems. In addition, major reports and databases in the field may reveal findings or data-based facts that call for additional investigation or suggest potential issues to be addressed. Looking at what theories need to be tested is another opportunity to develop a research problem.
How to Evaluate a Research Problem
Once you find your potential research problem, you will need to evaluate the problem and ensure that it is appropriate for research. A research problem is deemed appropriate when it is supported by the literature and considered significant, timely, novel, specific, and researchable. Stronger research problems are more likely to succeed in publication, presentation, and application.
Supported by the Literature
Your research problem should be relevant to the field and supported by a number of recent peer-reviewed studies in the field. Even if you identify the problem based on the recommendation of one journal article or dissertation, you will still need to conduct a literature search and ensure that other researchers support the problem and the need for conducting research to further address the problem.
Significant
Your research problem should have a positive impact on the field. The impact can be practical, in the form of direct application of the results in the field, or conceptual, where the work advances the field by filling a knowledge gap.
Your research problem should be related to the current needs in the field and well-suited for the present status of the issues in your field. Explore what topics are being covered in current journals in the field. Look at calls from relevant disciplinary organizations. Review your research center agenda and focused topics. For example, the topics of the Research Labs at the Center for Educational and Instructional Technology Research including critical thinking, social media and cultural competency, diversity, and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) in higher education are representative of the current timely topics in the field of education. Identifying a current question in the field and supporting the problem with recent literature can justify the problem's timeliness.
Your research problem should be original and unique. It should seek to address a gap in our knowledge or application. An exhaustive review of the literature can help you identify whether the problem has already been addressed with your particular sample and/or context. Talking to experts in the research area can illuminate a problem. Replication of an existing study warrants a discussion of value elsewhere, but the novelty can be found in determining if an already-resolved problem holds in a new sample and/or context.
Specific and Clear
Your research problem should be specific enough to set the direction of the study, raise research question(s), and determine an appropriate research method and design. Vague research problems may not be useful to specify the direction of the study or develop research questions.
Researchable
Research problems are solved through the scientific method. This means researchability, or feasibility of the problem, is more important than all of the above characteristics. You as the researcher should be able to solve the problem with your abilities and available research methods, designs, research sites, resources, and timeframe. If a research problem retains all of the aforementioned characteristics but it is not researchable, it may not be an appropriate research problem.
References and More Information
Bryman, Alan. “The Research Question in Social Research: What is its Role?” International Journal of Social Research Methodology 10 (2007): 5-20.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 1. Choosing a Research Problem
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Resources
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
In the social and behavioral sciences, the subject of analysis is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to discover new knowledge and understanding , formulate a set of solutions or recommended courses of action, and/or develop a more effective approach to applied practice. The research problem, therefore, is the main organizing principle guiding the analysis of your research. It establishes an occasion for writing and a focus that governs what you want to say. The research problem represents the essential subject matter of scholarly communication and the means by which scholars arrive at other topics of conversation within and outside of their area of study [i.e., their discipline].
Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Jacobs, Ronald L. “Developing a Dissertation Research Problem: A Guide for Doctoral Students in Human Resource Development and Adult Education.” New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development 25 (Summer 2013): 103-117; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011.
Types of Research Problems
A research problem sets the stage for how to design a study based, in part, on the type of conclusions, desired outcomes, recommended courses of action, or applications to practice that you are expecting as a result of your analysis and interpretation of the findings. In this context, a research problem not only serves as the main organizing principle of the study, but it helps frame the way in which you approach the topic.
There are at least seven interconnected ways research problems can be formulated to address the topic under investigation. Each example focuses on the theme of climate change to make it easier to differentiate among the types of research problems.
Action research problems most often relate to conducting investigations in socio-organizational settings that utilize qualitative methods of information gathering. The objective of formulating an action-based problem to study is to create outcomes leading to positive change within the research setting. Additionally, it is often the case that the topic may have personal significance to the researcher.
An example of an action research problem could be: A persistent challenge in transporting food aid to rural regions of Zimbabwe during persistent drought conditions is creating effective partnerships with local government and non-governmental entities that can support the delivery of goods and services. Working with local government leaders and nonprofit aid organizations, this study tests methods of outreach and collaboration aimed at improving transportation planning and operations in areas impacted by severe droughts.
The purpose of applied research is to focus on addressing problems that generate practical evidence-based solutions, interventions, or innovations that lead to measurable improvements to the human condition. Its primary objective is not only to add to existing knowledge and understanding about a topic, but to leverage this increased knowledge in ways that apply to real world situations. An aim of applied research studies is often to test theoretical assumptions in real life settings.
An example of an applied research problem could be:
Exploratory
Theoretical
Chinagozi, OSADEME Gloria. “Research Problems in Management Sciences: An Expository Approach.” International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science 7 (June 2023): 438-450; Kamper, Steven J. "Types of Research Questions: Descriptive, Predictive, or Causal." Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy 50 (August 2020): 468-469; Singh, Sunaina. "What is a Research Problem? Characteristics, Types, and Examples." Researcher.Life, August 22, 2023; Walia, Ashni and Priya Chetty. “Different Types of Research Problems and Their Examples.” Project Guru, June 1, 2020.
Choosing a Research Problem / How to Begin
Do not assume that identifying a problem to investigate will be a quick and easy task! You should be thinking about it during the beginning of the course. There are generally three ways you are asked to write about a research problem :
- Your professor provides you with a general topic related to the subject of the course from which you study a particular aspect;
- Your professor provides you with a list of possible topics to study and you choose a topic from that list; or,
- your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic and you only have to obtain permission to write about it before beginning your investigation.
I. How To Begin: You are given the topic to write about
Step 1 : Identify concepts and terms that make up the topic statement . These terms can be found in the description of the writing assignment. For example, your professor wants the class to focus on the following research problem: “Is the European Union a credible security actor with the capacity to contribute to confronting global terrorism?" The main concepts in this problem are: European Union, security, global terrorism, credibility [ hint : focus on identifying proper nouns, nouns or noun phrases, and action verbs in the assignment description]. Step 2 : Review related literature to help refine how you will approach examining the topic and finding a way to analyze it . You can begin by doing any or all of the following: reading through background information from materials listed in your course syllabus; searching the USC Libraries Catalog to find a recent book on the topic and, if appropriate, more specialized works about the topic; conducting a preliminary review of the research literature using multidisciplinary databases such as ProQuest or subject-specific databases from the " By Subject Area " drop down menu located above the list of databases.
Choose the advanced search option in the database and enter into each search box the main concept terms you developed in Step 1. Also consider using their synonyms to retrieve additional relevant records. This will help you refine and frame the scope of the research problem. You will likely need to do this several times before you can finalize how to approach writing about the topic. NOTE: Always review the references from your most relevant research results cited by the authors in footnotes, endnotes, or a bibliography to locate related research on your topic. This is a good strategy for identifying important prior research about the topic because titles that are repeatedly cited indicate their significance in laying a foundation for understanding the problem. However, if you’re having trouble at this point locating relevant research literature, ask a librarian for help!
ANOTHER NOTE: If you find an article from a database that's particularly helpful, paste it into Google Scholar , placing the title of the article in quotes. If the article record appears, look for a "cited by" reference followed by a number [e.g., C ited by 37] just below the record. This link indicates how many times other scholars have subsequently cited that article in their own research since it was first published. This is an effective strategy for identifying more current, related research on your topic. Finding additional cited by references from your original list of cited by references helps you navigate through the literature and, by so doing, understand the evolution of thought around a particular research problem. Step 3 : Since social science research papers are generally designed to encourage you to develop your own ideas and arguments, look for sources that can help broaden, modify, or strengthen your initial thoughts and arguments. For example, if you decide to argue that the European Union is inadequately prepared to take on responsibilities for broader global security because of the debt crisis in many EU countries, then focus on identifying sources that support as well as refute this position. From the advanced search option in ProQuest , a sample search would use "European Union" in one search box, "global security" in the second search box, and adding a third search box to include "debt crisis."
There are least four appropriate roles your related literature plays in helping you formulate how to begin your analysis :
- Sources of criticism -- frequently, you'll find yourself reading materials that are relevant to your chosen topic, but you disagree with the author's position. Therefore, one way that you can use a source is to describe the counter-argument, provide evidence from your own review of the literature as to why the prevailing argument is unsatisfactory, and to discuss how your approach is more appropriate based upon your interpretation of the evidence.
- Sources of new ideas -- while a general goal in writing college research papers in the social sciences is to examine a research problem with some basic idea of what position you'd like to take and on what basis you'd like to defend your position, it is certainly acceptable [and often encouraged] to read the literature and extend, modify, and refine your own position in light of the ideas proposed by others.
- Sources for historical context -- another role your related literature plays in formulating how to begin your analysis is to place issues and events in proper historical context. This can help to demonstrate familiarity with developments in relevant scholarship about your topic, provide a means of comparing historical versus contemporary issues and events, and identifying key people, places, and events that had an important role related to the research problem. Given its archival journal coverage, a good multidisciplinary database to use in this case is JSTOR .
- Sources of interdisciplinary insight -- an advantage of using databases like ProQuest to begin exploring your topic is that it covers publications from a variety of different disciplines. Another way to formulate how to study the topic is to look at it from different disciplinary perspectives. If the topic concerns immigration reform, for example, ask yourself, how do studies from sociological journals found by searching ProQuest vary in their analysis from those in political science journals. A goal in reviewing related literature is to provide a means of approaching a topic from multiple perspectives rather than the perspective offered from just one discipline.
NOTE: Remember to keep careful notes at every stage or utilize a citation management system like EndNotes or RefWorks . You may think you'll remember what you have searched and where you found things, but it’s easy to forget or get confused. Most databases have a search history feature that allows you to go back and see what searches you conducted previously as long as you haven't closed your session. If you start over, that history could be deleted.
Step 4 : Assuming you have done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of your initial search for related literature, you're ready to prepare a detailed outline for your paper that lays the foundation for a more in-depth and focused review of relevant research literature [after consulting with a librarian, if needed!]. How will you know you haven't done an effective job of synthesizing and thinking about the results of our initial search for related literature? A good indication is that you start composing the outline and gaps appear in how you want to approach the study. This indicates the need to gather further background information and analysis about the research problem.
II. How To Begin: You are provided a list of possible topics to choose from Step 1 : I know what you’re thinking--which topic on this list will be the easiest to find the most information on? An effective instructor would never include a topic that is so obscure or complex that no research is available to examine and from which to design an effective study. Therefore, don't approach a list of possible topics to study from the perspective of trying to identify the path of least resistance; choose a topic that you find interesting in some way, that is controversial and that you have a strong opinion about, that has some personal meaning for you, or relates to your major or a minor. You're going to be working on the topic for quite some time, so choose one that you find interesting and engaging or that motivates you to take a position. Embrace the opportunity to learn something new! Once you’ve settled on a topic of interest from the list provided by your professor, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed above to further develop it into a research paper.
NOTE: It’s ok to review related literature to help refine how you will approach analyzing a topic, and then discover that the topic isn’t all that interesting to you. In that case, choose a different topic from the list. Just don’t wait too long to make a switch and, of course, be sure to inform your professor that you are changing your topic.
III. How To Begin: Your professor leaves it up to you to choose a topic
Step 1 : Under this scenario, the key process is turning an idea or general thought into a topic that can be configured into a research problem. When given an assignment where you choose the topic, don't begin by thinking about what to write about, but rather, ask yourself the question, "What do I want to understand or learn about?" Treat an open-ended research assignment as an opportunity to gain new knowledge about something that's important or exciting to you in the context of the overall subject of the course.
Step 2 : If you lack ideas, or wish to gain focus, try any or all of the following strategies:
- Review your course readings, particularly the suggested readings, for topic ideas. Don't just review what you've already read, but jump ahead in the syllabus to readings that have not been covered yet.
- Search the USC Libraries Catalog for a recently published book and, if appropriate, more specialized works related to the discipline area of the course [e.g., for the course SOCI 335: Society and Population, search for books on "population and society" or "population and social impact"]. Reviewing the contents of a book about your area of interest can give you insight into what conversations scholars are having about the topic and, thus, how you might want to contribute your own ideas to these conversations through the research paper you write for the class.
- Browse through some current scholarly [a.k.a., academic, peer reviewed] journals in your subject discipline. Even if most of the articles are not relevant, you can skim through the contents quickly. You only need one to be the spark that begins the process of wanting to learn more about a topic. Consult with a librarian and/or your professor about what constitutes the core journals within the subject area of the writing assignment.
- Think about essays you have written for other courses you have taken or academic lectures and programs you have attended outside of class. Thinking back, ask yourself why did you want to take this class or attend this event? What interested you the most? What would you like to know more about? Place this question in the context of the current course assignment. Note that this strategy also applies to anything you've watched on TV or has been shared on social media.
- Search online news media sources, such as CNN , the Los Angeles Times , Huffington Post , MSNBC , Fox News , or Newsweek , to see if your idea has been covered by the media. Use this coverage to refine your idea into something that you'd like to investigate further, but in a more deliberate, scholarly way in relation to a particular problem that needs to be researched.
Step 3 : To build upon your initial idea, use the suggestions under this tab to help narrow , broaden , or increase the timeliness of your idea so you can write it out as a research problem.
Once you are comfortable with having turned your idea into a research problem, follow Steps 1 - 4 listed in Part I above to further develop it into an outline for a research paper.
Alderman, Jim. "Choosing a Research Topic." Beginning Library and Information Systems Strategies. Paper 17. Jacksonville, FL: University of North Florida Digital Commons, 2014; Alvesson, Mats and Jörgen Sandberg. Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research . London: Sage, 2013; Chapter 2: Choosing a Research Topic. Adrian R. Eley. Becoming a Successful Early Career Researcher . New York: Routledge, 2012; Answering the Question. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra; Brainstorming. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Brainstorming. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Chapter 1: Research and the Research Problem. Nicholas Walliman . Your Research Project: Designing and Planning Your Work . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2011; Choosing a Topic. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Mullaney, Thomas S. and Christopher Rea. Where Research Begins: Choosing a Research Project That Matters to You (and the World) . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2022; Coming Up With Your Topic. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; How To Write a Thesis Statement. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Identify Your Question. Start Your Research. University Library, University of California, Santa Cruz; The Process of Writing a Research Paper. Department of History. Trent University; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006.
Resources for Identifying a Topic
Resources for Identifying a Research Problem
If you are having difficulty identifying a topic to study or need basic background information, the following web resources and databases can be useful:
- CQ Researcher -- a collection of single-themed public policy reports that provide an overview of an issue. Each report includes background information, an assessment of the current policy situation, statistical tables and maps, pro/con statements from representatives of opposing positions, and a bibliography of key sources.
- New York Times Topics -- each topic page collects news articles, reference and archival information, photos, graphics, audio and video files. Content is available without charge on articles going back to 1981.
- Opposing Viewpoints In Context -- an online resource covering a wide range of social issues from a variety of perspectives. The database contains a media-rich collection of materials, including pro/con viewpoint essays, topic overviews, primary source materials, biographies of social activists and reformers, journal articles, statistical tables, charts and graphs, images, videos, and podcasts.
- Policy Commons -- platform for objective, fact-based research from the world’s leading policy experts, nonpartisan think tanks, and intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations. The database provides advanced searching across millions of pages of books, articles, working papers, reports, policy briefs, data sets, tables, charts, media, case studies, and statistical publications, including archived reports from more than 200 defunct think tanks. Coverage is international in scope.
Descriptions of resources are adapted or quoted from vendor websites.
Writing Tip
Not Finding Anything on Your Topic? Ask a Librarian!
Don't assume or jump to the conclusion that your topic is too narrowly defined or obscure just because your initial search has failed to locate any relevant studies. Librarians are experts in locating and critically assessing information and how it is organized. This information will help you develop strategies for analyzing existing knowledge in new ways. Therefore, always consult with a librarian before you consider giving up on finding information about what you want to investigate. If there isn't a lot of information about your topic, a librarian can help you identify a closely related topic to study. Use the Ask-A-Librarian link above to either chat with a librarian, send a general email to the librarians, or identify a subject expert librarian related to the course you are taking.
Another Writing Tip
A Research Problem is Not the Thesis Statement
A thesis statement and a research problem are two different parts of the introduction section of your paper. The thesis statement succinctly describes in one or two sentences, usually in the last paragraph of the introduction, what position you have reached about a topic. It includes an assertion that requires evidence and support, along with your argument about what you are researching and why. There are three general types of thesis statements that are intended to set forth a claim that you will seek to validate through the research you describe in your paper :
1) analytical statements that break down and evaluate the topic;
2) expository statements that present facts and research about the topic; and,
3) argumentative statements that make a claim about the topic and defend that claim. An argumentative thesis statement is the most common type of statement required in social sciences writing assignments.
Before the thesis statement, however, your introduction must include a statement about a problem in which you describe either a key area of concern, a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling issue that exists . The research problem describes something that can be empirically verified and measured and is often followed by a set of questions that underpin how you plan to approach investigating that problem. In short, the thesis statement presents your argument about the research problem and summarizes how you plan to address it.
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Write a Strong Thesis Statement! The Writing Center, University of Evansville; Thesis Statements. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tutorial #26: Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences. Writing Center, College of San Mateo; Creswell, John W. and J. David Creswell. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . 5th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2017.
Still Another Writing Tip
Don't be a Martyr!
In thinking about what to study, don't adopt the mindset of pursuing an esoteric or overly complicated topic just to impress your professor but that, in reality, does not have any real interest to you. Choose a topic that is challenging, but that has at least some interest to you or is something that you care about. Obviously, this is easier for courses within your major, but even for those nasty general education classes that you must take in order to graduate [and that provide an additional tuition revenue for the university], try to apply perspectives to the writing assignment that reflect your major.
For example, if you are an international relations major taking a GE philosophy class where the assignment asks you to apply the question of "what is truth" to some aspect of life, you could choose to study how government leaders attempt to shape truth through the use of nationalistic propaganda. Using this approach will not only help you engage with class assignment, but it can create opportunities to understand research problems within your major from an interdisciplinary perspective.
- << Previous: Glossary of Research Terms
- Next: Reading Research Effectively >>
- Last Updated: Nov 21, 2024 12:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Work With Us
Private Coaching
Done-For-You
Short Courses
Client Reviews
Free Resources
The Research Problem & Statement

I f you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Very interesting. Thank you. Please I need a PhD topic in climate change in relation to health.
Your posts have provided a clear, easy to understand, motivating literature, mainly when these topics tend to be considered “boring” in some careers.
Thank you, but i am requesting for a topic in records management
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide
Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide
Table of Contents
A research problem is the starting point of any study, as it defines the issue or challenge that the research intends to address. Clearly articulating a research problem is essential because it shapes the direction of the study, influencing research design, methodology, and analysis. This guide explores what a research problem is, the types of research problems, and how to develop one with clear examples to aid in understanding.

Research Problem
A research problem is a specific issue, difficulty, or gap in knowledge that prompts the need for investigation. It reflects the purpose of the research and the questions that the study aims to answer. Without a clear research problem, it is difficult to determine the scope, goals, and relevance of the research.
For example, in social sciences, a research problem might involve understanding factors that influence student motivation. In business, it could involve identifying reasons behind declining customer satisfaction.
Why is a Research Problem Important?
The research problem is the foundation of the research process because it:
- Defines the Study’s Purpose : It helps clarify what the research is trying to achieve.
- Guides the Research Design : It determines which methodologies and data collection techniques are suitable.
- Provides Focus and Direction : It prevents the study from being overly broad or unfocused.
- Establishes Relevance : A well-defined problem highlights the research’s significance and its contribution to knowledge.
Types of Research Problems
- Example : What are the psychological factors influencing digital addiction among young adults?
- Example : How can customer service training improve client retention in the hospitality industry?
- Example : How do rural and urban educational outcomes compare in terms of student performance?
- Example : What are the emerging behaviors associated with the use of augmented reality in retail shopping?
- Example : What are the common characteristics of high-performing teams in technology companies?
- Example : What effect does daily exercise have on reducing stress levels among college students?
Steps to Formulate a Research Problem
- Identify a Broad Topic Area Start by choosing a general area of interest. This could be anything from mental health and marketing to technology or education. Focusing on a topic you’re passionate about can make the research process more engaging.
- Conduct Preliminary Research Conducting initial research helps you understand existing knowledge and identify gaps. Look at recent studies, articles, or reports in your field to find areas that need further exploration.
- Narrow Down the Topic A broad topic needs to be narrowed to a specific issue. Consider the aspects of the topic that interest you most or that have limited research available. Narrowing the focus prevents the study from being too general and enhances its depth.
- Identify the Problem Clearly define the problem or gap that the research aims to address. Frame it as a statement that indicates the issue, its context, and its importance.
- Formulate Research Questions Develop research questions that provide a basis for investigating the problem. Good research questions are specific, clear, and feasible, guiding the research process and helping focus data collection.
- Assess Feasibility Evaluate if the research problem is manageable given available resources, time, and access to data. Feasibility ensures that the study is achievable and practical within constraints.
Examples of Research Problems
Example 1 : In Education
- Problem : Declining student engagement in online learning environments.
- Research Question : What factors contribute to decreased engagement in online courses compared to in-person learning?
Example 2 : In Business
- Problem : High employee turnover in customer service departments.
- Research Question : How does job satisfaction impact turnover rates among customer service employees?
Example 3 : In Healthcare
- Problem : Rising obesity rates among children in urban areas.
- Research Question : What are the primary lifestyle factors contributing to obesity among urban children?
Example 4 : In Psychology
- Problem : Increased rates of social media addiction among teenagers.
- Research Question : What psychological factors lead to social media addiction in teenagers?
Example 5 : In Environmental Studies
- Problem : Rapid decline in pollinator populations affecting crop yields.
- Research Question : What impact does pesticide usage have on pollinator populations in agricultural areas?
Tips for Defining a Strong Research Problem
- Make It Specific : Clearly state the issue you intend to investigate. Avoid overly broad topics that are difficult to address.
- Identify Relevance : Choose a problem that has practical, theoretical, or social importance, demonstrating why the study matters.
- Align with Research Goals : Ensure that the problem aligns with the overall objectives of your research or field of study.
- Keep It Manageable : Be realistic about what you can accomplish within your time frame, resources, and skills.
- Consider Originality : Aim to address a gap in the current literature, focusing on issues that have not been explored in depth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overly Broad Problems : A vague or broad problem can make it difficult to formulate research questions or collect relevant data.
- Irrelevant or Trivial Problems : Choose a problem that has value and contributes meaningfully to your field of study.
- Unfeasible Problems : Ensure that your research problem is practical and can be addressed with available resources.
- Confusing the Problem with the Method : Define the issue clearly instead of describing the method. For example, “Using interviews to study…” is a method, not a problem.
A well-defined research problem is crucial to successful research. By selecting a relevant, specific, and feasible problem, researchers set a strong foundation for their study. Whether you are studying education, business, psychology, or any other field, understanding the types and examples of research problems can help you structure a clear and focused investigation. Defining the problem carefully and creating focused research questions ultimately guides the research process, making your work impactful and meaningful.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Maxwell, J. A. (2013). Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach . Sage Publications.
- Kumar, R. (2019). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners . Sage Publications.
- Saunders, M., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2019). Research Methods for Business Students . Pearson Education.
- Punch, K. F. (2014). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches . Sage Publications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to...


Future Research – Thesis Guide

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and...

Purpose of Research – Objectives and Applications

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Research Problem? Characteristics, Types, and Examples

A research problem is a gap in existing knowledge, a contradiction in an established theory, or a real-world challenge that a researcher aims to address in their research. It is at the heart of any scientific inquiry, directing the trajectory of an investigation. The statement of a problem orients the reader to the importance of the topic, sets the problem into a particular context, and defines the relevant parameters, providing the framework for reporting the findings. Therein lies the importance of research problem s.
The formulation of well-defined research questions is central to addressing a research problem . A research question is a statement made in a question form to provide focus, clarity, and structure to the research endeavor. This helps the researcher design methodologies, collect data, and analyze results in a systematic and coherent manner. A study may have one or more research questions depending on the nature of the study.

Identifying and addressing a research problem is very important. By starting with a pertinent problem , a scholar can contribute to the accumulation of evidence-based insights, solutions, and scientific progress, thereby advancing the frontier of research. Moreover, the process of formulating research problems and posing pertinent research questions cultivates critical thinking and hones problem-solving skills.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Problem ?
Before you conceive of your project, you need to ask yourself “ What is a research problem ?” A research problem definition can be broadly put forward as the primary statement of a knowledge gap or a fundamental challenge in a field, which forms the foundation for research. Conversely, the findings from a research investigation provide solutions to the problem .
A research problem guides the selection of approaches and methodologies, data collection, and interpretation of results to find answers or solutions. A well-defined problem determines the generation of valuable insights and contributions to the broader intellectual discourse.
Characteristics of a Research Problem
Knowing the characteristics of a research problem is instrumental in formulating a research inquiry; take a look at the five key characteristics below:
Novel : An ideal research problem introduces a fresh perspective, offering something new to the existing body of knowledge. It should contribute original insights and address unresolved matters or essential knowledge.
Significant : A problem should hold significance in terms of its potential impact on theory, practice, policy, or the understanding of a particular phenomenon. It should be relevant to the field of study, addressing a gap in knowledge, a practical concern, or a theoretical dilemma that holds significance.
Feasible: A practical research problem allows for the formulation of hypotheses and the design of research methodologies. A feasible research problem is one that can realistically be investigated given the available resources, time, and expertise. It should not be too broad or too narrow to explore effectively, and should be measurable in terms of its variables and outcomes. It should be amenable to investigation through empirical research methods, such as data collection and analysis, to arrive at meaningful conclusions A practical research problem considers budgetary and time constraints, as well as limitations of the problem . These limitations may arise due to constraints in methodology, resources, or the complexity of the problem.
Clear and specific : A well-defined research problem is clear and specific, leaving no room for ambiguity; it should be easily understandable and precisely articulated. Ensuring specificity in the problem ensures that it is focused, addresses a distinct aspect of the broader topic and is not vague.
Rooted in evidence: A good research problem leans on trustworthy evidence and data, while dismissing unverifiable information. It must also consider ethical guidelines, ensuring the well-being and rights of any individuals or groups involved in the study.

Types of Research Problems
Across fields and disciplines, there are different types of research problems . We can broadly categorize them into three types.
- Theoretical research problems
Theoretical research problems deal with conceptual and intellectual inquiries that may not involve empirical data collection but instead seek to advance our understanding of complex concepts, theories, and phenomena within their respective disciplines. For example, in the social sciences, research problem s may be casuist (relating to the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience), difference (comparing or contrasting two or more phenomena), descriptive (aims to describe a situation or state), or relational (investigating characteristics that are related in some way).
Here are some theoretical research problem examples :
- Ethical frameworks that can provide coherent justifications for artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, especially in contexts involving autonomous decision-making and moral agency.
- Determining how mathematical models can elucidate the gradual development of complex traits, such as intricate anatomical structures or elaborate behaviors, through successive generations.
- Applied research problems
Applied or practical research problems focus on addressing real-world challenges and generating practical solutions to improve various aspects of society, technology, health, and the environment.
Here are some applied research problem examples :
- Studying the use of precision agriculture techniques to optimize crop yield and minimize resource waste.
- Designing a more energy-efficient and sustainable transportation system for a city to reduce carbon emissions.
- Action research problems
Action research problems aim to create positive change within specific contexts by involving stakeholders, implementing interventions, and evaluating outcomes in a collaborative manner.
Here are some action research problem examples :
- Partnering with healthcare professionals to identify barriers to patient adherence to medication regimens and devising interventions to address them.
- Collaborating with a nonprofit organization to evaluate the effectiveness of their programs aimed at providing job training for underserved populations.
These different types of research problems may give you some ideas when you plan on developing your own.
How to Define a Research Problem
You might now ask “ How to define a research problem ?” These are the general steps to follow:
- Look for a broad problem area: Identify under-explored aspects or areas of concern, or a controversy in your topic of interest. Evaluate the significance of addressing the problem in terms of its potential contribution to the field, practical applications, or theoretical insights.
- Learn more about the problem: Read the literature, starting from historical aspects to the current status and latest updates. Rely on reputable evidence and data. Be sure to consult researchers who work in the relevant field, mentors, and peers. Do not ignore the gray literature on the subject.
- Identify the relevant variables and how they are related: Consider which variables are most important to the study and will help answer the research question. Once this is done, you will need to determine the relationships between these variables and how these relationships affect the research problem .
- Think of practical aspects : Deliberate on ways that your study can be practical and feasible in terms of time and resources. Discuss practical aspects with researchers in the field and be open to revising the problem based on feedback. Refine the scope of the research problem to make it manageable and specific; consider the resources available, time constraints, and feasibility.
- Formulate the problem statement: Craft a concise problem statement that outlines the specific issue, its relevance, and why it needs further investigation.
- Stick to plans, but be flexible: When defining the problem , plan ahead but adhere to your budget and timeline. At the same time, consider all possibilities and ensure that the problem and question can be modified if needed.

Key Takeaways
- A research problem concerns an area of interest, a situation necessitating improvement, an obstacle requiring eradication, or a challenge in theory or practical applications.
- The importance of research problem is that it guides the research and helps advance human understanding and the development of practical solutions.
- Research problem definition begins with identifying a broad problem area, followed by learning more about the problem, identifying the variables and how they are related, considering practical aspects, and finally developing the problem statement.
- Different types of research problems include theoretical, applied, and action research problems , and these depend on the discipline and nature of the study.
- An ideal problem is original, important, feasible, specific, and based on evidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it important to define a research problem?
Identifying potential issues and gaps as research problems is important for choosing a relevant topic and for determining a well-defined course of one’s research. Pinpointing a problem and formulating research questions can help researchers build their critical thinking, curiosity, and problem-solving abilities.
How do I identify a research problem?
Identifying a research problem involves recognizing gaps in existing knowledge, exploring areas of uncertainty, and assessing the significance of addressing these gaps within a specific field of study. This process often involves thorough literature review, discussions with experts, and considering practical implications.
Can a research problem change during the research process?
Yes, a research problem can change during the research process. During the course of an investigation a researcher might discover new perspectives, complexities, or insights that prompt a reevaluation of the initial problem. The scope of the problem, unforeseen or unexpected issues, or other limitations might prompt some tweaks. You should be able to adjust the problem to ensure that the study remains relevant and aligned with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
How does a research problem relate to research questions or hypotheses?
A research problem sets the stage for the study. Next, research questions refine the direction of investigation by breaking down the broader research problem into manageable components. Research questions are formulated based on the problem , guiding the investigation’s scope and objectives. The hypothesis provides a testable statement to validate or refute within the research process. All three elements are interconnected and work together to guide the research.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

How Long Should Your Essay Be? Essential Tips for Every Type of Essay

What is a Research Paper Appendix?
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO

Academic Experience
How to identify and resolve research problems
Updated August 23, 2024
In this article, we’re going to take you through one of the most pertinent parts of conducting research: a research problem (also known as a research problem statement).
When trying to formulate a good research statement, and understand how to solve it for complex projects, it can be difficult to know where to start.
Not only are there multiple perspectives (from stakeholders to project marketers who want answers), you have to consider the particular context of the research topic: is it timely, is it relevant and most importantly of all, is it valuable?
In other words: are you looking at a research worthy problem?
The fact is, a well-defined, precise, and goal-centric research problem will keep your researchers, stakeholders, and business-focused and your results actionable.
And when it works well, it's a powerful tool to identify practical solutions that can drive change and secure buy-in from your workforce.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to market research
What is a research problem?
In social research methodology and behavioral sciences , a research problem establishes the direction of research, often relating to a specific topic or opportunity for discussion.
For example: climate change and sustainability, analyzing moral dilemmas or wage disparity amongst classes could all be areas that the research problem focuses on.
As well as outlining the topic and/or opportunity, a research problem will explain:
- why the area/issue needs to be addressed,
- why the area/issue is of importance,
- the parameters of the research study
- the research objective
- the reporting framework for the results and
- what the overall benefit of doing so will provide (whether to society as a whole or other researchers and projects).
Having identified the main topic or opportunity for discussion, you can then narrow it down into one or several specific questions that can be scrutinized and answered through the research process.
What are research questions?
Generating research questions underpinning your study usually starts with problems that require further research and understanding while fulfilling the objectives of the study.
A good problem statement begins by asking deeper questions to gain insights about a specific topic.
For example, using the problems above, our questions could be:
"How will climate change policies influence sustainability standards across specific geographies?"
"What measures can be taken to address wage disparity without increasing inflation?"
Developing a research worthy problem is the first step - and one of the most important - in any kind of research.
It’s also a task that will come up again and again because any business research process is cyclical. New questions arise as you iterate and progress through discovering, refining, and improving your products and processes. A research question can also be referred to as a "problem statement".
Note: good research supports multiple perspectives through empirical data. It’s focused on key concepts rather than a broad area, providing readily actionable insight and areas for further research.
Research question or research problem?
As we've highlighted, the terms “research question” and “research problem” are often used interchangeably, becoming a vague or broad proposition for many.
The term "problem statement" is far more representative, but finds little use among academics.
Instead, some researchers think in terms of a single research problem and several research questions that arise from it.
As mentioned above, the questions are lines of inquiry to explore in trying to solve the overarching research problem.
Ultimately, this provides a more meaningful understanding of a topic area.
It may be useful to think of questions and problems as coming out of your business data – that’s the O-data (otherwise known as operational data) like sales figures and website metrics.
What's an example of a research problem?
Your overall research problem could be: "How do we improve sales across EMEA and reduce lost deals?"
This research problem then has a subset of questions, such as:
"Why do sales peak at certain times of the day?"
"Why are customers abandoning their online carts at the point of sale?"
As well as helping you to solve business problems, research problems (and associated questions) help you to think critically about topics and/or issues (business or otherwise). You can also use your old research to aid future research -- a good example is laying the foundation for comparative trend reports or a complex research project.
(Also, if you want to see the bigger picture when it comes to research problems, why not check out our ultimate guide to market research? In it you'll find out: what effective market research looks like, the use cases for market research, carrying out a research study, and how to examine and action research findings).
The research process: why are research problems important?
A research problem has two essential roles in setting your research project on a course for success.
1. They set the scope
The research problem defines what problem or opportunity you’re looking at and what your research goals are. It stops you from getting side-tracked or allowing the scope of research to creep off-course .
Without a strong research problem or problem statement, your team could end up spending resources unnecessarily, or coming up with results that aren’t actionable - or worse, harmful to your business - because the field of study is too broad.
2. They tie your work to business goals and actions
To formulate a research problem in terms of business decisions means you always have clarity on what’s needed to make those decisions. You can show the effects of what you’ve studied using real outcomes.
Then, by focusing your research problem statement on a series of questions tied to business objectives, you can reduce the risk of the research being unactionable or inaccurate.
It's also worth examining research or other scholarly literature (you’ll find plenty of similar, pertinent research online) to see how others have explored specific topics and noting implications that could have for your research.
Four steps to defining your research problem
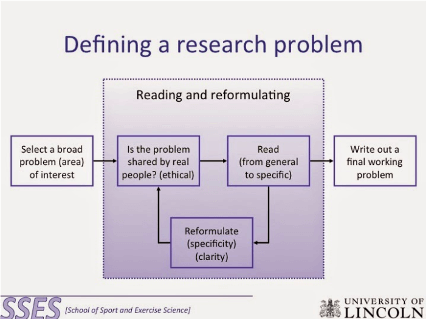
Image credit: http://myfreeschooltanzania.blogspot.com/2014/11/defining-research-problem.html
1. Observe and identify
Businesses today have so much data that it can be difficult to know which problems to address first. Researchers also have business stakeholders who come to them with problems they would like to have explored. A researcher’s job is to sift through these inputs and discover exactly what higher-level trends and key concepts are worth investing in.
This often means asking questions and doing some initial investigation to decide which avenues to pursue. This could mean gathering interdisciplinary perspectives identifying additional expertise and contextual information.
Sometimes, a small-scale preliminary study might be worth doing to help get a more comprehensive understanding of the business context and needs, and to make sure your research problem addresses the most critical questions.
This could take the form of qualitative research using a few in-depth interviews , an environmental scan, or reviewing relevant literature.
The sales manager of a sportswear company has a problem: sales of trail running shoes are down year-on-year and she isn’t sure why. She approaches the company’s research team for input and they begin asking questions within the company and reviewing their knowledge of the wider market.
2. Review the key factors involved
As a marketing researcher, you must work closely with your team of researchers to define and test the influencing factors and the wider context involved in your study. These might include demographic and economic trends or the business environment affecting the question at hand. This is referred to as a relational research problem.
To do this, you have to identify the factors that will affect the research and begin formulating different methods to control them.
You also need to consider the relationships between factors and the degree of control you have over them. For example, you may be able to control the loading speed of your website but you can’t control the fluctuations of the stock market.
Doing this will help you determine whether the findings of your project will produce enough information to be worth the cost.
You need to determine:
- which factors affect the solution to the research proposal.
- which ones can be controlled and used for the purposes of the company, and to what extent.
- the functional relationships between the factors.
- which ones are critical to the solution of the research study.
The research team at the running shoe company is hard at work. They explore the factors involved and the context of why YoY sales are down for trail shoes, including things like what the company’s competitors are doing, what the weather has been like – affecting outdoor exercise – and the relative spend on marketing for the brand from year to year.
The final factor is within the company’s control, although the first two are not. They check the figures and determine marketing spend has a significant impact on the company.
3. Prioritize
Once you and your research team have a few observations, prioritize them based on their business impact and importance. It may be that you can answer more than one question with a single study, but don’t do it at the risk of losing focus on your overarching research problem.
Questions to ask:
- Who? Who are the people with the problem? Are they end-users, stakeholders, teams within your business? Have you validated the information to see what the scale of the problem is?
- What? What is its nature and what is the supporting evidence?
- Why? What is the business case for solving the problem? How will it help?
- Where? How does the problem manifest and where is it observed?
To help you understand all dimensions, you might want to consider focus groups or preliminary interviews with external (including consumers and existing customers) and internal (salespeople, managers, and other stakeholders) parties to provide what is sometimes much-needed insight into a particular set of questions or problems.
After observing and investigating, the running shoe researchers come up with a few candidate questions, including:
- What is the relationship between US average temperatures and sales of our products year on year?
- At present, how does our customer base rank Competitor X and Competitor Y’s trail running shoe compared to our brand?
- What is the relationship between marketing spend and trail shoe product sales over the last 12 months?
They opt for the final question, because the variables involved are fully within the company’s control, and based on their initial research and stakeholder input, seem the most likely cause of the dive in sales. The research question is specific enough to keep the work on course towards an actionable result, but it allows for a few different avenues to be explored, such as the different budget allocations of offline and online marketing and the kinds of messaging used.
Get feedback from the key teams within your business to make sure everyone is aligned and has the same understanding of the research problem and questions, and the actions you hope to take based on the results. Now is also a good time to demonstrate the ROI of your research and lay out its potential benefits to your stakeholders.
Different groups may have different goals and perspectives on the issue. This step is vital for getting the necessary buy-in and pushing the project forward.
The running shoe company researchers now have everything they need to begin. They call a meeting with the sales manager and consult with the product team, marketing team, and C-suite to make sure everyone is aligned and has bought into the direction of the research topic. They identify and agree that the likely course of action will be a rethink of how marketing resources are allocated, and potentially testing out some new channels and messaging strategies .
Can you explore a broad area and is it practical to do so?
A broader research problem or report can be a great way to bring attention to prevalent issues, societal or otherwise, but are often undertaken by those with the resources to do so.
Take a typical government cybersecurity breach survey, for example. Most of these reports raise awareness of cybercrime, from the day-to-day threats businesses face to what security measures some organizations are taking. What these reports don't do, however, is provide actionable advice - mostly because every organization is different.
The point here is that while some researchers will explore a very complex issue in detail, others will provide only a snapshot to maintain interest and encourage further investigation. The "value" of the data is wholly determined by the recipients of it - and what information you choose to include.
To summarize, it can be practical to undertake a broader research problem, certainly, but it may not be possible to cover everything or provide the detail your audience needs. Likewise, a more systematic investigation of an issue or topic will be more valuable, but you may also find that you cover far less ground.
It's important to think about your research objectives and expected findings before going ahead.
Ensuring your research project is a success
A complex research project can be made significantly easier with clear research objectives, a descriptive research problem, and a central focus. All of which we've outlined in this article.
If you have previous research, even better. Use it as a benchmark
Remember: what separates a good research paper from an average one is actually very simple: valuable, empirical data that explores a prevalent societal or business issue and provides actionable insights.
And we can help.
Sophisticated research made simple with Qualtrics
Trusted by the world's best brands, our platform enables researchers from academic to corporate to tackle the hardest challenges and deliver the results that matter.
Our CoreXM platform supports the methods that define superior research and delivers insights in real-time. It's easy to use (thanks to drag-and-drop functionality) and requires no coding, meaning you'll be capturing data and gleaning insights in no time.
It also excels in flexibility; you can track consumer behavior across segments , benchmark your company versus competitors , carry out complex academic research, and do much more, all from one system.
It's one platform with endless applications, so no matter your research problem, we've got the tools to help you solve it. And if you don't have a team of research experts in-house, our market research team has the practical knowledge and tools to help design the surveys and find the respondents you need.
Of course, you may want to know where to begin with your own market research . If you're struggling, make sure to download our ultimate guide using the link below.
It's got everything you need and there’s always information in our research methods knowledge base.
Scott Smith
Scott Smith, Ph.D. is a contributor to the Qualtrics blog.
Related Articles
April 1, 2023
How to write great survey questions (with examples)
February 8, 2023
Smoothing the transition from school to work with work-based learning
December 6, 2022
How customer experience helps bring Open Universities Australia’s brand promise to life
August 9, 2022
3 things that will improve your teachers’ school experience
August 2, 2022
Why a sense of belonging at school matters for K-12 students
July 14, 2022
Improve the student experience with simplified course evaluations
March 17, 2022
Understanding what’s important to college students
February 18, 2022
Malala: ‘Education transforms lives, communities, and countries’
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

COMMENTS
Where to Find a Research Problem. Ideas for research problems tend to come from two sources: real life and the scholarly arena. First, identifying a research problem can be as simple as observing the complications and issues in your local workplace.
A research problem, or phenomenon as it might be called in many forms of qualitative methodology, is the topic you would like to address, investigate, or study, whether descriptively or experimentally.
Step 1: Identify a broad problem area. As you read about your topic, look for under-explored aspects or areas of concern, conflict, or controversy. Your goal is to find a gap that your research project can fill. Practical research problems.
In the social and behavioral sciences, the subject of analysis is most often framed as a problem that must be researched in order to discover new knowledge and understanding, formulate a set of solutions or recommended courses of action, and/or develop a more effective approach to applied practice. The research problem, therefore, is the main ...
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement. We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Table of Contents. A research problem is the starting point of any study, as it defines the issue or challenge that the research intends to address. Clearly articulating a research problem is essential because it shapes the direction of the study, influencing research design, methodology, and analysis.
Guidelines for Finding a Legitimate Problem Find topics/projects that might make important contributions to the field. Look around you. Read the literature. Attend professional conferences. Seek the advice of experts. Choose a topic that intrigues and motivates you. Choose a topic that others will find interesting and worthy of attention ...
This module discusses the concepts and activities for identifying, specifying, and stating a research problem in both quantitative and qualitative research and positioning it within a section that introduces a study, i.e., the “statement of the problem” section.
How do I identify a research problem? Identifying a research problem involves recognizing gaps in existing knowledge, exploring areas of uncertainty, and assessing the significance of addressing these gaps within a specific field of study. This process often involves thorough literature review, discussions with experts, and considering ...
Four steps to defining your research problem. Image credit: http://myfreeschooltanzania.blogspot.com/2014/11/defining-research-problem.html. 1. Observe and identify. Businesses today have so much data that it can be difficult to know which problems to address first.